Test accommodations provide tailored support to ensure fair access during examinations for individuals with disabilities or specific needs. These adjustments may include extended time, alternative formats, or assistive technologies designed to level the playing field. Explore the rest of the article to learn how test accommodations can help you succeed.
Table of Comparison
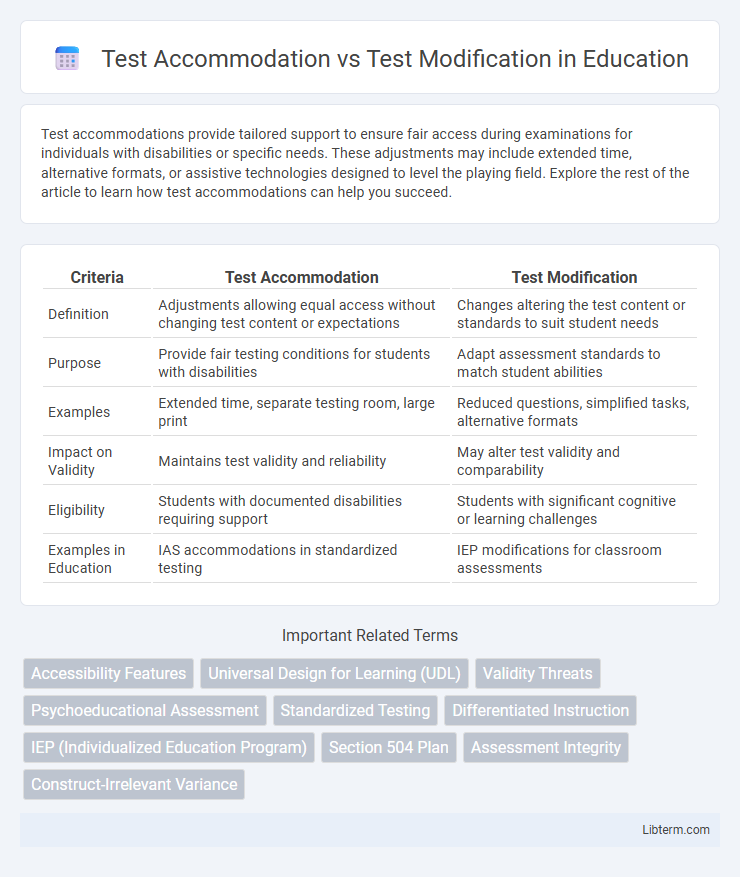
| Criteria | Test Accommodation | Test Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjustments allowing equal access without changing test content or expectations | Changes altering the test content or standards to suit student needs |
| Purpose | Provide fair testing conditions for students with disabilities | Adapt assessment standards to match student abilities |
| Examples | Extended time, separate testing room, large print | Reduced questions, simplified tasks, alternative formats |
| Impact on Validity | Maintains test validity and reliability | May alter test validity and comparability |
| Eligibility | Students with documented disabilities requiring support | Students with significant cognitive or learning challenges |
| Examples in Education | IAS accommodations in standardized testing | IEP modifications for classroom assessments |
Understanding Test Accommodation and Test Modification
Test accommodation refers to changes in the testing environment or format that allow students with disabilities to demonstrate their knowledge without altering what the test measures, such as extended time or alternative settings. Test modification involves altering the test content or criteria itself, which changes the standard of what is being assessed, like simplifying questions or reducing the number of items. Understanding these distinctions is critical for educators to provide appropriate support while maintaining the integrity of assessment outcomes.
Key Differences Between Test Accommodation and Modification
Test accommodation involves altering the testing environment or format without changing the content or standards, such as extended time or a quiet room, to help students with disabilities demonstrate their true abilities. Test modification changes the test's content, level, or expectations, like simplifying questions or reducing the number of items, which can affect the validity of the results. Key differences include accommodation preserving test integrity while providing equitable access, whereas modification adjusts the test itself, potentially impacting comparability and outcomes.
Purposes of Test Accommodation in Education
Test accommodations in education primarily aim to provide equal access to assessments for students with disabilities by minimizing barriers related to their individual needs. They modify how a test is administered or presented without altering the content or expectations, ensuring that the student's knowledge and skills are accurately measured. These accommodations promote fairness and enhance the validity of assessment results by accounting for diverse learning requirements.
When Are Test Modifications Appropriate?
Test modifications are appropriate when changes to the content or format of an assessment are necessary to accurately measure a student's knowledge without altering the intended learning outcomes. Modifications may include simplifying test questions, reducing the number of items, or allowing alternate methods of response, typically for students with significant cognitive or physical disabilities. These adjustments differ from accommodations, which provide support without changing test expectations or measuring standards.
Common Types of Test Accommodations
Common types of test accommodations include extended time, alternate test formats such as braille or large print, and the provision of a quiet or separate testing environment. These accommodations help students with disabilities access the same tests without altering the test content or expected outcomes. In contrast, test modifications involve changing the test's content or performance expectations, which may include simplifying questions or reducing the number of items.
Examples of Test Modifications in Practice
Test modifications involve altering the content or format of assessments to suit students' unique needs, such as simplifying language in test questions or reducing the number of answer choices. Examples include providing alternate test formats like oral exams instead of written ones or modifying the difficulty level by omitting certain sections. These modifications ensure the assessment measures the intended skills without compromising the test's validity for students requiring different evaluation approaches.
Impact on Student Assessment Outcomes
Test accommodations, such as extended time or alternate formats, help students demonstrate their true abilities by minimizing barriers without altering the test content, thus preserving the assessment's validity and reliability. Test modifications involve changing the test's content or expectations, which can affect comparability of results and may lead to less accurate measurement of student knowledge or skills. The choice between accommodations and modifications significantly impacts assessment outcomes, influencing identification of student needs and educational planning.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Test accommodations ensure equal access to assessments by altering the environment or presentation without changing the test's content, aligning with legal mandates such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act. Test modifications, which change the test's content or expectations, raise ethical concerns about fairness and validity, potentially compromising the integrity of the assessment and conflicting with legal standards. Educational institutions must carefully balance these considerations to provide equitable testing opportunities while maintaining compliance with federal laws and ethical guidelines.
Best Practices for Implementing Accommodations and Modifications
Effective implementation of test accommodations involves providing individualized supports such as extended time, alternate test formats, or assistive technology to ensure equitable access without altering test content or expectations. Test modifications require carefully adjusting test objectives or difficulty levels to align with the learner's abilities while maintaining valid assessment standards. Best practices include thorough documentation, collaboration among educators and specialists, training for test administrators, and ongoing monitoring to uphold fairness and accuracy in assessment outcomes.
Supporting Inclusive Assessment for Diverse Learners
Test accommodation involves changes in the testing environment or administration, such as extended time or alternative formats, to support diverse learners without altering the test content. Test modification refers to altering test content or expectations to meet the individual needs of students with disabilities, potentially affecting the validity of assessment outcomes. Supporting inclusive assessment requires balancing accommodations that provide equitable access while maintaining test integrity to accurately measure diverse learners' abilities.
Test Accommodation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com