Bilateral trade involves the exchange of goods and services between two countries, boosting economic ties and fostering mutual growth. This type of trade agreement can reduce tariffs, improve market access, and strengthen diplomatic relations. Discover how your country can benefit from bilateral trade and the key factors influencing its success by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
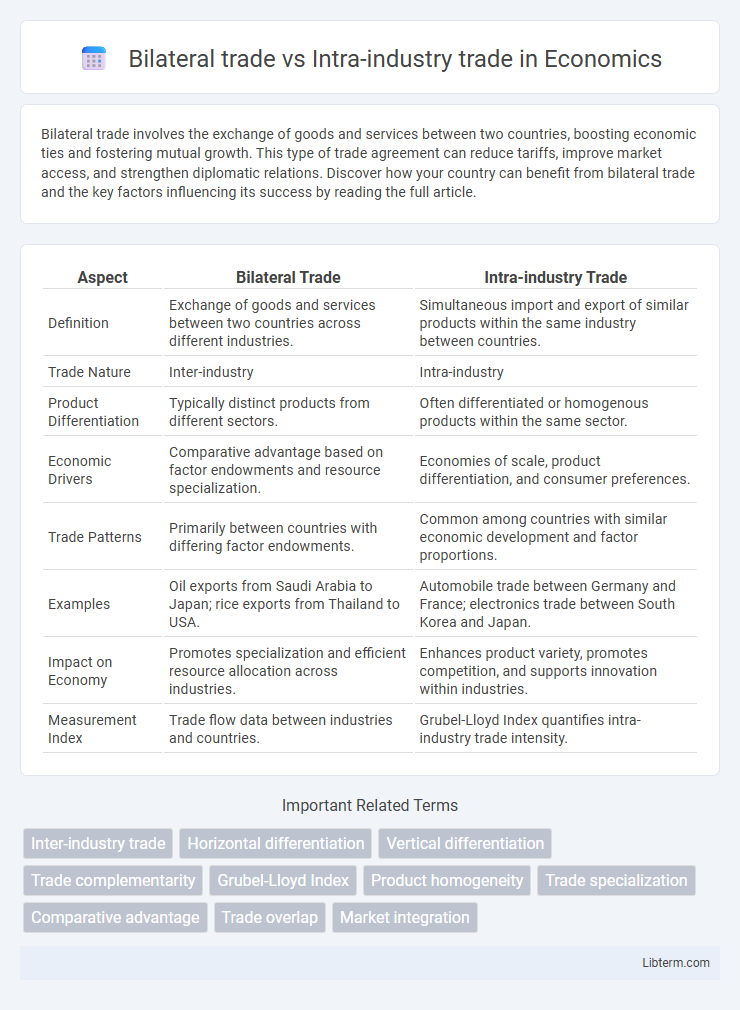
| Aspect | Bilateral Trade | Intra-industry Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of goods and services between two countries across different industries. | Simultaneous import and export of similar products within the same industry between countries. |
| Trade Nature | Inter-industry | Intra-industry |
| Product Differentiation | Typically distinct products from different sectors. | Often differentiated or homogenous products within the same sector. |
| Economic Drivers | Comparative advantage based on factor endowments and resource specialization. | Economies of scale, product differentiation, and consumer preferences. |
| Trade Patterns | Primarily between countries with differing factor endowments. | Common among countries with similar economic development and factor proportions. |
| Examples | Oil exports from Saudi Arabia to Japan; rice exports from Thailand to USA. | Automobile trade between Germany and France; electronics trade between South Korea and Japan. |
| Impact on Economy | Promotes specialization and efficient resource allocation across industries. | Enhances product variety, promotes competition, and supports innovation within industries. |
| Measurement Index | Trade flow data between industries and countries. | Grubel-Lloyd Index quantifies intra-industry trade intensity. |
Understanding Bilateral Trade: Key Concepts
Bilateral trade involves the exchange of goods and services between two countries, emphasizing comparative advantages and differences in resource endowments. It focuses on inter-industry trade, where countries export products from sectors in which they have competitive strengths and import from sectors where they lack efficiency. Understanding bilateral trade requires analyzing trade balances, tariff impacts, and the role of trade agreements in shaping two-nation trade flows.
What Is Intra-industry Trade?
Intra-industry trade refers to the exchange of similar products belonging to the same industry between countries, such as automobiles or electronics, allowing nations to specialize in different product varieties or quality levels. This trade contrasts with bilateral trade, which typically involves exchanging distinctly different goods, like agricultural products for machinery. Intra-industry trade enhances economic efficiency by increasing consumer choice and encouraging innovation through competitive differentiation within the same sector.
Major Differences Between Bilateral and Intra-industry Trade
Bilateral trade involves the exchange of different types of goods and services between two countries, primarily based on comparative advantages and factor endowments. In contrast, intra-industry trade consists of the simultaneous import and export of similar products within the same industry, driven by product differentiation, economies of scale, and consumer preferences. The key difference lies in bilateral trade emphasizing inter-industry exchange, whereas intra-industry trade focuses on horizontal or vertical trade within identical or related industries.
Economic Drivers Behind Bilateral Trade
Economic drivers behind bilateral trade primarily revolve around comparative advantage, resource endowments, and cost differentials between two countries, enabling specialization and efficient allocation of production. Bilateral trade often depends on factors such as factor intensity, technological disparities, and trade policies that influence export-import balances and market access. In contrast, intra-industry trade emphasizes product differentiation and economies of scale within similar industries rather than relying solely on comparative advantage.
Factors Influencing Intra-industry Trade Growth
Intra-industry trade growth is significantly influenced by factors such as product differentiation, economies of scale, and consumer demand for variety, which enable countries to both import and export similar goods within the same industry. Advanced technological development and innovation enhance production efficiency, supporting specialization and fostering intra-industry exchanges. Additionally, trade liberalization policies and regional economic integration reduce barriers, increasing intra-industry trade intensity by promoting competitive market environments.
Benefits and Challenges of Bilateral Trade
Bilateral trade enables two countries to specialize in the production of goods where they have a comparative advantage, fostering increased efficiency and economic growth by expanding markets and reducing tariffs through trade agreements. However, challenges include potential trade imbalances, political tensions arising from dependency on a single partner, and vulnerability to unilateral policy changes that can disrupt supply chains. Despite these drawbacks, bilateral trade agreements can enhance diplomatic relations and create stable conditions for long-term investment and cooperation.
Advantages of Intra-industry Trade for Modern Economies
Intra-industry trade enhances economic efficiency by enabling countries to specialize in specific product varieties and benefit from economies of scale, leading to reduced production costs and increased innovation. This form of trade supports higher consumer choice and product differentiation within the same industry, fostering competitive markets and driving technological advancement. Modern economies gain resilience and flexibility through intra-industry trade by diversifying export portfolios and reducing dependence on a limited number of trading partners.
Bilateral Trade Agreements vs Intra-industry Collaboration
Bilateral trade agreements facilitate the exchange of goods and services between two countries by reducing tariffs and aligning regulations, enhancing market access and economic integration. Intra-industry collaboration involves firms within the same industry across borders engaging in joint ventures, technology sharing, and co-production, driving innovation and competitive advantage. While bilateral trade agreements create a formal framework for trade, intra-industry collaboration deepens industrial ties and fosters value chain networks beyond standard trade flows.
Case Studies: Bilateral vs Intra-industry Trade in Global Markets
Bilateral trade involves the exchange of distinct goods and services between two countries, often reflecting comparative advantages, as seen in the US-China trade relationship centered on electronics and agriculture. Intra-industry trade occurs when countries simultaneously import and export similar products within the same industry, exemplified by Germany and France trading automobiles and machinery, driven by product differentiation and economies of scale. Case studies reveal that global markets with high economic integration, such as the European Union, experience significant intra-industry trade, while emerging economies rely more on traditional bilateral trade patterns.
Future Trends in International Trade: Bilateral or Intra-industry?
Future trends in international trade indicate a growing emphasis on intra-industry trade, driven by increased product differentiation and global value chains. Bilateral trade continues to be significant, especially for raw materials and commodities, but advanced economies are shifting toward exchanging similar but specialized products within the same industry. Emerging technologies and regional trade agreements will further enhance intra-industry trade, fostering diversification and resilience in global markets.
Bilateral trade Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com