Premium services offer unmatched quality and exclusive benefits tailored to your specific needs, ensuring superior satisfaction and value. Access to enhanced features and personalized support sets premium apart from standard options. Explore the full article to discover how upgrading to premium can transform your experience.
Table of Comparison
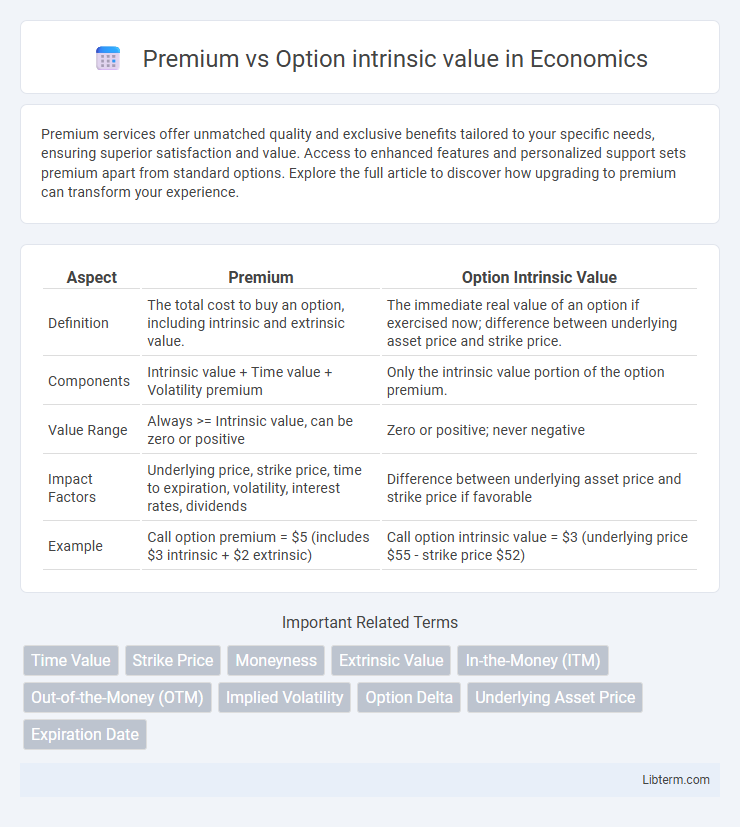
| Aspect | Premium | Option Intrinsic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The total cost to buy an option, including intrinsic and extrinsic value. | The immediate real value of an option if exercised now; difference between underlying asset price and strike price. |
| Components | Intrinsic value + Time value + Volatility premium | Only the intrinsic value portion of the option premium. |
| Value Range | Always >= Intrinsic value, can be zero or positive | Zero or positive; never negative |
| Impact Factors | Underlying price, strike price, time to expiration, volatility, interest rates, dividends | Difference between underlying asset price and strike price if favorable |
| Example | Call option premium = $5 (includes $3 intrinsic + $2 extrinsic) | Call option intrinsic value = $3 (underlying price $55 - strike price $52) |
Introduction to Options: Premium vs Intrinsic Value
Option premium comprises intrinsic value and time value, representing the total price paid by the buyer to the seller in the options market. Intrinsic value measures the immediate profit potential, calculated as the difference between the underlying asset's price and the option's strike price when favorable. Premium exceeds intrinsic value due to time value, reflecting the possibility of further price movement before expiration.
Defining Option Premium: What Does It Include?
Option premium includes intrinsic value and time value, representing the total price paid by the buyer to acquire the option contract. Intrinsic value measures how much an option is in-the-money by calculating the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price. Time value accounts for potential price movement until expiration, reflecting factors like volatility, time remaining, and market expectations.
What Is Intrinsic Value in Options?
Intrinsic value in options represents the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price, reflecting the option's real, tangible worth. For a call option, intrinsic value equals the underlying price minus the strike price if positive, otherwise zero; for a put option, it is the strike price minus the underlying price if positive, otherwise zero. Premium includes intrinsic value plus time value, indicating the total option price paid by the buyer, whereas intrinsic value solely measures the in-the-money portion of the option.
How to Calculate Option Intrinsic Value
Option intrinsic value represents the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price, reflecting the immediate profit potential. For a call option, intrinsic value equals the current stock price minus the strike price, while for a put option, it is the strike price minus the current stock price, both calculated only when in-the-money. Premium includes intrinsic value plus time value, so calculating option intrinsic value requires subtracting any extrinsic components from the total premium.
Distinguishing Intrinsic Value and Extrinsic Value
Intrinsic value in options represents the immediate profit if exercised, calculated as the difference between the underlying asset's price and the option's strike price, applicable only when in-the-money. The premium encompasses both intrinsic value and extrinsic value, the latter reflecting time value, volatility, and market demand beyond immediate exercise profit. Distinguishing intrinsic value from extrinsic value is crucial for accurate options pricing and strategic decision-making.
Factors Influencing Option Premium
Option premium is influenced by intrinsic value, which represents the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price, reflecting immediate exercisability. Time to expiration, implied volatility, interest rates, and dividends significantly affect the option premium beyond its intrinsic value. Higher volatility and longer time to expiration generally increase the premium due to greater potential for favorable price movements.
Premium vs Intrinsic Value: Key Differences
The premium of an option includes both intrinsic value and time value, reflecting the total price paid by the option buyer. Intrinsic value measures the real, immediate profit potential by comparing the option's strike price to the underlying asset's market price. Premium exceeds intrinsic value when time value exists, representing factors like volatility and time until expiration, which do not affect intrinsic value directly.
The Role of Intrinsic Value in Option Pricing Strategies
Intrinsic value plays a crucial role in option pricing strategies by representing the immediate profit potential of an option if exercised. The premium of an option consists of intrinsic value plus time value, reflecting both current profitability and future potential. Traders prioritize intrinsic value to gauge the true worth of the option relative to the underlying asset's price movements, enabling informed decisions on buying, selling, or exercising options.
Why Intrinsic Value Matters for Option Traders
Intrinsic value represents the real, tangible profit potential of an option if exercised immediately, crucial for option traders to assess true asset worth beyond premiums. Premiums include intrinsic value plus time value, reflecting market expectations and risk, but only intrinsic value guarantees exercise profit. Understanding intrinsic value enables traders to identify undervalued options and make informed decisions, optimizing entry and exit strategies for maximizing returns.
Making Informed Trades: Evaluating Premium vs Intrinsic Value
Evaluating options premium versus intrinsic value is crucial for making informed trades, as the premium represents the total market price including time value and volatility, while intrinsic value reflects the actual profit potential if exercised immediately. Traders must understand that a premium exceeding intrinsic value indicates extrinsic value, which decreases as expiration approaches and impacts option pricing strategies. Thorough analysis of these components enables better risk assessment and decision-making in options trading.
Premium Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com