Interest rate risk refers to the potential for investment losses due to fluctuations in interest rates, significantly impacting bond prices and loan values. Managing this risk is crucial for maintaining your portfolio's stability and achieving long-term financial goals. Explore the full article to understand effective strategies for mitigating interest rate risk and protecting your investments.
Table of Comparison
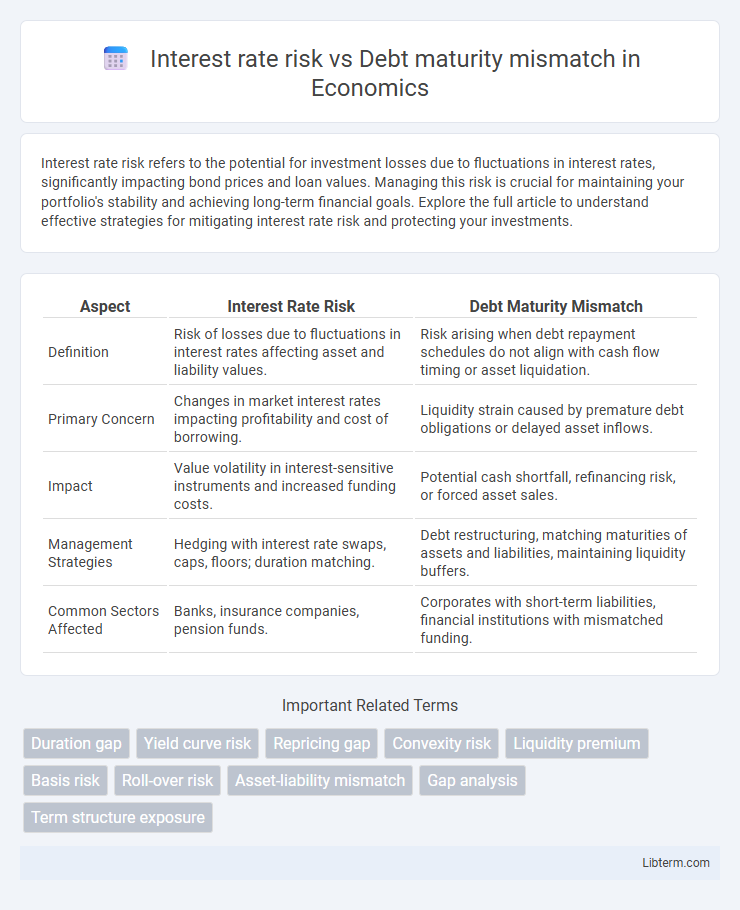
| Aspect | Interest Rate Risk | Debt Maturity Mismatch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk of losses due to fluctuations in interest rates affecting asset and liability values. | Risk arising when debt repayment schedules do not align with cash flow timing or asset liquidation. |
| Primary Concern | Changes in market interest rates impacting profitability and cost of borrowing. | Liquidity strain caused by premature debt obligations or delayed asset inflows. |
| Impact | Value volatility in interest-sensitive instruments and increased funding costs. | Potential cash shortfall, refinancing risk, or forced asset sales. |
| Management Strategies | Hedging with interest rate swaps, caps, floors; duration matching. | Debt restructuring, matching maturities of assets and liabilities, maintaining liquidity buffers. |
| Common Sectors Affected | Banks, insurance companies, pension funds. | Corporates with short-term liabilities, financial institutions with mismatched funding. |
Understanding Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk arises when fluctuations in interest rates affect the cost of borrowing or the return on investments, impacting financial stability. Debt maturity mismatch occurs when short-term liabilities are financed with long-term assets, increasing vulnerability to interest rate changes. Understanding interest rate risk involves analyzing how variable rate debt and refinancing timing influence cash flows and funding costs.
Defining Debt Maturity Mismatch
Debt maturity mismatch occurs when a company's short-term liabilities significantly exceed the maturities of its short-term assets, exposing it to refinancing risks and liquidity shortfalls. This imbalance forces firms to continuously roll over debt, increasing vulnerability to changing interest rates and market conditions. Interest rate risk compounds this challenge by potentially raising borrowing costs during refinancing, amplifying the financial strain caused by debt maturity mismatch.
Key Differences Between Interest Rate Risk and Maturity Mismatch
Interest rate risk refers to the potential for investment losses resulting from fluctuations in interest rates, impacting the market value of interest-sensitive assets and liabilities. Debt maturity mismatch occurs when the timing of cash inflows and outflows are misaligned, leading to refinancing risk if short-term liabilities cannot be rolled over into long-term debt. Key differences include interest rate risk affecting the cost and valuation of debt, while maturity mismatch primarily influences liquidity and rollover risk related to debt repayment schedules.
How Interest Rate Changes Impact Debt Obligations
Interest rate changes directly affect the cost of servicing variable-rate debt, increasing interest expenses when rates rise and decreasing them when rates fall. Debt maturity mismatches expose firms to refinancing risk, forcing them to repay or roll over short-term liabilities at potentially higher rates during unfavorable interest rate environments. Managing these risks requires aligning debt maturities with cash flow stability to mitigate the impact of fluctuating interest rates on overall debt obligations.
The Role of Duration in Interest Rate Risk
Duration measures the sensitivity of a bond's price to interest rate changes, playing a crucial role in managing interest rate risk in debt portfolios. A longer duration indicates greater price volatility when rates fluctuate, increasing risk exposure during periods of rate increases. Aligning the duration of assets and liabilities helps mitigate the impact of interest rate risk caused by debt maturity mismatches.
Common Causes of Debt Maturity Mismatches
Debt maturity mismatches commonly arise from companies issuing short-term liabilities to finance long-term assets, creating exposure to refinancing risks and interest rate fluctuations. This imbalance often results from liquidity constraints, inaccurate cash flow forecasting, or strategic decisions aiming for lower short-term financing costs. Such mismatches increase vulnerability to market disruptions and rising interest rates, amplifying both refinancing risk and interest rate risk simultaneously.
Impact on Corporate Balance Sheets
Interest rate risk significantly affects corporate balance sheets by altering the cost of debt servicing, potentially increasing interest expenses and reducing net income when rates rise. Debt maturity mismatch exposes firms to refinancing risks, as companies may face liquidity shortages or higher costs if short-term liabilities must be rolled over in unfavorable market conditions. Both factors can lead to volatility in asset-liability management, impacting financial stability and credit ratings.
Risk Management Strategies for Both Risks
Interest rate risk and debt maturity mismatch require tailored risk management strategies to enhance financial stability. Interest rate risk is mitigated through interest rate swaps, caps, and collars to stabilize cash flows and protect against rate fluctuations. Managing debt maturity mismatch involves laddering debt maturities and maintaining liquidity reserves to ensure timely refinancing and reduce rollover risk.
Real-World Examples: Banks and Interest Rate Fluctuations
Banks often face interest rate risk when their assets and liabilities reprice at different times, causing fluctuations in net interest income during changing market rates. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, many banks experienced losses due to debt maturity mismatch, where long-term loans were funded by short-term liabilities that needed frequent refinancing at higher rates. The combination of rising interest rates and debt maturity mismatch forced institutions like Lehman Brothers into liquidity crises, highlighting the critical importance of managing both interest rate risk and maturity mismatches in banking portfolios.
Best Practices for Mitigating Financial Risk
Effective risk management involves aligning debt maturities with cash flow projections to minimize debt maturity mismatch and reduce refinancing risk. Implementing interest rate hedging strategies, such as interest rate swaps or caps, mitigates exposure to fluctuating borrowing costs. Maintaining a diversified debt portfolio with staggered maturities enhances financial flexibility and strengthens resilience against interest rate volatility.
Interest rate risk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com