Fiat currency is government-issued money not backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver, relying instead on trust and government regulation to maintain its value. It serves as the primary medium of exchange in most economies worldwide, facilitating everyday transactions from buying groceries to paying bills. Discover more about how fiat currency impacts your financial decisions and the global economy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
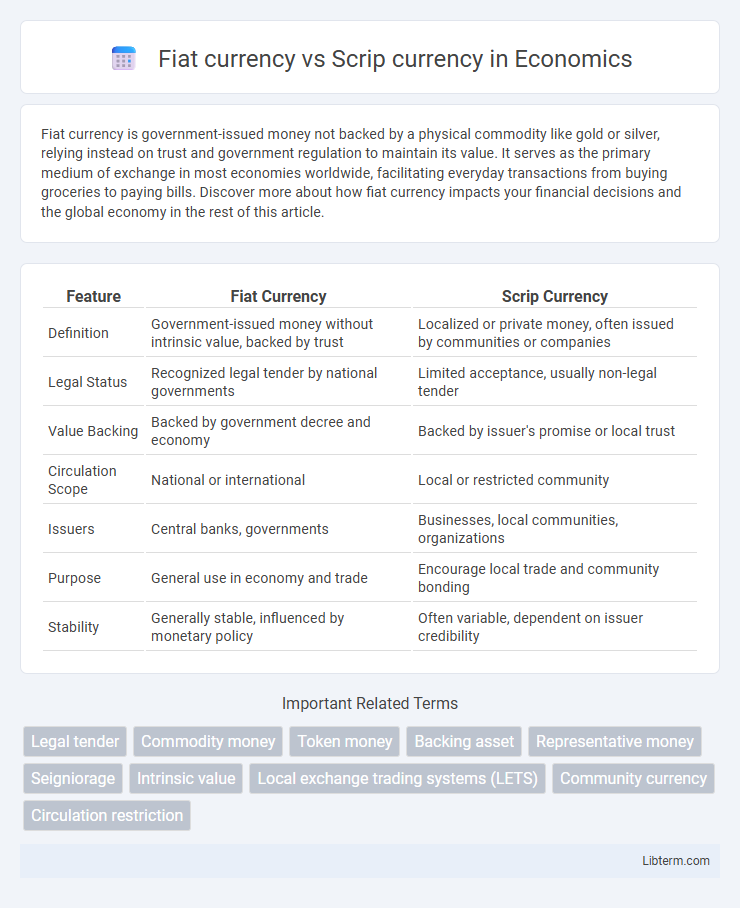
| Feature | Fiat Currency | Scrip Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-issued money without intrinsic value, backed by trust | Localized or private money, often issued by communities or companies |
| Legal Status | Recognized legal tender by national governments | Limited acceptance, usually non-legal tender |
| Value Backing | Backed by government decree and economy | Backed by issuer's promise or local trust |
| Circulation Scope | National or international | Local or restricted community |
| Issuers | Central banks, governments | Businesses, local communities, organizations |
| Purpose | General use in economy and trade | Encourage local trade and community bonding |
| Stability | Generally stable, influenced by monetary policy | Often variable, dependent on issuer credibility |
Understanding Fiat Currency: Definition and History
Fiat currency is government-issued money that has no intrinsic value but is established as legal tender by government decree, enabling its acceptance in exchange for goods and services. Its origins trace back to ancient China during the Tang and Song dynasties, with widespread modern adoption occurring in the 20th century after the abandonment of the gold standard. Unlike scrip currency, which is typically issued by private entities for limited use within specific communities or companies, fiat currency maintains national economic stability through centralized monetary policy control.
What is Scrip Currency? Origins and Purpose
Scrip currency refers to a substitute form of money issued by private entities, companies, or local governments, primarily used in limited areas or communities to facilitate trade when official fiat currency is scarce or unavailable. Originating in the 19th and early 20th centuries, scrip currency was commonly issued by mining companies, plantations, and company towns to pay workers and enable transactions within isolated economies. Its primary purpose was to maintain local economic stability and labor payment systems, although scrip often lacked the widespread acceptance and legal backing of fiat currency.
Key Differences Between Fiat and Scrip Currency
Fiat currency is government-issued money recognized as legal tender, backed by trust in the issuing authority rather than a physical commodity, whereas scrip currency is a form of private or local currency often issued by businesses or communities for limited use. Fiat currency circulates broadly within a nation's economy and is universally accepted for debts and transactions, while scrip is restricted to specific regions or establishments, lacking widespread acceptance. The value of fiat currency is maintained by monetary policy and government regulation, in contrast to scrip whose value depends on local acceptance and specific agreements.
How Fiat Currency Works in Modern Economies
Fiat currency operates as legal tender backed by government decree rather than physical commodities, enabling central banks to regulate money supply through monetary policy tools like interest rates and open market operations. Its value is maintained by public trust and the stability of the issuing government, facilitating efficient transactions, pricing, and economic growth. Modern economies rely on fiat currency systems to implement inflation control, manage liquidity, and support fiscal policies essential for economic stability.
The Role of Scrip Currency in Local and Alternative Markets
Scrip currency plays a critical role in local and alternative markets by providing a medium of exchange that operates independently from national fiat currencies, often enhancing community resilience during economic instability. It facilitates localized trade, supports small businesses, and encourages circular economies by keeping value within specific regions or groups. Unlike fiat currency, which relies on government backing, scrip currencies derive value from mutual trust and agreements within user communities.
Advantages of Fiat Currency Systems
Fiat currency systems enable governments to control money supply, enhancing economic stability through monetary policy tools like interest rate adjustments and inflation targeting. Unlike scrip currency, fiat currency is widely accepted for all debts, public and private, fostering seamless trade and investment within and across borders. This universal acceptance reduces transaction costs and increases liquidity, driving economic growth and development.
Strengths and Limitations of Scrip Currency
Scrip currency offers localized control and can stimulate economic activity within specific communities or organizations due to its limited circulation and targeted use. However, its limitations include lack of widespread acceptance, lower liquidity compared to fiat currency, and susceptibility to devaluation if not backed by a credible institution. Unlike fiat currency, which is government-backed and universally accepted, scrip currency often faces challenges in scalability and trust outside its issuing entity.
Economic Stability: Fiat vs. Scrip Currency
Fiat currency, backed by government regulation and accepted as legal tender, provides greater economic stability by facilitating standardized monetary policy and controlling inflation. Scrip currency, issued by private entities or local communities, often lacks widespread acceptance and regulatory oversight, leading to limited stability and potential devaluation. The centralized control of fiat currency supports broader economic integration and confidence compared to the localized and fluctuating nature of scrip currency systems.
Use Cases and Real-World Examples of Each System
Fiat currency, backed by government authority, is widely used for daily transactions, savings, and international trade, exemplified by the US Dollar and Euro, facilitating stable economic systems and monetary policies. Scrip currency, often issued by private companies or local communities, serves niche use cases such as corporate dividends, loyalty programs, or local economies, with notable examples like company-issued scrip during the Great Depression or local community currencies like the Bristol Pound. Each system supports different economic needs, where fiat provides broad acceptance and legal tender status, while scrip offers targeted incentives and localized monetary circulation.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Fiat and Scrip Currency
The future outlook of fiat currency involves increased digitalization and integration with blockchain technologies, enhancing transparency and security in monetary transactions. Scrip currency, often utilized in localized or alternative economies, is evolving through mobile payment systems and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to improve accessibility and reduce reliance on centralized banking. Innovations in both fiat and scrip currencies are poised to redefine economic exchanges by fostering inclusivity and efficiency across global and community-based financial ecosystems.
Fiat currency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com