Intuitive teaching taps into your natural ability to understand and convey concepts without rigid structures, enhancing student engagement and retention. This method fosters a learning environment where creativity and personal insight drive the educational process, making lessons more relatable and impactful. Explore the full article to discover how embracing intuitive teaching can transform your educational approach.
Table of Comparison
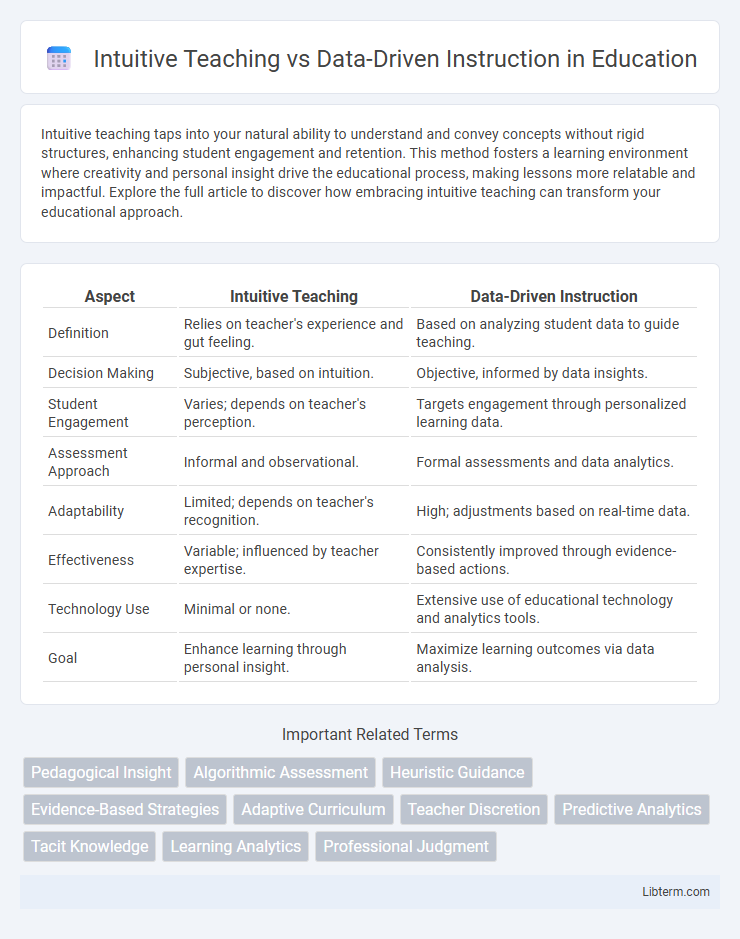
| Aspect | Intuitive Teaching | Data-Driven Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relies on teacher's experience and gut feeling. | Based on analyzing student data to guide teaching. |
| Decision Making | Subjective, based on intuition. | Objective, informed by data insights. |
| Student Engagement | Varies; depends on teacher's perception. | Targets engagement through personalized learning data. |
| Assessment Approach | Informal and observational. | Formal assessments and data analytics. |
| Adaptability | Limited; depends on teacher's recognition. | High; adjustments based on real-time data. |
| Effectiveness | Variable; influenced by teacher expertise. | Consistently improved through evidence-based actions. |
| Technology Use | Minimal or none. | Extensive use of educational technology and analytics tools. |
| Goal | Enhance learning through personal insight. | Maximize learning outcomes via data analysis. |
Understanding Intuitive Teaching
Intuitive teaching relies on educators' experiential knowledge and instinctive judgment to tailor lessons dynamically, promoting responsiveness to student needs without strictly adhering to predefined data. This approach emphasizes classroom interaction and teacher intuition to gauge comprehension and adapt methods in real-time. Understanding intuitive teaching underscores the value of professional expertise and contextual awareness in fostering effective learning environments beyond quantitative metrics.
Defining Data-Driven Instruction
Data-driven instruction involves systematically collecting and analyzing student performance data to inform teaching strategies and improve learning outcomes. It relies on assessments, learning analytics, and evidence-based practices to tailor instruction to individual student needs. This approach contrasts with intuitive teaching, which depends primarily on a teacher's experience and judgment without extensive data analysis.
Historical Perspectives on Education Methods
Historical perspectives on education reveal a longstanding tension between intuitive teaching and data-driven instruction, with early pedagogical approaches relying heavily on teacher intuition and observational insights. The rise of standardized testing and educational psychology in the 20th century marked a shift toward data-driven methods, emphasizing measurable outcomes and evidence-based strategies. Contemporary education seeks to balance these paradigms, integrating teacher expertise with data analytics to enhance student learning outcomes.
Key Benefits of Intuitive Teaching
Intuitive teaching enhances student engagement by allowing educators to tailor lessons based on immediate classroom feedback and emotional cues. It fosters creativity and adaptability, enabling teachers to respond effectively to diverse learning styles and unexpected challenges. This approach builds strong teacher-student relationships, promoting a supportive learning environment that data alone cannot capture.
Advantages of Data-Driven Instruction
Data-driven instruction enhances personalized learning by using student performance data to tailor teaching strategies effectively. This approach enables educators to identify learning gaps quickly, allocate resources efficiently, and improve overall student outcomes with measurable progress. Integrating real-time analytics fosters informed decision-making, leading to continuous instructional improvement.
Challenges of Relying on Intuition
Relying on intuition in teaching often leads to inconsistent student outcomes due to subjective biases and incomplete information. Teachers may misjudge student needs or overlook data trends that could inform better instructional strategies. Without evidence-based feedback, it becomes challenging to measure progress and tailor interventions effectively.
Limitations of Data-Centric Approaches
Data-centric instruction often overlooks the nuanced understanding of student emotions and creativity, limiting the teacher's ability to adapt lessons spontaneously. Excessive reliance on standardized testing data can stifle individualized learning experiences and fail to capture critical cognitive and social skills. This approach may also reinforce biases present in data sets, skewing educational outcomes and equity.
Balancing Intuition and Data in the Classroom
Balancing intuition and data in the classroom enhances teaching effectiveness by leveraging teachers' experiential insights alongside objective student performance metrics. Intuitive teaching taps into educators' ability to read non-verbal cues and adapt lessons dynamically, while data-driven instruction relies on assessment analytics and learning management systems to inform targeted interventions. Combining these approaches fosters a responsive learning environment that addresses diverse student needs and promotes continuous improvement through evidence-based strategies.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies reveal that intuitive teaching often leverages teacher expertise to adapt lessons dynamically, fostering personalized learning environments that respond to student needs in real-time. Data-driven instruction utilizes analytics from assessments and learning management systems to identify gaps and tailor interventions, enhancing measurable student outcomes. Schools implementing hybrid models report improved engagement and achievement by blending intuitive insights with data-backed strategies for a balanced educational approach.
Future Trends in Instructional Strategies
Future trends in instructional strategies are increasingly leaning toward a hybrid approach that blends intuitive teaching with data-driven instruction, leveraging artificial intelligence and learning analytics to personalize education. Machine learning algorithms enable real-time adaptation of teaching methods based on student performance and engagement metrics, enhancing both intuitive insights and empirical evidence. This convergence aims to optimize learning outcomes by combining the teacher's experiential knowledge with actionable data insights for more responsive and effective pedagogy.
Intuitive Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com