Game theory analyzes strategic interactions where the outcome depends on the choices of all participants, providing valuable insights into competitive and cooperative scenarios. It applies mathematical models to predict decision-making in economics, politics, and psychology, enhancing your understanding of rational behavior. Explore the rest of this article to discover how game theory influences everyday decisions and complex negotiations.
Table of Comparison
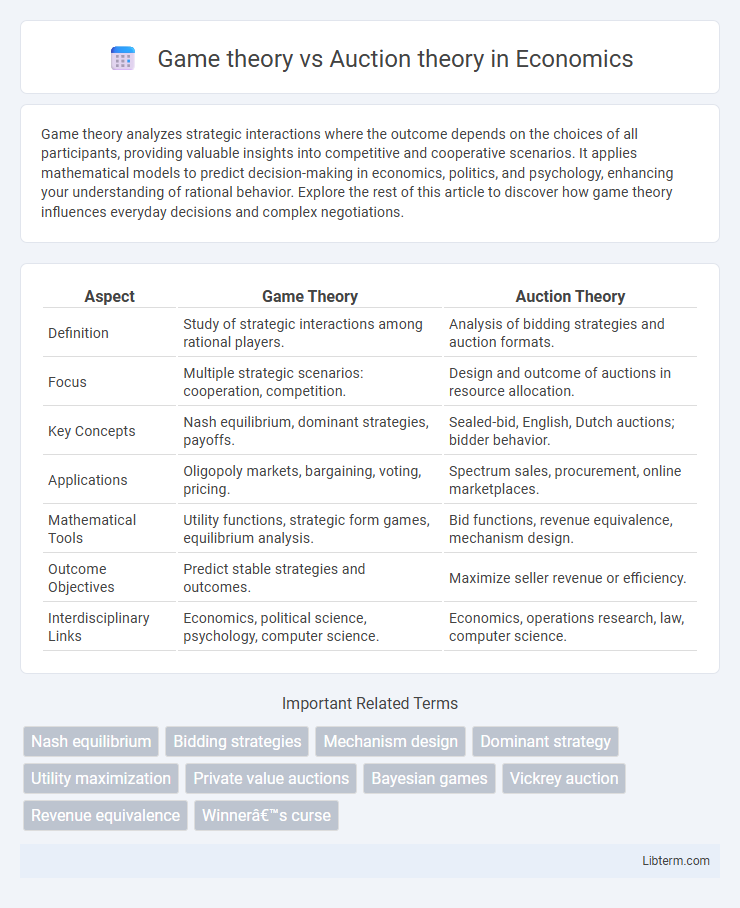
| Aspect | Game Theory | Auction Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of strategic interactions among rational players. | Analysis of bidding strategies and auction formats. |
| Focus | Multiple strategic scenarios: cooperation, competition. | Design and outcome of auctions in resource allocation. |
| Key Concepts | Nash equilibrium, dominant strategies, payoffs. | Sealed-bid, English, Dutch auctions; bidder behavior. |
| Applications | Oligopoly markets, bargaining, voting, pricing. | Spectrum sales, procurement, online marketplaces. |
| Mathematical Tools | Utility functions, strategic form games, equilibrium analysis. | Bid functions, revenue equivalence, mechanism design. |
| Outcome Objectives | Predict stable strategies and outcomes. | Maximize seller revenue or efficiency. |
| Interdisciplinary Links | Economics, political science, psychology, computer science. | Economics, operations research, law, computer science. |
Introduction to Game Theory and Auction Theory
Game theory studies strategic interactions among rational decision-makers, analyzing choices in competitive and cooperative environments through models like Nash equilibrium. Auction theory, a specialized branch of game theory, focuses on bidding strategies and mechanisms to allocate goods or services efficiently under different auction formats such as English, Dutch, and sealed-bid auctions. Both theories utilize mathematical frameworks to predict outcomes, optimize strategies, and design systems that maximize participants' utility and market efficiency.
Fundamental Concepts in Game Theory
Game theory examines strategic interactions where players make decisions to maximize their outcomes based on others' choices, emphasizing concepts like Nash equilibrium, dominant strategies, and payoff matrices. Auction theory, a specialized subset of game theory, studies bidding strategies and market design to allocate resources efficiently under competitive scenarios. Fundamental game theory concepts include player rationality, strategy profiles, and equilibrium analysis, which underpin the design and analysis of auction mechanisms.
Core Principles of Auction Theory
Auction theory centers on the design and analysis of bidding strategies and outcomes in various auction formats, emphasizing how information asymmetry and bidder behavior influence price discovery and allocation efficiency. Key principles include the Revelation Principle, which asserts that truthful bidding can lead to optimal outcomes, and the Winner's Curse, highlighting the risk of overpaying in common value auctions. Unlike game theory's broad study of strategic interaction in competitive scenarios, auction theory applies specific equilibrium concepts such as Bayesian Nash Equilibrium to model bidder strategies under uncertainty.
Key Differences Between Game Theory and Auction Theory
Game theory analyzes strategic interactions among rational decision-makers across various scenarios, while auction theory is a specialized branch focusing on bidding strategies and price determination within auction formats. Game theory encompasses a broad range of models including cooperative and non-cooperative games, whereas auction theory specifically studies mechanisms such as English, Dutch, sealed-bid, and Vickrey auctions. The primary difference lies in the scope: game theory addresses general strategic behavior, whereas auction theory applies those principles to the design and outcome prediction of auction markets.
Types of Games versus Types of Auctions
Game theory explores strategic interactions in various types of games, including cooperative games where players work together, non-cooperative games focusing on individual strategies, zero-sum games with strictly opposing interests, and repeated or sequential games involving multiple rounds of play. Auction theory categorizes auctions primarily into English auctions with ascending bids, Dutch auctions featuring descending prices, sealed-bid auctions where bids are secret, and Vickrey auctions which are second-price sealed-bid formats designed to incentivize truthful bidding. Understanding these distinctions highlights how game theory models broad strategic scenarios, while auction theory applies these principles to specific bidding mechanisms and market designs.
Applications of Game Theory in Economics
Game theory applies to economics by modeling strategic interactions among rational agents, enabling analysis of market competition, bargaining, and cooperation. Key applications include oligopoly market behavior, auction design, and mechanism design to optimize resource allocation and incentives. These models facilitate prediction of outcomes in economic scenarios where individual decisions affect collective results.
Auction Theory in Market Design and Practice
Auction theory plays a critical role in market design by providing frameworks for allocating resources efficiently and determining prices in competitive environments. It enables the creation of mechanisms that maximize revenue, ensure fairness, and promote strategic bidding behavior, which are essential in markets such as spectrum sales, online advertising, and electricity trading. By combining economic incentives and game-theoretic principles, auction theory helps design practical systems that balance supply and demand while preventing market manipulation.
Strategic Decision Making: Game Theory vs Auction Theory
Game theory analyzes strategic decision-making by modeling interactions among rational players, emphasizing equilibrium concepts like Nash equilibrium to predict outcomes in competitive and cooperative scenarios. Auction theory, a subset of game theory, focuses on the design and bidding strategies within various auction formats, optimizing revenue and efficiency based on bidder behavior and information asymmetry. Both fields provide critical insights into strategic behavior, yet auction theory applies these principles specifically to market-based mechanisms and resource allocation.
Limitations and Challenges in Both Theories
Game theory faces challenges in modeling complex human behaviors and incomplete information scenarios, often relying on assumptions of rationality that may not hold in real-world situations. Auction theory, while a subset of game theory, struggles with designing auctions that maximize revenue and efficiency amid bidder collusion, information asymmetry, and strategic manipulation. Both theories encounter limitations in scalability and computational complexity when applied to large, dynamic markets with multiple interacting agents.
Future Trends in Game Theory and Auction Theory
Future trends in game theory emphasize integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to model complex strategic interactions in dynamic environments. Auction theory is advancing towards designing more efficient and fair algorithms for digital marketplaces, incorporating blockchain technology for enhanced transparency and security. Both fields are converging with big data analytics to optimize decision-making processes in economic, social, and technological systems.
Game theory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com