Pump and dump schemes manipulate stock prices by artificially inflating shares to sell at a profit before the price collapses, leaving investors with losses. Understanding how these fraudulent tactics work can protect Your investments from severe financial damage. Continue reading to learn how to identify and avoid pump and dump scams effectively.
Table of Comparison
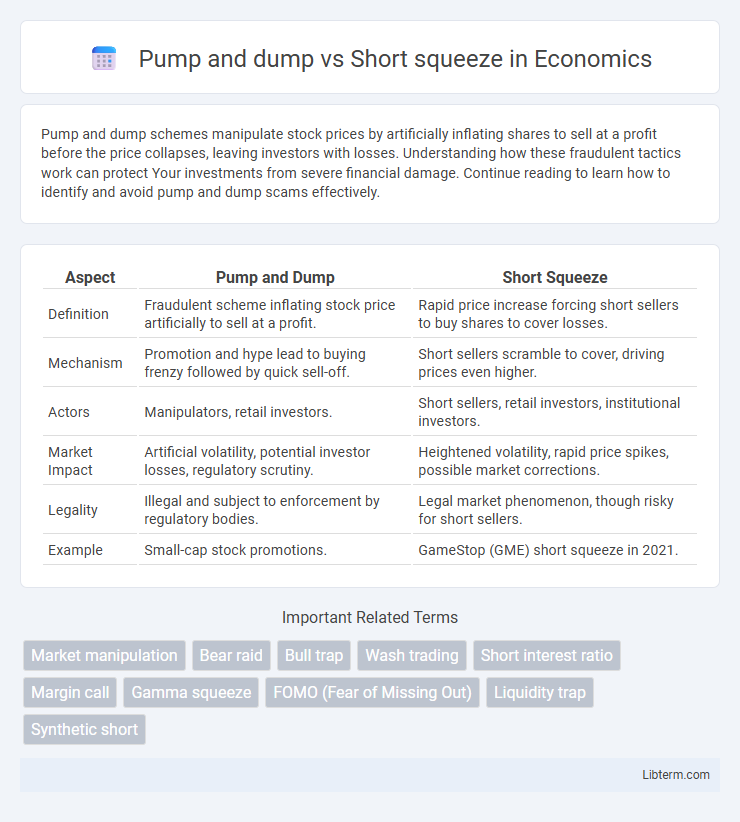
| Aspect | Pump and Dump | Short Squeeze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fraudulent scheme inflating stock price artificially to sell at a profit. | Rapid price increase forcing short sellers to buy shares to cover losses. |
| Mechanism | Promotion and hype lead to buying frenzy followed by quick sell-off. | Short sellers scramble to cover, driving prices even higher. |
| Actors | Manipulators, retail investors. | Short sellers, retail investors, institutional investors. |
| Market Impact | Artificial volatility, potential investor losses, regulatory scrutiny. | Heightened volatility, rapid price spikes, possible market corrections. |
| Legality | Illegal and subject to enforcement by regulatory bodies. | Legal market phenomenon, though risky for short sellers. |
| Example | Small-cap stock promotions. | GameStop (GME) short squeeze in 2021. |
Introduction: Understanding Pump and Dump vs Short Squeeze
Pump and dump schemes involve artificially inflating a stock's price through misleading positive statements to sell shares at a profit, causing significant losses for unsuspecting investors. In contrast, a short squeeze occurs when heavily shorted stocks experience a rapid price increase, forcing short sellers to buy shares to cover their positions, further driving up the price. These phenomena highlight distinct market manipulations and trading behaviors impacting stock volatility and investor risk.
Defining Pump and Dump Schemes
Pump and dump schemes involve artificially inflating the price of a stock through misleading or false statements to attract investors, followed by selling off shares at the elevated price. This manipulation is common in low-volume, small-cap stocks where market control is easier. Short squeeze, by contrast, occurs when a heavily shorted stock's price rises sharply, forcing short sellers to buy shares to cover losses, further driving up the price.
What is a Short Squeeze?
A short squeeze occurs when a heavily shorted stock experiences a rapid price increase, forcing short sellers to buy shares to cover their positions and limit losses. This surge in buying pressure drives the stock price even higher, often leading to significant volatility. Unlike pump and dump schemes, which manipulate prices through false or misleading information, a short squeeze results from market dynamics and short interest levels.
Key Differences Between Pump and Dump and Short Squeeze
Pump and dump schemes involve artificially inflating a stock's price through misleading positive statements, leading investors to buy before insiders sell at a profit, causing the price to plummet. Short squeezes occur when a heavily shorted stock's price rises rapidly, forcing short sellers to cover positions by buying shares, which further drives up the price. The key difference lies in pump and dump being a deliberate manipulation for profit, whereas short squeezes result from market dynamics and forced buying pressure on short sellers.
Historical Examples of Pump and Dump
Pump and dump schemes have been historically exemplified by the case of the 1920s "Blue Sky" stock manipulations, where fraudulent promoters inflated prices before selling off shares at a profit. The 2000s saw penny stocks, such as those frequently exposed by the SEC, manipulated through aggressive promotion to artificially boost prices before a rapid collapse. Unlike short squeezes like the 2021 GameStop event driven by coordinated short covering, pump and dump scams focus on deceptive price inflation followed by mass sell-offs to realize gains.
Notable Short Squeeze Cases
Notable short squeeze cases include the 2021 GameStop (GME) event, where retail investors coordinated to drive up the stock price, forcing short sellers to cover their positions at significant losses. Another prominent example is Volkswagen's 2008 short squeeze, which briefly made it the most valuable company in the world due to a limited supply of shares and heavy short interest. These events highlight the risks faced by short sellers when unexpected buying pressure overwhelms the market, contrasting with pump and dump schemes that rely on misleading information to inflate prices artificially.
Market Impact: Comparing Both Phenomena
Pump and dump schemes artificially inflate stock prices through misleading promotions, leading to sharp crashes and significant investor losses once the hype subsides. Short squeezes occur when heavily shorted stocks experience rapid price surges, forcing short sellers to buy shares at escalating prices, which intensifies market volatility. Both phenomena cause extreme price distortions, but pump and dumps often result in abrupt collapses, while short squeezes create sustained upward momentum before prices stabilize.
Legal and Regulatory Perspectives
Pump and dump schemes involve artificially inflating a stock's price through misleading statements to sell shares at a profit, violating securities laws enforced by the SEC and other regulatory bodies. Short squeezes occur when short sellers are forced to cover positions due to rising prices, generally considered a natural market phenomenon but can attract scrutiny if manipulated. Regulatory frameworks focus on distinguishing illegal market manipulation in pump and dump cases from the legitimate market dynamics driving short squeezes.
How Investors Can Protect Themselves
Investors can protect themselves from pump and dump schemes by conducting thorough research on a stock's fundamentals and avoiding investments driven by hype or unverified tips. To guard against short squeezes, monitoring the short interest ratio and being cautious with heavily shorted stocks can help prevent sudden, volatile price spikes. Employing stop-loss orders and maintaining a diversified portfolio also mitigates risks associated with both manipulation tactics.
Conclusion: Navigating Volatile Markets
Understanding the key differences between pump and dump schemes and short squeezes is essential for navigating volatile markets successfully. Pump and dump involves artificially inflating a stock's price to lure investors before a rapid sell-off, while a short squeeze results from sharp price increases forcing short sellers to cover positions, further driving prices up. Recognizing these patterns and maintaining cautious, research-driven strategies can help investors avoid losses and capitalize on market movements.
Pump and dump Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com