Monetary policy shapes economic stability by regulating money supply and interest rates to control inflation and stimulate growth. Central banks use tools like open market operations and reserve requirements to influence borrowing, spending, and investment. Explore the full article to understand how your financial decisions are impacted by these critical policy measures.
Table of Comparison
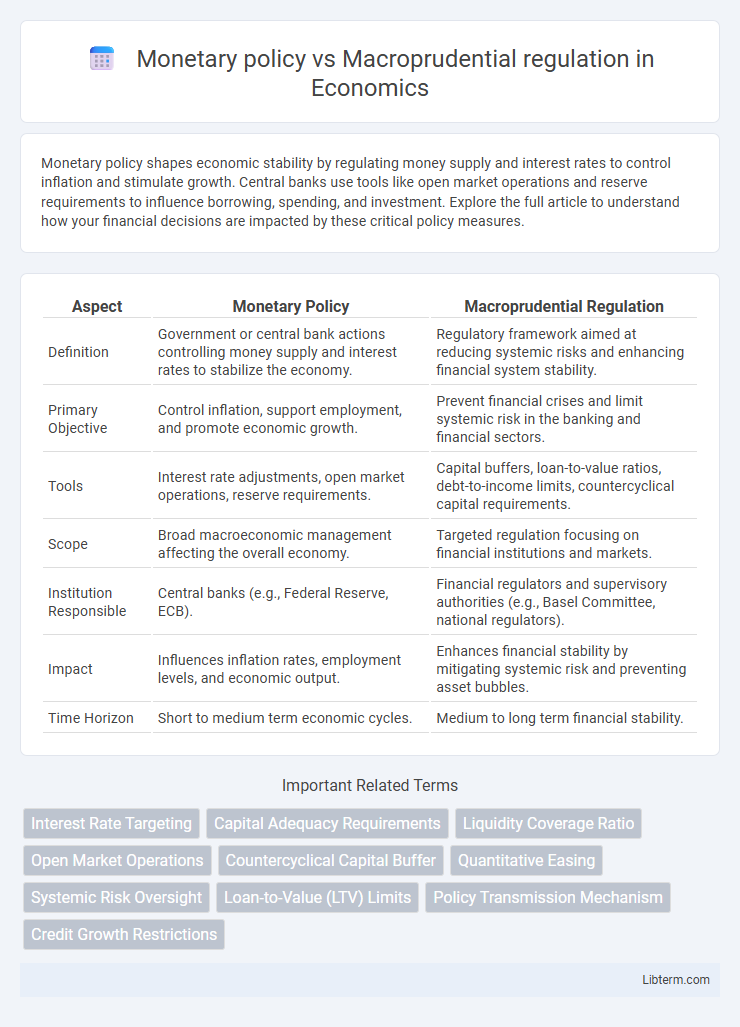
| Aspect | Monetary Policy | Macroprudential Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government or central bank actions controlling money supply and interest rates to stabilize the economy. | Regulatory framework aimed at reducing systemic risks and enhancing financial system stability. |
| Primary Objective | Control inflation, support employment, and promote economic growth. | Prevent financial crises and limit systemic risk in the banking and financial sectors. |
| Tools | Interest rate adjustments, open market operations, reserve requirements. | Capital buffers, loan-to-value ratios, debt-to-income limits, countercyclical capital requirements. |
| Scope | Broad macroeconomic management affecting the overall economy. | Targeted regulation focusing on financial institutions and markets. |
| Institution Responsible | Central banks (e.g., Federal Reserve, ECB). | Financial regulators and supervisory authorities (e.g., Basel Committee, national regulators). |
| Impact | Influences inflation rates, employment levels, and economic output. | Enhances financial stability by mitigating systemic risk and preventing asset bubbles. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term economic cycles. | Medium to long term financial stability. |
Introduction to Monetary Policy and Macroprudential Regulation
Monetary policy involves managing a nation's money supply and interest rates to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, stabilizing currency, and promoting economic growth. Macroprudential regulation focuses on safeguarding the financial system by addressing systemic risks and preventing financial crises through regulatory tools targeting institutions and markets. Both frameworks work together to ensure economic stability, with monetary policy influencing economic conditions broadly while macroprudential regulation targets financial sector vulnerabilities.
Defining Monetary Policy: Tools and Objectives
Monetary policy involves the central bank's use of interest rates, open market operations, and reserve requirements to control inflation, stabilize currency, and promote economic growth. Its primary objectives include maintaining price stability, achieving full employment, and ensuring moderate long-term interest rates. These tools influence money supply, credit availability, and overall demand within the economy, directly impacting inflation and economic cycles.
Macroprudential Regulation: Scope and Mechanisms
Macroprudential regulation targets the stability of the entire financial system by addressing systemic risks through tools such as countercyclical capital buffers, loan-to-value (LTV) limits, and stress testing. Its scope includes mitigating interconnected risks among banks, non-bank financial institutions, and markets to prevent financial crises. Key mechanisms involve monitoring systemic vulnerabilities, implementing macroprudential capital requirements, and coordinating with monetary policy to maintain economic stability.
Key Differences Between Monetary Policy and Macroprudential Regulation
Monetary policy primarily targets inflation control and economic growth by adjusting interest rates and money supply through central banks like the Federal Reserve. Macroprudential regulation focuses on maintaining financial system stability by addressing systemic risks, leveraging tools such as capital requirements and stress testing for banks. While monetary policy influences aggregate demand broadly, macroprudential regulation targets specific vulnerabilities within the financial sector to prevent crises.
Interactions and Overlaps in Practice
Monetary policy primarily targets inflation and economic growth through interest rate adjustments, while macroprudential regulation focuses on financial system stability by managing systemic risks and preventing asset bubbles. Both frameworks interact through channels such as credit growth and leverage, where tightening monetary policy can reinforce macroprudential tools by curbing excessive lending and risk-taking. Overlaps occur as coordinated efforts help mitigate financial vulnerabilities, yet they require clear communication and policy design to avoid conflicting signals impacting credit supply and economic activity.
Impact on Financial Stability and Economic Growth
Monetary policy primarily influences economic growth by adjusting interest rates and controlling inflation, which affects credit availability and consumer spending. Macroprudential regulation targets financial stability by mitigating systemic risks through measures such as capital buffers and leverage ratios that prevent asset bubbles and financial crises. Coordinated application of both policies strengthens overall economic resilience, balancing growth objectives with the containment of financial system vulnerabilities.
Case Studies: Global Approaches and Effects
Monetary policy, primarily managed by central banks, adjusts interest rates and controls money supply to influence economic activity, while macroprudential regulation targets financial system stability through measures like capital buffers and stress tests. Case studies from the 2008 global financial crisis reveal how U.S. Federal Reserve interest rate policies stabilized liquidity but required macroprudential tools such as Dodd-Frank Act regulations to mitigate systemic risks. In contrast, the European Central Bank's single monetary policy coupled with varied national macroprudential frameworks demonstrates diverse impacts on credit growth and banking sector resilience across member states.
Challenges in Coordination and Implementation
Monetary policy and macroprudential regulation face significant challenges in coordination and implementation due to differing objectives--monetary policy aims at price stability and economic growth, while macroprudential regulation targets financial system stability and risk mitigation. Conflicts arise when interest rate adjustments necessary for inflation control inadvertently increase systemic risk by encouraging excessive borrowing or asset bubbles, complicating policy synchronization. Effective coordination requires enhanced communication between central banks and regulatory authorities, along with integrated frameworks to balance short-term economic goals and long-term financial stability.
Future Trends in Monetary and Macroprudential Policies
Future trends in monetary policy emphasize the integration of digital currencies and real-time economic data analysis to enhance responsiveness and precision. Macroprudential regulation is evolving towards stronger systemic risk oversight, incorporating climate-related financial risks and advanced stress testing methodologies. Both policies are increasingly coordinated to balance economic growth with financial stability in an interconnected global economy.
Conclusion: Achieving Balanced Financial Governance
Monetary policy primarily aims to control inflation and stabilize economic growth by adjusting interest rates and money supply, while macroprudential regulation focuses on mitigating systemic risks and ensuring financial stability through sector-specific rules and capital requirements. Achieving balanced financial governance requires integrating both tools to address short-term economic fluctuations and long-term financial vulnerabilities effectively. Coordinated implementation enhances resilience against crises, promotes sustainable growth, and safeguards the overall banking and financial system stability.
Monetary policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com