Import quotas restrict the quantity of specific goods that can be brought into a country, helping protect domestic industries from foreign competition. These limits often lead to higher prices and reduced availability of certain products in the market. Discover how import quotas impact global trade and your purchasing choices by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
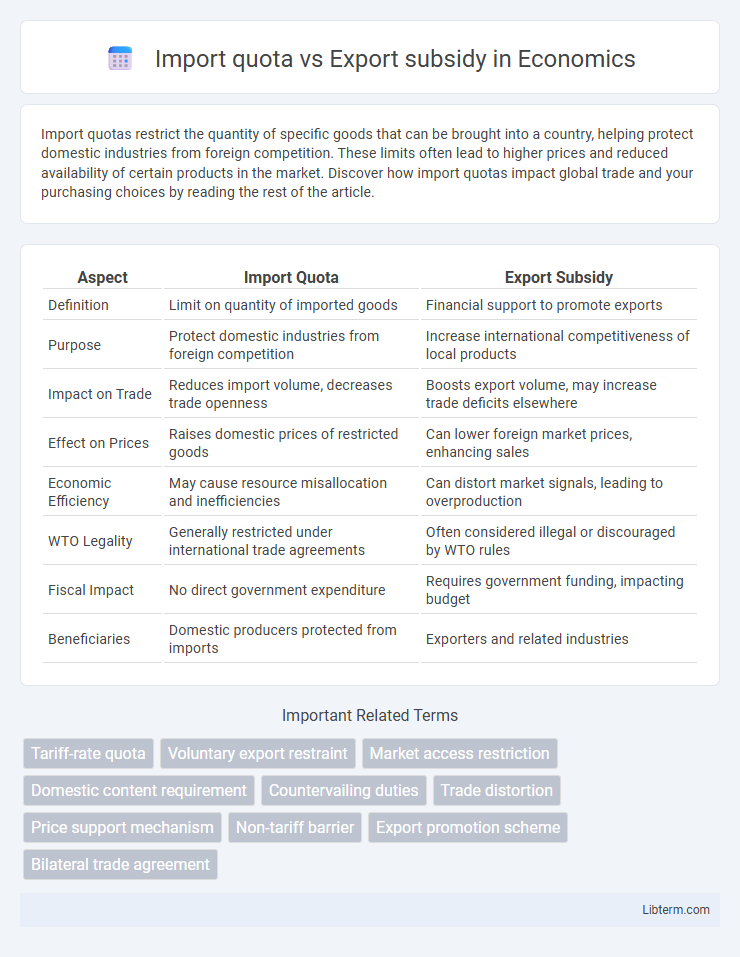
| Aspect | Import Quota | Export Subsidy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Limit on quantity of imported goods | Financial support to promote exports |
| Purpose | Protect domestic industries from foreign competition | Increase international competitiveness of local products |
| Impact on Trade | Reduces import volume, decreases trade openness | Boosts export volume, may increase trade deficits elsewhere |
| Effect on Prices | Raises domestic prices of restricted goods | Can lower foreign market prices, enhancing sales |
| Economic Efficiency | May cause resource misallocation and inefficiencies | Can distort market signals, leading to overproduction |
| WTO Legality | Generally restricted under international trade agreements | Often considered illegal or discouraged by WTO rules |
| Fiscal Impact | No direct government expenditure | Requires government funding, impacting budget |
| Beneficiaries | Domestic producers protected from imports | Exporters and related industries |
Introduction to Import Quotas and Export Subsidies
Import quotas restrict the quantity of specific goods that can be imported into a country, protecting domestic industries from foreign competition and controlling market supply. Export subsidies provide financial assistance to domestic producers, encouraging increased production and competitiveness in international markets by reducing costs. Both policies aim to influence trade balances, support local economies, and affect global market dynamics.
Definition and Key Concepts
Import quota is a government-imposed limit on the quantity or value of goods that can be imported into a country during a specific period, aimed at protecting domestic industries and controlling trade balances. Export subsidy refers to financial assistance or incentives provided by a government to domestic producers to encourage exports, enhance global competitiveness, and increase foreign market share. Both import quotas and export subsidies are trade policy tools used to influence international trade flows and support domestic economic objectives.
Objectives of Import Quotas
Import quotas restrict the quantity of specific goods that can enter a country to protect domestic industries from foreign competition and preserve local employment. These quotas aim to balance trade deficits by limiting imports, safeguarding national security by controlling strategic resources, and promoting domestic production. By regulating market supply, import quotas also help maintain stable prices for local producers and consumers.
Goals of Export Subsidies
Export subsidies aim to enhance a country's export competitiveness by lowering producers' costs, enabling them to offer goods at reduced prices in international markets. These subsidies stimulate domestic production, promote economic growth, and increase market share globally. By targeting key industries, governments seek to boost employment and improve trade balances through expanded export volumes.
Mechanisms of Action: How Import Quotas Operate
Import quotas restrict the quantity of specific goods that can be imported into a country, directly limiting supply and protecting domestic industries from foreign competition. By setting a maximum import volume, import quotas create scarcity in the domestic market, often leading to higher prices and increased demand for locally produced products. This mechanism contrasts with export subsidies, which enhance competitiveness by lowering production costs for domestic exporters rather than limiting imports.
Mechanisms of Action: How Export Subsidies Work
Export subsidies work by providing financial support from the government to domestic producers, reducing their costs and enabling them to sell goods at lower prices in international markets. This mechanism encourages increased exports by making products more competitive abroad, often leading to expanded market share for subsidized goods. Unlike import quotas, which limit the quantity of foreign goods, export subsidies specifically enhance the profitability and volume of outbound shipments.
Economic Impacts: Import Quota Effects
Import quotas restrict the quantity of goods that can be imported, leading to higher domestic prices and reduced consumer choice. This protectionist measure benefits local producers by limiting foreign competition but often results in inefficiencies and resource misallocation in the economy. Consumers face higher costs, and retaliatory trade measures may further impact overall economic growth and international trade relations.
Economic Impacts: Export Subsidy Effects
Export subsidies increase a country's export volumes by making domestically produced goods cheaper in international markets, leading to enhanced trade balances and higher employment in export-oriented industries. These subsidies can distort global markets by giving domestic producers an unfair competitive advantage, often triggering retaliatory trade measures and trade disputes. While export subsidies may boost short-term economic growth, they can strain government budgets and provoke inefficiencies by encouraging overproduction and misallocation of resources.
Comparison: Import Quotas vs. Export Subsidies
Import quotas restrict the quantity of goods that can enter a country, directly limiting supply and protecting domestic industries from foreign competition. Export subsidies provide financial support to domestic producers to boost their exports, making their goods more competitive in international markets without limiting production volume. Unlike import quotas that restrict market access, export subsidies incentivize production for foreign markets, influencing trade balance and potentially provoking retaliatory measures.
Policy Implications and Global Trade Considerations
Import quotas restrict the quantity of goods that can enter a country, protecting domestic industries but potentially raising consumer prices and inviting trade retaliation. Export subsidies encourage domestic producers to sell more abroad by lowering costs, which can distort global markets and provoke disputes under World Trade Organization rules. Both policies impact trade balances and require careful analysis of their effects on economic efficiency, international relations, and compliance with multilateral trade agreements.
Import quota Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com