Venture capital fuels innovation by providing startups with essential funding and strategic guidance to accelerate growth and market expansion. Investors seek high-potential companies that demonstrate scalable business models and strong management teams. Discover how venture capital can transform your business ideas into thriving enterprises by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
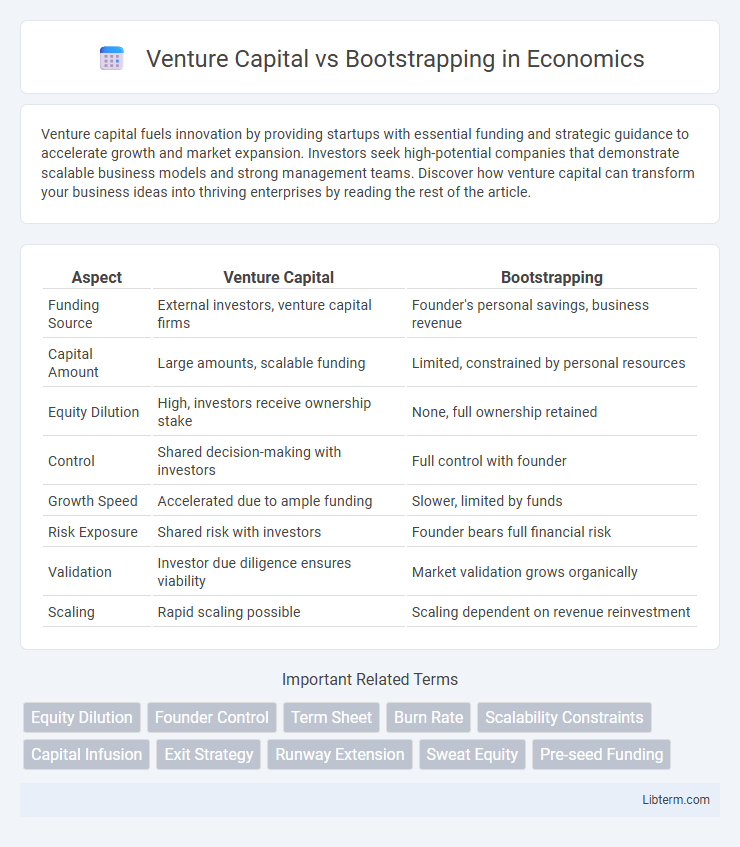
| Aspect | Venture Capital | Bootstrapping |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | External investors, venture capital firms | Founder's personal savings, business revenue |
| Capital Amount | Large amounts, scalable funding | Limited, constrained by personal resources |
| Equity Dilution | High, investors receive ownership stake | None, full ownership retained |
| Control | Shared decision-making with investors | Full control with founder |
| Growth Speed | Accelerated due to ample funding | Slower, limited by funds |
| Risk Exposure | Shared risk with investors | Founder bears full financial risk |
| Validation | Investor due diligence ensures viability | Market validation grows organically |
| Scaling | Rapid scaling possible | Scaling dependent on revenue reinvestment |
Understanding Venture Capital: An Overview
Venture capital involves raising funds from investors to accelerate business growth in exchange for equity ownership, often targeting high-potential startups in technology, healthcare, and other innovative sectors. This form of financing provides not only capital but also strategic guidance, industry connections, and credibility essential for scaling operations rapidly. Understanding venture capital requires recognizing its impact on ownership dilution, decision-making power, and the rigorous due diligence process investors implement before funding.
What is Bootstrapping? Key Principles Explained
Bootstrapping refers to building a startup using personal savings, reinvested earnings, and minimal external funding to maintain control and reduce debt. Key principles include lean operations, focusing on customer revenue, and iterative growth driven by market demand. Entrepreneurs prioritize financial discipline and resourcefulness to scale sustainably without relying on venture capital.
Funding Stages: VC Investment vs Self-Financing
Venture capital funding typically occurs in distinct stages such as seed, Series A, B, and beyond, allowing startups to access large capital injections to scale rapidly. Bootstrapping relies on self-financing through personal savings, revenue generation, and minimal external support, emphasizing gradual organic growth without dilution of ownership. VC investments involve external stakeholders seeking equity, while bootstrapping maintains full control but may limit funding size and growth speed.
Control and Ownership: Comparing VC and Bootstrapping
Venture capital financing often requires entrepreneurs to give up a significant portion of ownership and control to investors, who typically demand board seats and decision-making influence. In contrast, bootstrapping allows founders to retain full ownership and maintain complete control over their business operations and strategic direction. This trade-off between growth capital and autonomy is a crucial consideration for startups when choosing between venture capital and self-funding.
Speed of Growth: Accelerated Scale vs Sustainable Pace
Venture capital enables accelerated scale by providing substantial funding and resources, allowing startups to rapidly expand market share and innovate at a faster rate. Bootstrapping promotes a sustainable pace of growth, relying on internal cash flow and careful budgeting to maintain financial control and reduce risk. Companies choosing venture capital often experience quick market penetration, whereas bootstrapped firms prioritize long-term stability and gradual development.
Risk and Reward: Balancing Stakes in Both Approaches
Venture capital involves external funding that accelerates growth but increases risk by diluting ownership and imposing pressure for rapid returns. Bootstrapping relies on internal resources, reducing financial risk and maintaining full control, but often limits scalability and slows expansion. Balancing stakes requires evaluating tolerance for control loss versus growth speed to align risk appetite with long-term business goals.
Strategic Partnerships: Opportunities and Limitations
Venture capital offers startups access to strategic partnerships with established industry leaders, accelerating market entry and resource availability. Bootstrapping limits immediate partnership opportunities due to constrained funding but fosters independence and flexible decision-making. Understanding these dynamics helps entrepreneurs balance growth potential with operational control when choosing between venture capital and self-funding.
Financial Commitments and Investor Expectations
Venture capital requires significant financial commitment from investors who expect rapid growth and high returns within a defined timeframe, often influencing business decisions and strategies. Bootstrapping relies on personal savings or revenue reinvestment, minimizing external financial obligations and maintaining full control but potentially limiting scalability and speed of growth. Investor expectations in venture capital include board involvement, performance milestones, and exit strategies, whereas bootstrapped companies face fewer external pressures and focus solely on sustainable, organic growth.
Success Stories: VC-Backed vs Bootstrapped Startups
VC-backed startups like Airbnb and Uber achieved rapid global scale through significant funding, leveraging investor networks and marketing resources to disrupt traditional industries. In contrast, bootstrapped companies such as Mailchimp and Basecamp emphasize sustainable growth, maintaining control and profitability without external capital. Both pathways showcase distinct success patterns, with venture capital enabling fast expansion while bootstrapping fosters operational efficiency and long-term stability.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between venture capital and bootstrapping depends on factors such as the startup's growth ambitions, risk tolerance, and control preferences. Venture capital suits high-growth companies needing significant funding and expert guidance, while bootstrapping is ideal for founders prioritizing autonomy and sustainable scaling without external influence. Evaluating market demand, financial projections, and long-term vision helps determine the optimal funding strategy.
Venture Capital Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com