Liquidation value represents the estimated amount an asset or business can fetch if sold quickly, often under distressed conditions where market value may be lower than book value. Understanding liquidation value is crucial for investors, creditors, and business owners to assess potential recoveries in bankruptcy or forced sale scenarios. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to accurately calculate liquidation value and its impact on financial decision-making.
Table of Comparison
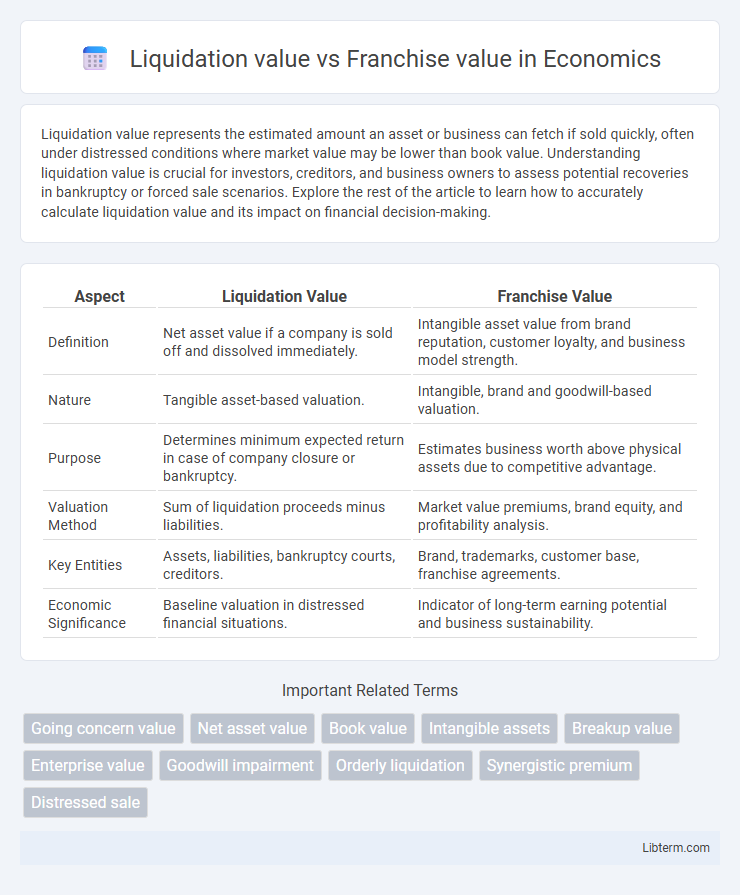
| Aspect | Liquidation Value | Franchise Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net asset value if a company is sold off and dissolved immediately. | Intangible asset value from brand reputation, customer loyalty, and business model strength. |
| Nature | Tangible asset-based valuation. | Intangible, brand and goodwill-based valuation. |
| Purpose | Determines minimum expected return in case of company closure or bankruptcy. | Estimates business worth above physical assets due to competitive advantage. |
| Valuation Method | Sum of liquidation proceeds minus liabilities. | Market value premiums, brand equity, and profitability analysis. |
| Key Entities | Assets, liabilities, bankruptcy courts, creditors. | Brand, trademarks, customer base, franchise agreements. |
| Economic Significance | Baseline valuation in distressed financial situations. | Indicator of long-term earning potential and business sustainability. |
Introduction to Liquidation Value and Franchise Value
Liquidation value represents the estimated amount a business's assets would fetch if sold quickly, typically under distressed conditions, reflecting tangible asset worth rather than ongoing operations. Franchise value captures the premium associated with an established brand, customer loyalty, and business models that generate consistent profit beyond asset values. Understanding the distinction highlights how liquidation value emphasizes short-term asset liquidation, while franchise value centers on long-term business viability and market position.
Defining Liquidation Value
Liquidation value refers to the estimated amount that can be realized from the sale of a company's assets when the business is closed or dissolved, typically under distressed conditions. It represents the net cash that would be received if assets were sold quickly, often below market value, prioritizing speed over maximizing price. Unlike franchise value, which captures ongoing business profitability and brand strength, liquidation value strictly assesses asset liquidation proceeds.
Understanding Franchise Value
Franchise value represents the premium a business commands over its liquidation value due to its established brand, customer loyalty, and ongoing operational profitability. Unlike liquidation value, which estimates net asset value if the business is dismantled, franchise value captures intangible assets such as patents, trademarks, and market position that drive future cash flows. Understanding franchise value is crucial for investors assessing long-term growth potential and sustainability beyond mere asset liquidation.
Key Differences Between Liquidation Value and Franchise Value
Liquidation value represents the net amount a company can obtain by selling its assets quickly, typically under distressed conditions, while franchise value reflects the premium a business enjoys over its asset value due to brand strength, customer loyalty, and operational efficiency. Liquidation value often serves as a conservative baseline in valuation, whereas franchise value captures future earning potential and market position. Key differences include time horizon, purpose of valuation, and the inclusion of intangible assets, making franchise value higher and more speculative compared to the often lower and more concrete liquidation value.
Factors Affecting Liquidation Value
Liquidation value is primarily influenced by asset condition, market demand, and time constraints, which can significantly reduce the amount recoverable from selling assets quickly. Unlike franchise value, which reflects ongoing business profitability and brand reputation, liquidation value depends on the physical sale of tangible and intangible assets under distressed conditions. Economic environment, legal issues, and buyer urgency also play critical roles in determining the final liquidation price.
Factors Influencing Franchise Value
Franchise value is heavily influenced by factors such as brand strength, customer loyalty, and the quality of proprietary systems or products, which together drive long-term profit potential. Market positioning, competitive advantage, and management expertise also play critical roles in enhancing franchise value beyond mere asset liquidation. Unlike liquidation value, which reflects the immediate sale price of tangible assets, franchise value encompasses intangible assets and future earning power essential for sustained business success.
Importance in Business Valuation
Liquidation value represents the estimated amount a business's assets would fetch if sold off quickly, providing a critical baseline during financial distress or bankruptcy scenarios. Franchise value reflects the premium attributed to a brand's reputation, customer loyalty, and established market presence, often exceeding tangible asset worth in ongoing business valuation. Understanding both values ensures accurate assessment of a company's worth, guiding investors and stakeholders in strategic decision-making and risk management.
Practical Examples: Liquidation vs Franchise Value
Liquidation value represents the estimated amount a business's assets would fetch if sold quickly, often at a discounted price during bankruptcy or closure, typically lower than the business's ongoing worth. Franchise value reflects the premium attached to a profitable, operational brand with established customer loyalty and market presence, often measured by the difference between the company's market value and its liquidation value. For example, a restaurant chain forced to close may receive a liquidation value for its assets such as kitchen equipment and real estate, whereas the franchise value considers its brand recognition, customer base, and future profit potential, greatly exceeding the liquidation figure.
Implications for Investors and Stakeholders
Liquidation value represents the net amount an investor or stakeholder can expect if a company's assets are sold off quickly, often at a discount, signaling financial distress or insolvency risks. Franchise value reflects the premium investors place on a company's brand strength, customer loyalty, and future earning potential, influencing long-term investment decisions. Understanding the divergence between liquidation and franchise values helps stakeholders assess risk exposure, prioritize asset recovery strategies, and gauge sustainable profitability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Valuation Approach
Selecting the proper valuation method depends on the business's purpose and financial context, with liquidation value best suited for assessing asset worth in distress or closure scenarios. Franchise value captures the ongoing enterprise's intangible benefits, including brand strength, customer loyalty, and growth potential, guiding decisions in profitable operational assessments. Prioritizing franchise value favors strategic holders seeking future earnings, while liquidation value serves creditors or investors focusing on asset recovery.
Liquidation value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com