Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities, enabling deeper understanding through direct experience rather than passive observation. This method enhances skill retention, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving abilities by engaging learners in active participation and reflection. Discover how incorporating experiential learning can transform your educational approach in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
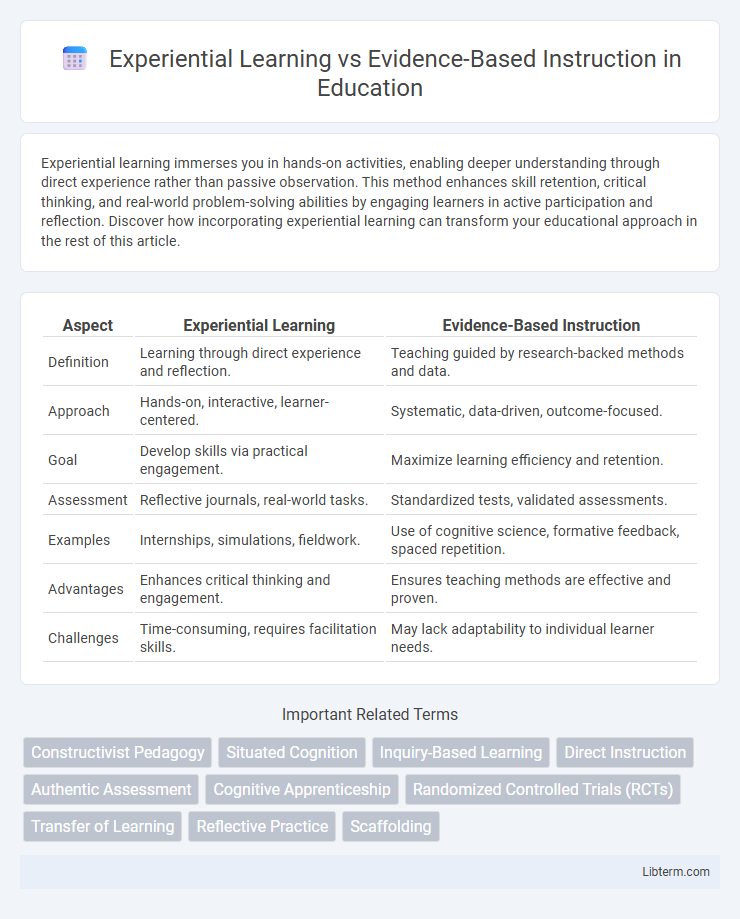
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Evidence-Based Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Teaching guided by research-backed methods and data. |
| Approach | Hands-on, interactive, learner-centered. | Systematic, data-driven, outcome-focused. |
| Goal | Develop skills via practical engagement. | Maximize learning efficiency and retention. |
| Assessment | Reflective journals, real-world tasks. | Standardized tests, validated assessments. |
| Examples | Internships, simulations, fieldwork. | Use of cognitive science, formative feedback, spaced repetition. |
| Advantages | Enhances critical thinking and engagement. | Ensures teaching methods are effective and proven. |
| Challenges | Time-consuming, requires facilitation skills. | May lack adaptability to individual learner needs. |
Introduction to Experiential Learning and Evidence-Based Instruction
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and reflection through real-world experiences, enabling learners to construct knowledge by engaging directly with tasks and challenges. Evidence-based instruction relies on empirical research and data-driven strategies to inform teaching practices, ensuring that methods applied have been systematically validated for effectiveness. Both approaches prioritize improved learning outcomes but differ in their foundational principles--experiential learning centers on hands-on involvement, while evidence-based instruction focuses on proven methodologies backed by scientific evidence.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is defined as a hands-on approach to education where learners actively engage in real-world experiences to acquire knowledge and develop skills. This method emphasizes reflection on doing, enabling learners to connect theory with practice through activities such as projects, simulations, or fieldwork. It contrasts with traditional evidence-based instruction by prioritizing direct involvement and personal experience as the foundation for understanding.
Understanding Evidence-Based Instruction
Evidence-Based Instruction relies on teaching strategies and techniques supported by empirical research and data, ensuring effective learning outcomes through validated methods. It emphasizes systematic assessment, use of proven interventions, and continuous evaluation to adapt instruction based on measurable evidence. This approach contrasts with Experiential Learning, which prioritizes hands-on experiences without always requiring rigorous scientific validation.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on the core principles of active participation, reflection, and concrete experience, allowing learners to engage directly with content through hands-on activities and real-world application. This approach contrasts with evidence-based instruction, which prioritizes proven techniques and data-driven methods to inform teaching practices. By emphasizing personal experience and critical reflection, experiential learning fosters deeper understanding and skill development beyond traditional, theory-focused evidence-based models.
Key Features of Evidence-Based Instruction
Evidence-Based Instruction relies on rigorously tested strategies supported by empirical research to enhance learning outcomes. Key features include systematic use of data-driven assessments, implementation of instructional methods validated by peer-reviewed studies, and continuous monitoring of student progress to inform instructional adjustments. This approach emphasizes reproducibility and measurable effectiveness, ensuring that teaching practices are grounded in scientific evidence rather than anecdotal experience.
Comparing Teaching Methodologies
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences that actively involve students in the learning process, promoting deeper understanding through reflection and application. Evidence-based instruction relies on teaching strategies supported by empirical research and data, ensuring methods are effective and measurable. Comparing these methodologies highlights experiential learning's focus on engagement and practice versus evidence-based instruction's foundation in validated outcomes and systematic evaluation.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances knowledge retention by engaging learners in hands-on activities that simulate real-world scenarios, promoting deeper understanding and skill development. It fosters critical thinking and problem-solving abilities by allowing students to actively participate in their learning process rather than passively receiving information. This approach also increases motivation and learner engagement, resulting in improved academic performance and long-term application of concepts.
Advantages of Evidence-Based Instruction
Evidence-based instruction enhances learning outcomes by integrating research-validated strategies that improve knowledge retention and application. It offers systematic evaluation through data-driven assessments, ensuring teaching methods are effective and adaptable to diverse learning needs. This approach promotes consistency and accountability, bridging theory and practice to optimize educational success.
Challenges and Considerations in Both Approaches
Experiential learning faces challenges such as ensuring real-world relevance and balancing hands-on activities with theoretical understanding, which can complicate assessment and scalability. Evidence-based instruction struggles with translating research findings into diverse classroom settings and addressing individual learner differences while maintaining fidelity to proven methods. Both approaches require careful consideration of context, learner needs, and resource availability to maximize effectiveness and foster meaningful educational outcomes.
Integrating Experiential and Evidence-Based Methods
Integrating experiential learning with evidence-based instruction enhances student engagement and knowledge retention by combining hands-on activities with research-supported teaching strategies. Utilizing real-world scenarios alongside validated assessment tools fosters critical thinking and practical application of concepts. This blended approach aligns educational outcomes with cognitive science principles, maximizing both understanding and skill development.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com