Mastering effective instructions elevates communication and task execution by providing clear, concise, and actionable steps that minimize confusion. Prioritizing clarity and simplicity ensures your message is easily understood and followed, enhancing overall productivity. Explore the full article to discover powerful techniques for writing instructions that truly guide and inspire action.
Table of Comparison
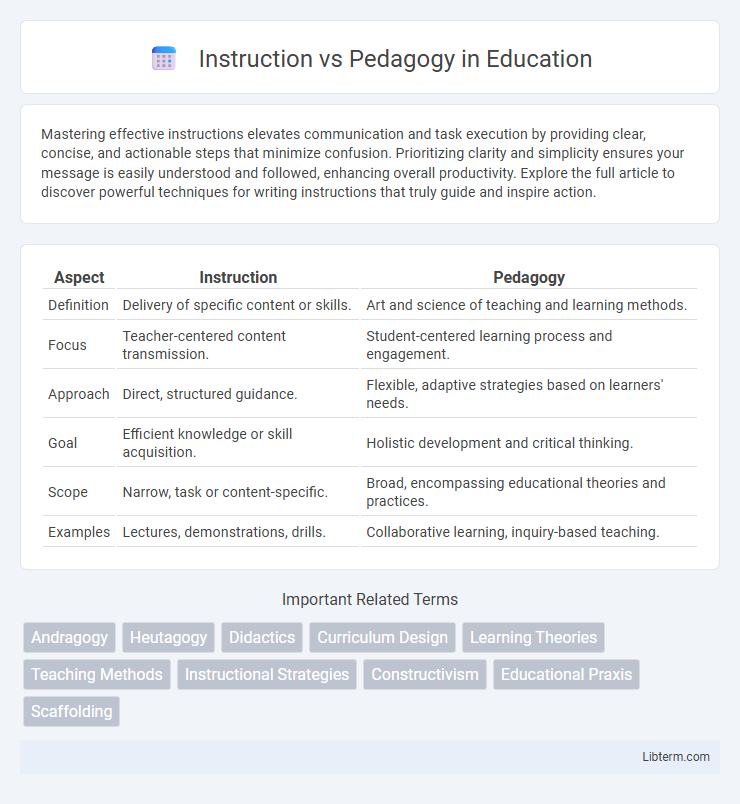
| Aspect | Instruction | Pedagogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery of specific content or skills. | Art and science of teaching and learning methods. |
| Focus | Teacher-centered content transmission. | Student-centered learning process and engagement. |
| Approach | Direct, structured guidance. | Flexible, adaptive strategies based on learners' needs. |
| Goal | Efficient knowledge or skill acquisition. | Holistic development and critical thinking. |
| Scope | Narrow, task or content-specific. | Broad, encompassing educational theories and practices. |
| Examples | Lectures, demonstrations, drills. | Collaborative learning, inquiry-based teaching. |
Understanding the Concepts: Instruction and Pedagogy
Instruction refers to the specific methods and techniques used to deliver content and facilitate learning, focusing on the practical implementation of teaching. Pedagogy encompasses the broader theory and philosophy behind education, including the principles, strategies, and approaches that guide instructional design and learner interaction. Understanding the distinction helps educators align teaching methods with desired learning outcomes and theoretical frameworks for effective education.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Approaches
Instruction, traditionally centered on the direct transmission of knowledge, evolved through the Renaissance as humanist educators emphasized critical thinking and learner engagement. By the 20th century, pedagogy expanded to include developmental theories from Piaget and Vygotsky, integrating constructivist approaches that focus on learners' active participation. This shift from instruction to pedagogy highlights the transformation from teacher-centered methods to learner-centered frameworks in the historical evolution of teaching approaches.
Key Differences Between Instruction and Pedagogy
Instruction refers to the specific methods and techniques used to deliver content and facilitate learning in a structured manner. Pedagogy encompasses the broader theory and practice of education, including the principles, strategies, and approaches that guide how instruction is designed and implemented. The key differences lie in instruction's focus on the act of teaching itself, while pedagogy addresses the underlying educational philosophy and learner-centered considerations shaping the entire learning experience.
Philosophical Foundations of Pedagogy
Instruction emphasizes the transmission of knowledge and skills through structured methods, while pedagogy encompasses the broader philosophical foundations influencing educational practices and learner engagement. Philosophical foundations of pedagogy include constructivism, which advocates active learner participation in knowledge construction, and pragmatism, emphasizing experiential learning and critical thinking. These foundations shape how educators design curricula, assess understanding, and adapt teaching to diverse learner needs, promoting holistic development beyond mere instruction.
Models and Methods of Instruction
Instruction involves structured delivery of content through specific Models such as Direct Instruction, Inquiry-Based Learning, and Cooperative Learning, which guide the systematic presentation of knowledge and skills. Pedagogy encompasses broader teaching philosophies and approaches that influence the selection and adaptation of instructional Models and Methods, aiming to optimize student engagement and learning outcomes. Methods of Instruction include techniques like scaffolding, differentiation, and formative assessment, which tailor the learning process to diverse student needs within various pedagogical frameworks.
Role of the Teacher: Instructor vs. Pedagogue
The role of the teacher as an instructor centers on delivering structured content and clear directives to facilitate knowledge acquisition efficiently. In contrast, a pedagogue prioritizes fostering critical thinking, creativity, and holistic development by adapting teaching methods to individual learner needs. This pedagogical approach emphasizes mentorship and active engagement over mere content transmission.
Learner Engagement in Instructional vs. Pedagogical Settings
Learner engagement in instructional settings typically centers on the effective delivery of content using structured methods and clear objectives, emphasizing active participation through focused tasks. Pedagogical environments prioritize holistic learner development by integrating cognitive, emotional, and social dimensions, fostering critical thinking and intrinsic motivation. Engagement metrics often show higher retention and deeper understanding in pedagogical settings due to personalized interaction and adaptive feedback mechanisms.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Instruction directly influences learning outcomes by providing clear, structured guidance tailored to specific content and skills, enhancing student comprehension and retention. Pedagogy shapes the broader educational environment, integrating teaching methods, learner engagement, and contextual factors that foster critical thinking and deeper understanding. Optimizing both instruction and pedagogy leads to measurable improvements in academic achievement and long-term knowledge application.
Integrating Instruction and Pedagogy in Modern Classrooms
Instruction emphasizes the delivery of content and skills, while pedagogy encompasses the methods and strategies used to facilitate effective learning. Integrating instruction and pedagogy in modern classrooms involves using learner-centered approaches, such as differentiated instruction and formative assessment, to address diverse student needs and enhance engagement. Technology integration, culturally responsive teaching, and collaborative learning environments are key components that align instruction with pedagogical principles for improved educational outcomes.
Future Trends in Educational Theory and Practice
Instruction emphasizes the structured delivery of content and skills, while pedagogy encompasses the broader art and science of teaching, including learner engagement and context. Future trends in educational theory highlight adaptive learning technologies and personalized instruction, which blend explicit teaching methods with pedagogical strategies tailored to individual needs. Emerging practices integrate AI-driven analytics, fostering dynamic, student-centered environments that optimize both instructional efficiency and pedagogical effectiveness.
Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com