Welfare universalism ensures that social benefits and services are provided to all citizens regardless of income or employment status, promoting equality and social cohesion. This approach contrasts with means-tested systems by reducing stigmatization and administrative complexity, making it easier for citizens to access support. Discover how welfare universalism can transform your community by enhancing social protection and inclusivity throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
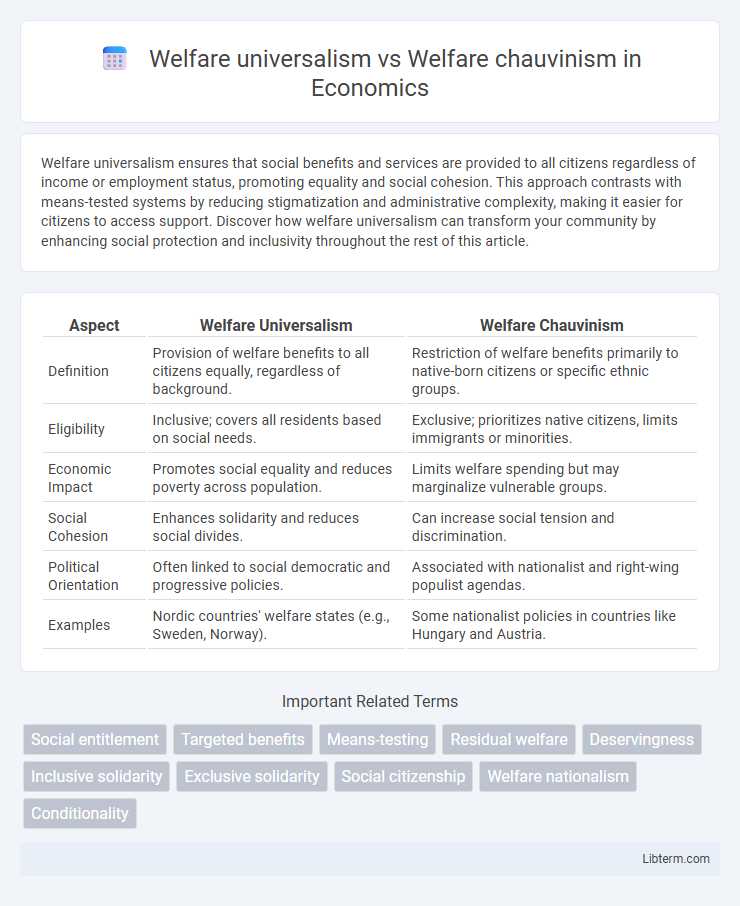
| Aspect | Welfare Universalism | Welfare Chauvinism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Provision of welfare benefits to all citizens equally, regardless of background. | Restriction of welfare benefits primarily to native-born citizens or specific ethnic groups. |
| Eligibility | Inclusive; covers all residents based on social needs. | Exclusive; prioritizes native citizens, limits immigrants or minorities. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes social equality and reduces poverty across population. | Limits welfare spending but may marginalize vulnerable groups. |
| Social Cohesion | Enhances solidarity and reduces social divides. | Can increase social tension and discrimination. |
| Political Orientation | Often linked to social democratic and progressive policies. | Associated with nationalist and right-wing populist agendas. |
| Examples | Nordic countries' welfare states (e.g., Sweden, Norway). | Some nationalist policies in countries like Hungary and Austria. |
Defining Welfare Universalism and Welfare Chauvinism
Welfare universalism refers to a social policy approach that guarantees equal access to welfare benefits and services for all citizens, regardless of their background or status, promoting inclusivity and social solidarity. Welfare chauvinism, in contrast, advocates for restricting welfare benefits exclusively to native-born citizens or specific in-groups, often excluding immigrants and minorities to preserve resources for the dominant population. These opposing ideologies shape debates on social welfare eligibility, equity, and the extent of state responsibility.
Historical Origins of Welfare Approaches
Welfare universalism emerged from post-World War II social democratic movements in Scandinavia, emphasizing inclusive social rights and broad-based state provision of benefits to all citizens regardless of income or status. In contrast, welfare chauvinism roots trace back to nationalist and protectionist ideologies prevalent in late 20th-century Europe, advocating for welfare restrictions primarily favoring native-born populations while excluding immigrants and minorities. These historical origins highlight the ideological divide between inclusive social solidarity in universalism and exclusionary social protectionism in chauvinism.
Key Principles of Universalism in Social Policy
Key principles of universalism in social policy emphasize equal access to welfare benefits for all citizens regardless of income or social status, ensuring comprehensive coverage that promotes social inclusion and reduces inequality. Universalism advocates for state responsibility in providing healthcare, education, and social security as fundamental rights, fostering social cohesion and solidarity within society. This approach contrasts sharply with welfare chauvinism, which limits benefits to certain groups based on nationality or ethnicity, undermining the principle of universality.
Core Features of Welfare Chauvinism
Welfare chauvinism is characterized by the belief that social welfare benefits should be restricted to native citizens, excluding immigrants and minority groups from access to public resources. It emphasizes national identity and prioritizes in-group members, often linking social welfare provisions to cultural or ethnic criteria. This approach contrasts sharply with welfare universalism, which advocates for equal and unconditional access to social benefits regardless of background.
Policy Approaches: Inclusion vs. Exclusion
Welfare universalism advocates for inclusive policy approaches that provide social benefits and services to all citizens regardless of background, promoting equal access and social solidarity. In contrast, welfare chauvinism emphasizes exclusionary policies, restricting welfare benefits primarily to native-born citizens or specific groups, often prioritizing national identity over universal rights. These divergent approaches influence social cohesion, with universalism fostering integration through inclusivity and chauvinism creating divisions by limiting entitlement based on nationality or ethnicity.
Socioeconomic Outcomes of Universal and Chauvinist Welfare Models
Universal welfare models promote inclusive social benefits that reduce income inequality and improve overall health and education outcomes across diverse populations. Chauvinist welfare systems restrict access to social services based on ethnicity or citizenship, often exacerbating socioeconomic disparities and limiting upward mobility for marginalized groups. Empirical studies demonstrate that inclusive welfare policies correlate with higher social cohesion, lower poverty rates, and enhanced economic productivity compared to exclusionary welfare approaches.
Political Drivers Behind Welfare Model Choices
Political drivers behind welfare universalism emphasize inclusive social policies aimed at reducing inequality and promoting social cohesion, often supported by center-left parties advocating comprehensive benefits for all citizens regardless of origin. In contrast, welfare chauvinism is driven by right-wing populist agendas prioritizing native citizens' access to social benefits, fueled by nationalist rhetoric and concerns about immigration's impact on welfare systems. These political strategies shape welfare model choices by aligning social policy design with broader ideological goals around identity, solidarity, and state responsibility.
Public Attitudes Toward Welfare Distribution
Public attitudes toward welfare distribution reveal contrasting support levels for welfare universalism and welfare chauvinism. Welfare universalism advocates for equal access to social benefits regardless of background, emphasizing inclusivity and social solidarity, often gaining broader public approval in diverse societies. Conversely, welfare chauvinism restricts benefits to native-born citizens, driven by nationalist sentiments and concerns over immigration, which appeals to segments of the population prioritizing resource allocation to in-group members.
Case Studies: Countries Illustrating Both Models
Sweden exemplifies welfare universalism with its comprehensive social security system accessible to all citizens, promoting equality and social cohesion. In contrast, Denmark illustrates welfare chauvinism by restricting benefits primarily to native-born citizens, prioritizing immigrants' access to social welfare based on national belonging. These case studies reveal how welfare universalism fosters inclusivity, while welfare chauvinism emphasizes protectionism and national identity in social policy.
Future Trends and Policy Recommendations
Future trends in welfare universalism emphasize expanding inclusive social benefits to address growing inequality and technological disruptions in labor markets, promoting comprehensive access regardless of nationality or ethnicity. Welfare chauvinism is likely to face challenges amid demographic shifts and increasing migration, potentially driving stricter eligibility criteria and prioritized access for native populations. Policy recommendations suggest balancing universal welfare provisions with targeted support to integrate marginalized groups, fostering social cohesion while maintaining fiscal sustainability amid changing socioeconomic dynamics.
Welfare universalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com