The Big Push Strategy focuses on coordinated, large-scale investments to overcome market failures and achieve rapid industrial growth. By mobilizing resources across multiple sectors simultaneously, it creates economies of scale and accelerates development. Discover how this strategy can transform economies and why it might be the solution your business needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
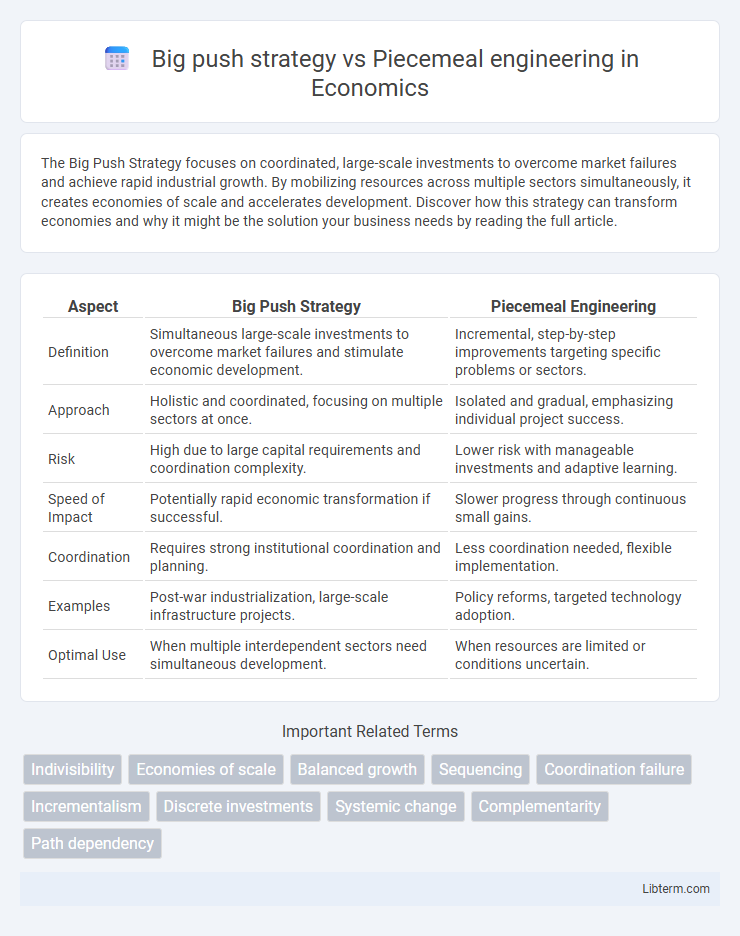
| Aspect | Big Push Strategy | Piecemeal Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous large-scale investments to overcome market failures and stimulate economic development. | Incremental, step-by-step improvements targeting specific problems or sectors. |
| Approach | Holistic and coordinated, focusing on multiple sectors at once. | Isolated and gradual, emphasizing individual project success. |
| Risk | High due to large capital requirements and coordination complexity. | Lower risk with manageable investments and adaptive learning. |
| Speed of Impact | Potentially rapid economic transformation if successful. | Slower progress through continuous small gains. |
| Coordination | Requires strong institutional coordination and planning. | Less coordination needed, flexible implementation. |
| Examples | Post-war industrialization, large-scale infrastructure projects. | Policy reforms, targeted technology adoption. |
| Optimal Use | When multiple interdependent sectors need simultaneous development. | When resources are limited or conditions uncertain. |
Introduction to Development Strategies
Big push strategy emphasizes large-scale, coordinated investments to stimulate rapid economic development, targeting infrastructure, industrial sectors, and human capital simultaneously. Piecemeal engineering involves gradual, incremental improvements focusing on small-scale projects or sector-specific interventions, allowing for flexibility and adaptation. Both strategies address development challenges but differ in scale, risk, and the speed of economic transformation.
Understanding the Big Push Strategy
The Big Push Strategy involves simultaneous, large-scale investment across multiple sectors to stimulate rapid economic growth, relying on economies of scale and coordinated efforts to overcome market failures. It contrasts with Piecemeal Engineering, which focuses on gradual, incremental improvements in specific areas without widespread coordination. Understanding the Big Push Strategy emphasizes its role in catalyzing structural transformation by leveraging collective investments and synchronized development initiatives to achieve sustainable growth.
Key Principles of Piecemeal Engineering
Piecemeal engineering emphasizes incremental development, allowing continuous adaptation and learning from feedback at each stage to improve system design. It prioritizes modularity, enabling independent subsystems to be integrated gradually, reducing risks and enhancing flexibility compared to the Big Push strategy. This approach supports iterative testing and refinement, fostering robustness and alignment with evolving user requirements throughout the engineering process.
Historical Context and Evolution
Big push strategy emerged during the mid-20th century as a development economics approach advocating large-scale, coordinated investments to overcome market failures and propel industrialization. In contrast, piecemeal engineering reflects incremental, step-by-step interventions emphasizing adaptability and learning from smaller projects, rooted in systems engineering and reformist policy applications. The evolution from big push to piecemeal methods highlights shifts toward more flexible, context-sensitive development strategies responding to complex socio-economic challenges and implementation constraints.
Core Differences: Big Push vs Piecemeal Engineering
Big Push strategy involves simultaneous, large-scale investments across multiple sectors to create synergistic economic growth, while Piecemeal engineering focuses on incremental, isolated improvements in specific industries or projects. The Big Push approach aims for coordination to overcome market failures and achieve rapid development, contrasting with the more flexible but slower, step-by-step process of Piecemeal engineering. Core differences revolve around scale, synchronization of efforts, and the speed of economic transformation.
Advantages of the Big Push Approach
The Big Push strategy accelerates product development by integrating all components simultaneously, ensuring coherence and reducing integration issues. It enhances cross-functional collaboration, leading to improved innovation and faster time-to-market. This approach minimizes rework and allows for comprehensive testing, resulting in higher-quality outcomes compared to Piecemeal Engineering.
Benefits of Piecemeal Engineering
Piecemeal engineering allows for incremental development, reducing initial investment risks while enabling continuous improvement based on real-world feedback. This approach enhances flexibility, adapting to changing requirements and technological advancements without large-scale resource commitments. It fosters faster deployment of components, improving time-to-market and enabling organizations to respond swiftly to user needs and competitive pressures.
Criticisms and Limitations
Big push strategy often faces criticism for its high upfront costs and risks, potentially leading to widescale failure if initial assumptions prove wrong. Piecemeal engineering is limited by incremental progress that can result in suboptimal integration and slower overall development. Both approaches struggle with balancing flexibility and scalability when adapting to changing market conditions or technological advancements.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Big push strategy, exemplified in the rapid industrialization campaigns of South Korea and China, demonstrates how simultaneous investments across multiple sectors can accelerate economic development and infrastructure growth. In contrast, piecemeal engineering, seen in incremental urban development projects like the expansion of New York City's subway system, focuses on phased improvements to reduce risk and adapt to evolving needs. Case studies reveal big push strategies often require substantial upfront capital and coordination, while piecemeal approaches allow flexibility and scalability with lower initial costs.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Economic Development
Choosing the right economic development strategy hinges on the scale and immediacy of targeted growth outcomes. The Big Push strategy involves simultaneous, large-scale investments in multiple sectors to overcome coordination failures and achieve rapid industrialization. In contrast, Piecemeal engineering emphasizes incremental, sector-specific projects that allow flexibility and adaptation but may face slower overall economic transformation.
Big push strategy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com