Forward guidance shapes market expectations by communicating a central bank's future policy intentions, aiming to influence interest rates and economic behavior today. Clear and consistent forward guidance can stabilize financial markets and enhance policy transparency, helping You make informed investment decisions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how forward guidance impacts economic growth and monetary policy effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
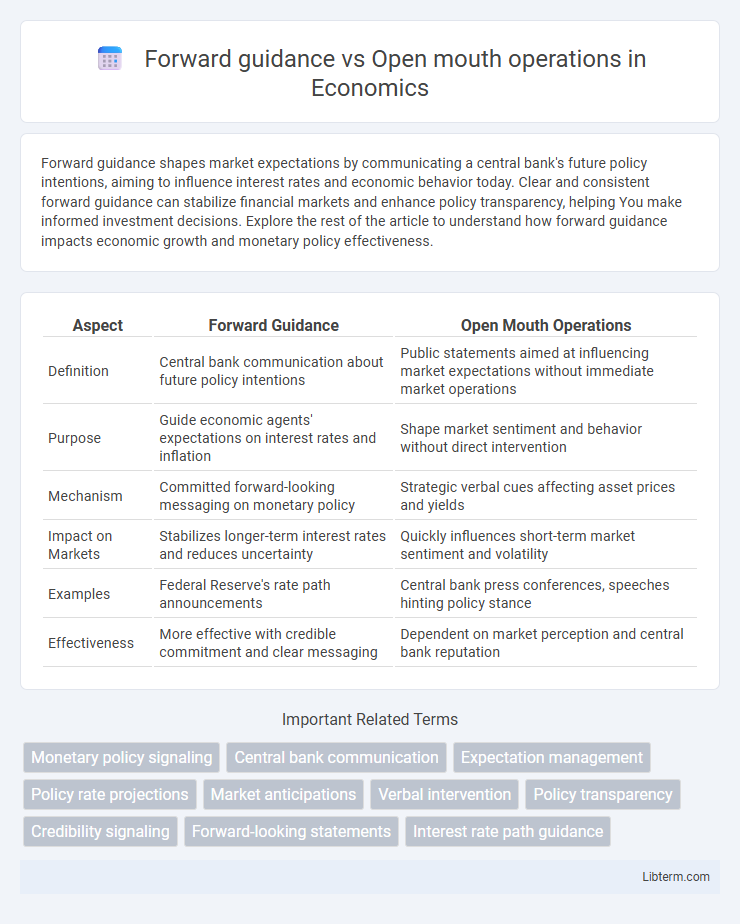
| Aspect | Forward Guidance | Open Mouth Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank communication about future policy intentions | Public statements aimed at influencing market expectations without immediate market operations |
| Purpose | Guide economic agents' expectations on interest rates and inflation | Shape market sentiment and behavior without direct intervention |
| Mechanism | Committed forward-looking messaging on monetary policy | Strategic verbal cues affecting asset prices and yields |
| Impact on Markets | Stabilizes longer-term interest rates and reduces uncertainty | Quickly influences short-term market sentiment and volatility |
| Examples | Federal Reserve's rate path announcements | Central bank press conferences, speeches hinting policy stance |
| Effectiveness | More effective with credible commitment and clear messaging | Dependent on market perception and central bank reputation |
Introduction to Forward Guidance and Open Mouth Operations
Forward guidance involves central banks communicating expected future monetary policy actions to influence market expectations and economic behavior, enhancing policy transparency and effectiveness. Open mouth operations refer to deliberate public statements by policymakers aimed at shaping financial markets without immediate actual interventions, leveraging communication as a tool for economic stabilization. Both strategies serve as non-conventional monetary policy instruments designed to manage interest rates and guide inflation expectations.
Defining Forward Guidance in Monetary Policy
Forward guidance in monetary policy involves central banks communicating future intentions for interest rates and monetary policy to influence market expectations and economic behavior. This strategy aims to provide clarity and reduce uncertainty by signaling the likely path of monetary policy, thereby shaping long-term interest rates and investment decisions. Open mouth operations refer to deliberate verbal communication by policymakers to steer financial markets without immediate policy action.
What Are Open Mouth Operations?
Open mouth operations refer to central bank communications aimed at influencing market expectations and shaping economic behavior without direct intervention in financial markets. This strategy relies on verbal signals, policy statements, and public speeches to guide investor and consumer decisions. Unlike forward guidance, which provides explicit indications of future monetary policy, open mouth operations are more subtle and informal in managing economic perceptions.
Key Differences Between Forward Guidance and Open Mouth Operations
Forward guidance involves central banks communicating future monetary policy intentions to influence market expectations and economic behavior, whereas open mouth operations refer to the strategic use of verbal interventions to stabilize financial markets without immediate policy changes. Forward guidance provides structured, transparent signals about interest rates or asset purchases over a set period, enhancing predictability for investors and consumers. Open mouth operations are typically reactive, aiming to quell market volatility through timely statements, relying on credibility rather than explicit policy commitments.
Historical Evolution of Communication Tools in Central Banking
Forward guidance emerged as a strategic tool in the early 1990s, allowing central banks to influence expectations about future policy rates through explicit verbal commitments. Open mouth operations date back to the 1970s and 1980s, when brief public statements aimed to signal policy intentions without formal policy changes, serving as an early form of communication before forward guidance was institutionalized. The evolution from open mouth operations to forward guidance reflects a growing recognition of central banks' ability to shape market behavior through transparent, anticipatory messaging.
Effectiveness: Forward Guidance vs Open Mouth Operations
Forward guidance influences market expectations by signaling future central bank policies, enhancing transparency and reducing uncertainty in interest rate forecasts. Open mouth operations rely on central bank communication to stabilize markets without actual asset purchases, but their effectiveness depends heavily on the credibility and clarity of the messages conveyed. Empirical studies show forward guidance tends to have a more consistent impact on long-term interest rates, while open mouth operations are more situational and less predictable in influencing investor behavior.
Impact on Financial Markets and Expectations
Forward guidance shapes financial markets by providing explicit central bank communication regarding future policy paths, reducing uncertainty and influencing investor expectations on interest rates and inflation. Open mouth operations, through strategic verbal interventions without immediate policy changes, aim to adjust market sentiment and short-term asset prices by signaling central bank intentions. Both tools significantly impact bond yields, stock valuations, and currency stability by aligning market forecasts with central bank objectives.
Case Studies: Global Examples and Outcomes
Forward guidance and open mouth operations have been pivotal tools in monetary policy, with case studies from the US Federal Reserve showcasing the impact of explicit communication on market expectations during the 2008 financial crisis. Japan's experience with open mouth operations demonstrated how central bank verbal interventions influenced short-term interest rates without immediate asset purchases, affecting yield curves and inflation expectations. Emerging markets like Brazil employed a blend of these strategies, leveraging forward guidance to stabilize inflation while using open mouth operations to manage exchange rate volatility, highlighting diverse outcomes based on institutional frameworks and economic conditions.
Challenges and Limitations of Verbal Policy Tools
Forward guidance faces challenges such as market misinterpretation and credibility issues, which can reduce its effectiveness in influencing expectations and financial conditions. Open mouth operations risk inconsistent messaging that can cause volatility and uncertainty in financial markets, limiting their reliability as policy tools. Both tools depend heavily on clear communication and market confidence, making them vulnerable to ambiguity and changing economic environments.
Future Trends in Central Bank Communication Strategies
Forward guidance is evolving to become more data-driven and transparent, allowing markets to better anticipate central bank policy moves based on explicit economic conditions. Open mouth operations rely heavily on strategic, timely statements that influence expectations without immediate policy changes, increasingly leveraging digital platforms for broader reach. Future trends indicate a blend of nuanced communication and AI analytics to enhance precision and responsiveness in shaping monetary policy expectations.
Forward guidance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com