The teacher-centered approach emphasizes the instructor's role as the primary source of knowledge, directing the learning process through lectures and structured lessons. This method prioritizes content delivery and factual accuracy, often limiting student interaction and critical thinking opportunities. Discover how this approach impacts your learning experience and explore its advantages and drawbacks in the rest of the article.
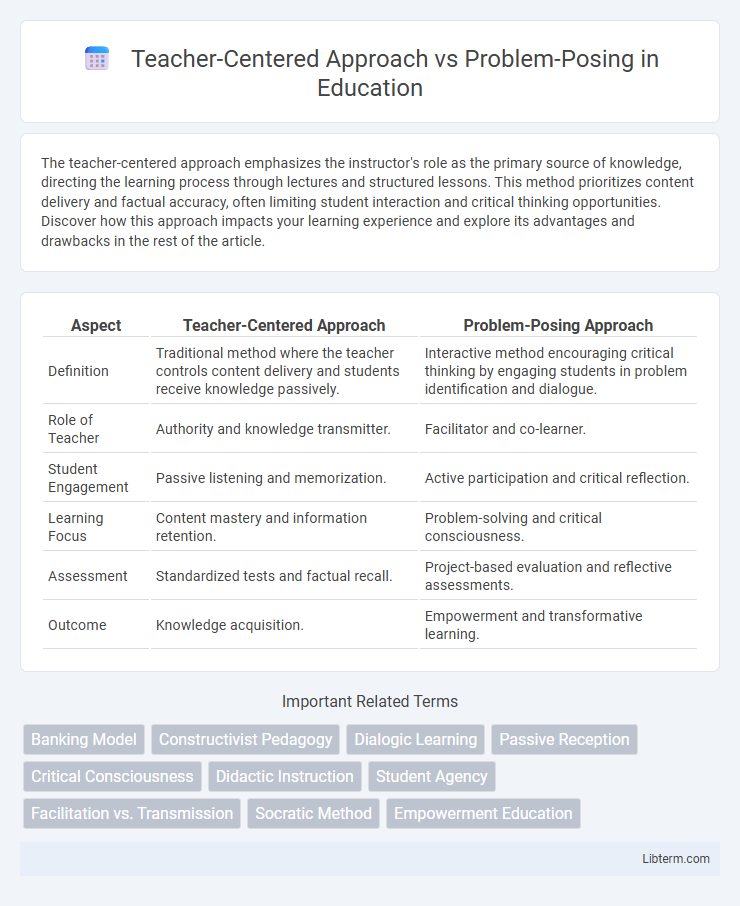
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered Approach | Problem-Posing Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional method where the teacher controls content delivery and students receive knowledge passively. | Interactive method encouraging critical thinking by engaging students in problem identification and dialogue. |
| Role of Teacher | Authority and knowledge transmitter. | Facilitator and co-learner. |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening and memorization. | Active participation and critical reflection. |
| Learning Focus | Content mastery and information retention. | Problem-solving and critical consciousness. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and factual recall. | Project-based evaluation and reflective assessments. |
| Outcome | Knowledge acquisition. | Empowerment and transformative learning. |
Introduction to Teaching Methodologies
Teacher-Centered Approach emphasizes direct instruction where the teacher controls the learning process, prioritizing content delivery and memorization. Problem-Posing Method fosters critical thinking by engaging students in dialogue and reflection, encouraging active participation and real-world problem solving. These methodologies highlight contrasting educational paradigms shaping student engagement and knowledge construction in teaching environments.
Defining the Teacher-Centered Approach
The Teacher-Centered Approach emphasizes a traditional model where the instructor directs the learning process, delivering information through lectures and structured lessons. This method prioritizes content mastery, authority, and standardized assessment, often limiting student interaction and critical thinking. It contrasts with problem-posing pedagogy, which encourages dialogue, inquiry, and active student participation.
Understanding Problem-Posing Education
Problem-Posing Education fosters critical thinking by encouraging dialogue and reflection, contrasting with the Teacher-Centered Approach that emphasizes rote memorization and passive learning. Paulo Freire's methodology in Problem-Posing Education promotes active student engagement through questioning and problem-solving, enhancing deeper understanding. This approach shifts the classroom dynamic toward collaboration, empowering learners to develop critical consciousness and address real-world issues.
Historical Context and Philosophy
The Teacher-Centered Approach originated from traditional educational models rooted in early 20th-century authority-driven pedagogy, emphasizing rote memorization and passive knowledge reception. In contrast, the Problem-Posing method, influenced by Paulo Freire's critical pedagogy in the 1960s, promotes dialogue, critical thinking, and learner empowerment through active engagement with real-world issues. These philosophical differences underscore a shift from hierarchical knowledge transmission to collaborative, transformative learning experiences.
Key Characteristics of Teacher-Centered Learning
Teacher-centered learning emphasizes structured instruction where the teacher directs the content delivery, controls classroom activities, and evaluates student performance. It prioritizes memorization, passive reception of information, and standardized assessments, often limiting student interaction and critical thinking. This approach is characterized by a clear hierarchy with the teacher as the primary knowledge authority.
Core Principles of Problem-Posing Pedagogy
Problem-posing pedagogy emphasizes active dialogue, critical thinking, and the co-creation of knowledge, contrasting with the traditional teacher-centered approach where the instructor solely transmits information. Core principles include fostering reflective inquiry, encouraging students to question assumptions, and promoting collaborative problem-solving to develop deeper understanding. This approach transforms learners into active participants in their education, enhancing engagement and critical consciousness.
Advantages and Limitations of Teacher-Centered Approach
The Teacher-Centered Approach offers structured learning, clear expectations, and efficient content delivery, which benefits large classrooms and standardized curriculum requirements. It allows teachers to maintain control and ensures consistent coverage of essential knowledge, but it often limits student engagement, creativity, and critical thinking development. This approach can hinder personalized learning and discourage active participation, leading to potential disengagement and superficial understanding.
Benefits and Challenges of Problem-Posing Education
Problem-Posing education fosters critical thinking and active learning by encouraging students to question and engage with content, enhancing deeper understanding and retention. This approach promotes collaboration and dialogue, allowing learners to develop problem-solving skills and greater autonomy. Challenges include the need for skilled facilitators to manage diverse perspectives and the potential for slower content coverage compared to the traditional Teacher-Centered approach.
Impact on Student Engagement and Critical Thinking
The Teacher-Centered Approach often limits student engagement and critical thinking by promoting passive learning through lectures and rote memorization. In contrast, the Problem-Posing method fosters active participation and deeper cognitive processing by encouraging students to question, analyze, and collaboratively solve real-world problems. Research indicates that Problem-Posing significantly enhances critical thinking skills and intrinsic motivation, leading to more meaningful and sustained learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Modern Classrooms
Selecting the right teaching approach in modern classrooms depends on fostering critical thinking and student engagement. The teacher-centered approach emphasizes direct instruction and content delivery, ideal for foundational knowledge acquisition and structured learning environments. Conversely, problem-posing encourages interactive dialogue and collaborative problem-solving, promoting deeper understanding and adaptability essential for 21st-century skills development.
Teacher-Centered Approach Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com