Positive economics focuses on describing and explaining economic phenomena based on observable facts and data, avoiding value judgments. It aims to analyze cause-and-effect relationships to predict economic outcomes objectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how positive economics shapes economic policy and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
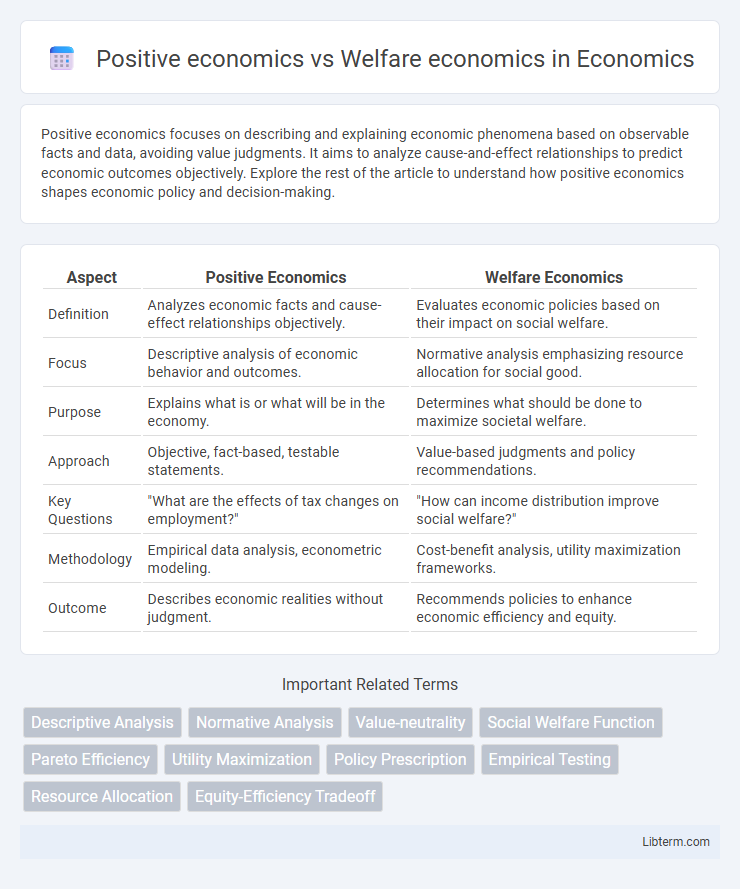
| Aspect | Positive Economics | Welfare Economics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes economic facts and cause-effect relationships objectively. | Evaluates economic policies based on their impact on social welfare. |
| Focus | Descriptive analysis of economic behavior and outcomes. | Normative analysis emphasizing resource allocation for social good. |
| Purpose | Explains what is or what will be in the economy. | Determines what should be done to maximize societal welfare. |
| Approach | Objective, fact-based, testable statements. | Value-based judgments and policy recommendations. |
| Key Questions | "What are the effects of tax changes on employment?" | "How can income distribution improve social welfare?" |
| Methodology | Empirical data analysis, econometric modeling. | Cost-benefit analysis, utility maximization frameworks. |
| Outcome | Describes economic realities without judgment. | Recommends policies to enhance economic efficiency and equity. |
Introduction to Positive and Welfare Economics
Positive economics examines economic behavior and outcomes using factual data and objective analysis to explain "what is," focusing on cause-and-effect relationships without value judgments. Welfare economics evaluates economic policies and resource allocations based on their impact on social well-being and economic efficiency, emphasizing normative assessments of "what ought to be." Both branches provide essential frameworks: positive economics helps understand market mechanisms, while welfare economics guides policy decisions to improve overall societal welfare.
Defining Positive Economics
Positive economics defines economic phenomena through objective analysis and empirical evidence, focusing on "what is" rather than "what ought to be." It involves the description, quantification, and explanation of economic behavior and outcomes without incorporating value judgments. Contrarily, welfare economics evaluates economic policies based on their impact on social welfare and normative criteria.
Defining Welfare Economics
Welfare economics is a branch of economics that evaluates economic policies based on their impact on the overall well-being and economic efficiency of society, emphasizing the allocation of resources to maximize social welfare. It contrasts with positive economics, which objectively describes and predicts economic phenomena without making value judgments. Key concepts in welfare economics include Pareto efficiency, social welfare functions, and the analysis of externalities and market failures to improve societal outcomes.
Key Differences Between Positive and Welfare Economics
Positive economics analyzes objective cause-and-effect relationships and focuses on describing economic phenomena using empirical data without value judgments. Welfare economics evaluates economic policies and outcomes based on normative criteria aimed at maximizing social welfare and equitable resource distribution. Key differences include the emphasis on factual analysis in positive economics versus the normative goals and ethical considerations inherent in welfare economics.
Methodologies Used in Positive Economics
Positive economics employs empirical data analysis, mathematical modeling, and statistical techniques to describe and predict economic phenomena objectively, without value judgments. It relies on hypothesis testing, controlled experiments, and econometric methods to validate theories and establish cause-effect relationships in economic behavior. These methodologies emphasize factual evidence and reproducibility, distinguishing positive economics from welfare economics, which involves normative evaluations and ethical considerations.
Evaluative Criteria in Welfare Economics
Evaluative criteria in welfare economics primarily focus on efficiency and equity to assess economic policies and outcomes, considering both Pareto optimality and social welfare functions. Unlike positive economics, which describes and predicts economic behavior without judgment, welfare economics involves normative analysis by incorporating value judgments about resource allocation and distribution. Key criteria such as Pareto efficiency, compensation principle, and equity guide policymakers in determining policies that maximize social welfare while addressing fairness and income distribution concerns.
The Role of Value Judgments
Positive economics strictly involves objective analysis of economic phenomena, relying on empirical data without incorporating personal values or opinions. Welfare economics, in contrast, explicitly addresses value judgments by evaluating economic policies based on their impact on social welfare and equity. The role of value judgments is central in welfare economics as it determines normative decisions aiming to improve collective well-being, whereas positive economics remains descriptive and fact-based.
Applications of Positive Economics
Positive economics primarily analyzes objective data to explain and predict economic behavior, facilitating policy formulation based on empirical evidence. Its applications include assessing market trends, measuring GDP growth, and evaluating the impact of taxation or monetary changes without value judgments. By contrast, welfare economics uses these factual findings to recommend policies aimed at improving social welfare and resource allocation efficiency.
Policy Implications of Welfare Economics
Welfare economics centers on evaluating economic policies based on their impact on social welfare and equity, guiding policymakers to design interventions that maximize overall well-being and reduce inequalities. Unlike positive economics, which describes and predicts economic phenomena without judgment, welfare economics provides normative analysis that supports decisions on resource allocation, taxation, and public goods provision. Policies influenced by welfare economics often prioritize redistribution, externality corrections, and social safety nets to achieve a more efficient and equitable economy.
Conclusion: Integrating Positive and Welfare Approaches
Integrating positive economics, which objectively analyzes economic phenomena, with welfare economics, focused on social welfare and resource allocation, enhances policy development by grounding normative decisions in empirical data. This synthesis allows for more effective evaluation of economic policies by combining measurable outcomes with value-based assessments of well-being. Policymakers benefit from this integrated approach by designing interventions that are both evidence-based and aligned with societal welfare goals.
Positive economics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com