Rent-seeking involves individuals or firms trying to gain economic benefits without contributing to productivity, often by manipulating the political or regulatory environment. This behavior can lead to inefficiencies and slow down economic growth by diverting resources away from innovation and value creation. Explore the article to understand how rent-seeking impacts your economy and steps you can take to minimize its effects.
Table of Comparison
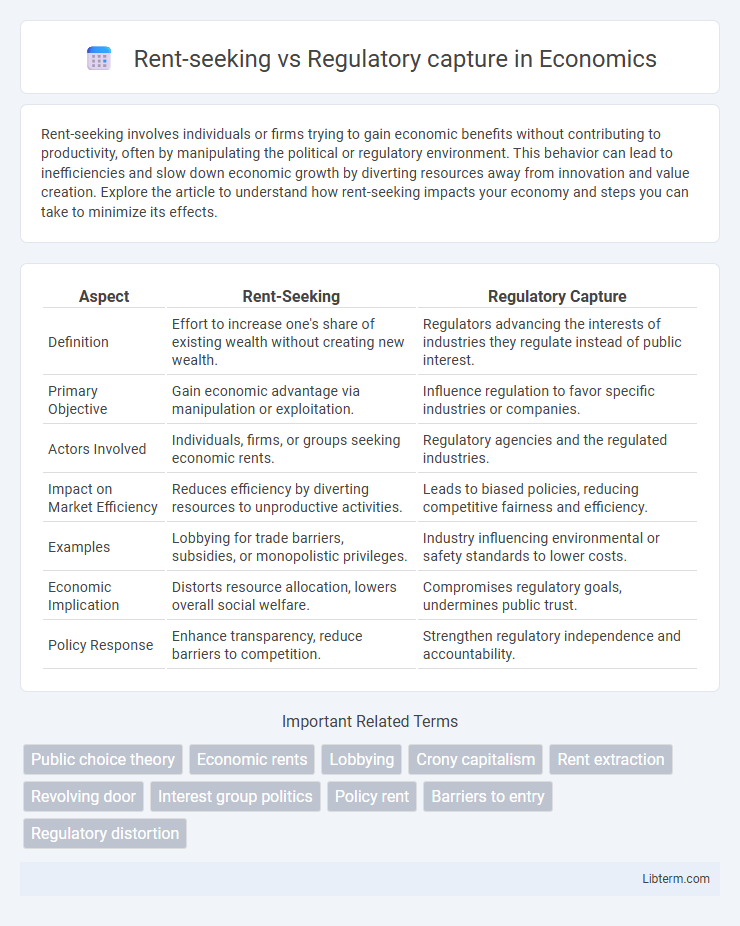
| Aspect | Rent-Seeking | Regulatory Capture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Effort to increase one's share of existing wealth without creating new wealth. | Regulators advancing the interests of industries they regulate instead of public interest. |
| Primary Objective | Gain economic advantage via manipulation or exploitation. | Influence regulation to favor specific industries or companies. |
| Actors Involved | Individuals, firms, or groups seeking economic rents. | Regulatory agencies and the regulated industries. |
| Impact on Market Efficiency | Reduces efficiency by diverting resources to unproductive activities. | Leads to biased policies, reducing competitive fairness and efficiency. |
| Examples | Lobbying for trade barriers, subsidies, or monopolistic privileges. | Industry influencing environmental or safety standards to lower costs. |
| Economic Implication | Distorts resource allocation, lowers overall social welfare. | Compromises regulatory goals, undermines public trust. |
| Policy Response | Enhance transparency, reduce barriers to competition. | Strengthen regulatory independence and accountability. |
Introduction to Rent-Seeking and Regulatory Capture
Rent-seeking occurs when individuals or firms use resources to gain economic advantages through manipulation or exploitation of the regulatory environment rather than through productive activities. Regulatory capture happens when regulatory agencies become dominated by the industries or interests they are supposed to regulate, leading to policies that favor incumbents over the public good. Both concepts highlight inefficiencies in market regulation, where private interests distort policy outcomes at the expense of social welfare.
Defining Rent-Seeking: Economic and Political Perspectives
Rent-seeking refers to efforts by individuals or firms to gain economic benefits through manipulation or exploitation of the political environment rather than through productive economic activities. This behavior often involves lobbying, bribery, or other forms of influence aimed at securing favorable regulations, subsidies, or monopolistic privileges. Economic perspectives highlight rent-seeking as a source of inefficiency and resource misallocation, while political perspectives emphasize its impact on policy distortion and governance quality.
What is Regulatory Capture?
Regulatory capture occurs when regulatory agencies created to act in the public's interest instead advance the commercial or political concerns of special interest groups that dominate the industry they are charged with regulating. This phenomenon leads to a regulatory environment favoring incumbents, reducing competition, and potentially harming consumers through ineffective oversight. Key examples include financial sectors, environmental agencies, and telecommunications commissions where industry insiders influence rule-making to secure favorable outcomes.
Key Differences Between Rent-Seeking and Regulatory Capture
Rent-seeking involves individuals or firms manipulating economic policies to increase their own wealth without creating value, often through lobbying or influencing legislation. Regulatory capture occurs when regulatory agencies become dominated by the industries they are supposed to regulate, resulting in regulations that benefit the industry rather than the public. Key differences include rent-seeking as a proactive effort by private interests to shape policies, while regulatory capture is a gradual process where regulators align with industry interests, compromising regulatory objectives.
Mechanisms of Rent-Seeking Behavior
Rent-seeking behavior involves efforts by individuals or firms to obtain economic gains through manipulation or exploitation of the political environment rather than productive activities, often by influencing regulations or government policies. Mechanisms include lobbying for favorable regulations, securing subsidies, or obtaining exclusive rights that create barriers to entry and limit competition. This behavior distorts market efficiency and can lead to regulatory capture, where regulatory agencies prioritize industry interests over public welfare.
How Regulatory Capture Occurs
Regulatory capture occurs when regulatory agencies, established to act in the public interest, become dominated by the industries or interests they are charged with regulating, leading to decisions that favor those industries over public welfare. Key mechanisms include revolving doors between industry and regulators, where employees move back and forth, creating conflicts of interest and regulatory bias. The phenomenon results in weakened regulations, reduced enforcement, and policies that prioritize corporate profits at the expense of consumers and the environment.
Economic and Social Impacts of Rent-Seeking
Rent-seeking diverts resources from productive economic activities toward securing economic rents through manipulation or exploitation of the regulatory environment, leading to inefficiencies and reduced overall welfare. This behavior can exacerbate income inequality by concentrating wealth among rent-seeking entities, weakening social cohesion and trust in institutions. Unlike regulatory capture, which involves the regulatory agencies favoring industry interests, rent-seeking broadly reduces innovation and economic growth by prioritizing personal gain over public benefit.
Consequences of Regulatory Capture in Various Industries
Regulatory capture results in industries benefiting disproportionately as regulatory agencies favor established firms, leading to reduced competition and innovation stagnation. In sectors like finance, energy, and pharmaceuticals, this distorts market dynamics, often causing higher prices and compromised public safety. The long-term consequence includes weakened regulatory effectiveness, eroding consumer trust and impeding economic growth.
Strategies to Prevent Rent-Seeking and Regulatory Capture
Effective strategies to prevent rent-seeking and regulatory capture include enhancing transparency and accountability in regulatory agencies, promoting competitive markets, and implementing strong conflict-of-interest rules for policymakers. Establishing independent oversight bodies and encouraging public participation in the regulatory process also reduce the risk of undue influence by special interest groups. Leveraging data-driven monitoring systems ensures early detection of regulatory deviations that favor specific entities at the expense of broader economic welfare.
Conclusion: Addressing Rent-Seeking and Regulatory Capture for Better Governance
Addressing rent-seeking and regulatory capture requires strengthening transparency and accountability mechanisms within public institutions. Implementing robust anti-corruption laws and enhancing stakeholder participation reduce undue influence by private interests over regulatory agencies. Effective governance hinges on promoting fair competition and ensuring policies serve the broader public interest rather than specific rent-seeking groups.
Rent-seeking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com