Per capita government expenditure reflects the average amount of public funds spent per person within a country, providing insight into the allocation of resources for services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. Understanding this metric helps gauge the government's commitment to social welfare and economic development. Discover how variations in per capita government expenditure impact your community and national growth in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
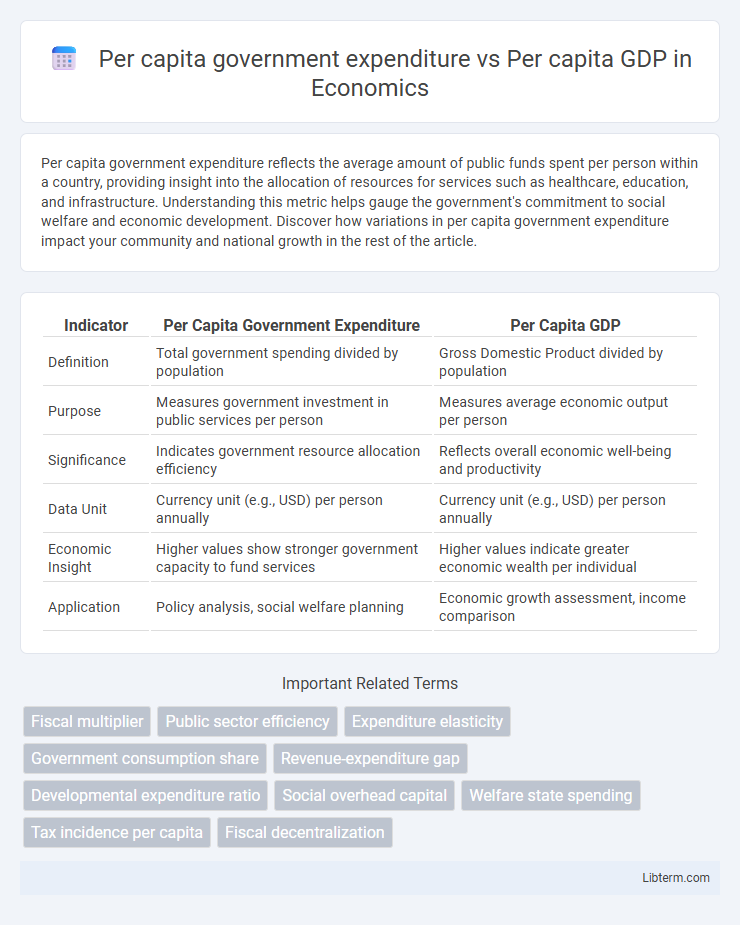
| Indicator | Per Capita Government Expenditure | Per Capita GDP |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total government spending divided by population | Gross Domestic Product divided by population |
| Purpose | Measures government investment in public services per person | Measures average economic output per person |
| Significance | Indicates government resource allocation efficiency | Reflects overall economic well-being and productivity |
| Data Unit | Currency unit (e.g., USD) per person annually | Currency unit (e.g., USD) per person annually |
| Economic Insight | Higher values show stronger government capacity to fund services | Higher values indicate greater economic wealth per individual |
| Application | Policy analysis, social welfare planning | Economic growth assessment, income comparison |
Introduction to Per Capita Government Expenditure and Per Capita GDP
Per capita government expenditure measures the average public spending per individual, reflecting the allocation of government resources for services, infrastructure, and social programs. Per capita GDP, calculated by dividing a country's total gross domestic product by its population, indicates the average economic output per person and serves as a key indicator of economic prosperity. Comparing these metrics helps assess the balance between public investment and overall economic performance, guiding fiscal policy and resource distribution.
Defining Key Economic Indicators
Per capita government expenditure measures the average government spending per person, reflecting public investment and service provision within an economy. Per capita GDP indicates the average economic output per individual, serving as a primary gauge of economic prosperity and living standards. Comparing these indicators highlights the balance between government resource allocation and overall economic productivity essential for fiscal policy analysis.
Importance of Analyzing Per Capita Metrics
Analyzing per capita government expenditure and per capita GDP reveals critical insights into a country's economic health and public service efficiency by standardizing data relative to population size. This comparison highlights how government spending translates into economic output and living standards, offering a clearer understanding of resource allocation and fiscal policy effectiveness. Policymakers use these metrics to identify disparities, optimize budgets, and promote equitable growth across different population segments.
Methodology for Comparing Per Capita Government Expenditure and GDP
Analyzing per capita government expenditure relative to per capita GDP involves normalizing total government spending and GDP figures by population size to enable direct comparison across regions or countries. This methodology employs Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) adjustments to account for cost-of-living differences, ensuring that expenditure and income values reflect real economic capacity and government efficiency. Data sources such as national accounts, IMF databases, and World Bank statistics are utilized, with statistical tools applied to assess correlations, trends, and deviations in fiscal policy impacts on economic output.
Global Trends in Per Capita Government Expenditure vs GDP
Global trends reveal that per capita government expenditure generally increases in tandem with rising per capita GDP, indicating stronger fiscal capacity in wealthier nations. Developed countries often allocate a higher proportion of GDP to public spending per capita, reflecting enhanced social services and infrastructure investments. Emerging economies display more variability, with government expenditure per capita growing at a slower pace relative to GDP due to differing policy priorities and fiscal constraints.
Correlation Between Government Spending and Economic Growth
Per capita government expenditure often shows a positive correlation with per capita GDP, indicating that higher government spending can stimulate economic growth through infrastructure development, public services, and social welfare programs. Empirical studies reveal that efficient allocation of government funds enhances productivity and boosts overall economic output. However, excessive or mismanaged spending may lead to fiscal deficits and reduced economic efficiency, highlighting the importance of balanced fiscal policies.
Regional Differences: High-Income vs Low-Income Countries
Per capita government expenditure tends to be significantly higher in high-income countries compared to low-income countries, reflecting their greater fiscal capacity and broader public service provision. High-income nations often allocate a larger proportion of their GDP to sectors such as healthcare, education, and social security, leading to more comprehensive welfare systems. In contrast, low-income countries face budgetary constraints that limit government spending despite often having a greater need for development-oriented public investment.
Impact on Public Services and Social Welfare
Higher per capita government expenditure relative to per capita GDP typically enhances public services, including healthcare, education, and infrastructure, leading to improved social welfare outcomes. When government spending is efficiently allocated, it can reduce inequality and increase access to essential services, promoting overall economic well-being. Conversely, lower per capita government expenditure may limit public service quality and availability, negatively affecting social safety nets and citizen welfare.
Policy Implications and Budgetary Strategies
Per capita government expenditure relative to per capita GDP highlights fiscal space and resource allocation efficiency, influencing policy decisions on public investment and social welfare programs. Higher government spending as a proportion of GDP often necessitates strategic budgetary measures to ensure sustainability, such as prioritizing sectors with high multiplier effects or implementing fiscal consolidation during economic downturns. Policymakers should balance expenditure to stimulate growth while controlling deficits, leveraging data on GDP elasticity and sectoral impact for optimized budget planning.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
Rising per capita government expenditure aligned with increasing per capita GDP indicates stronger fiscal capacity to invest in public services and infrastructure. Future outlook suggests sustainable economic growth must be supported by efficient allocation of government resources to maintain balanced development. Recommendations emphasize enhancing transparency, prioritizing social welfare programs, and fostering innovation-driven policies to maximize the impact of government spending on GDP growth.
Per capita government expenditure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com