Balanced literacy integrates phonics, guided reading, writing, and word study to develop comprehensive reading skills. This approach tailors instruction to meet diverse learning needs, ensuring students build fluency and comprehension simultaneously. Discover how balanced literacy can transform your teaching strategies by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
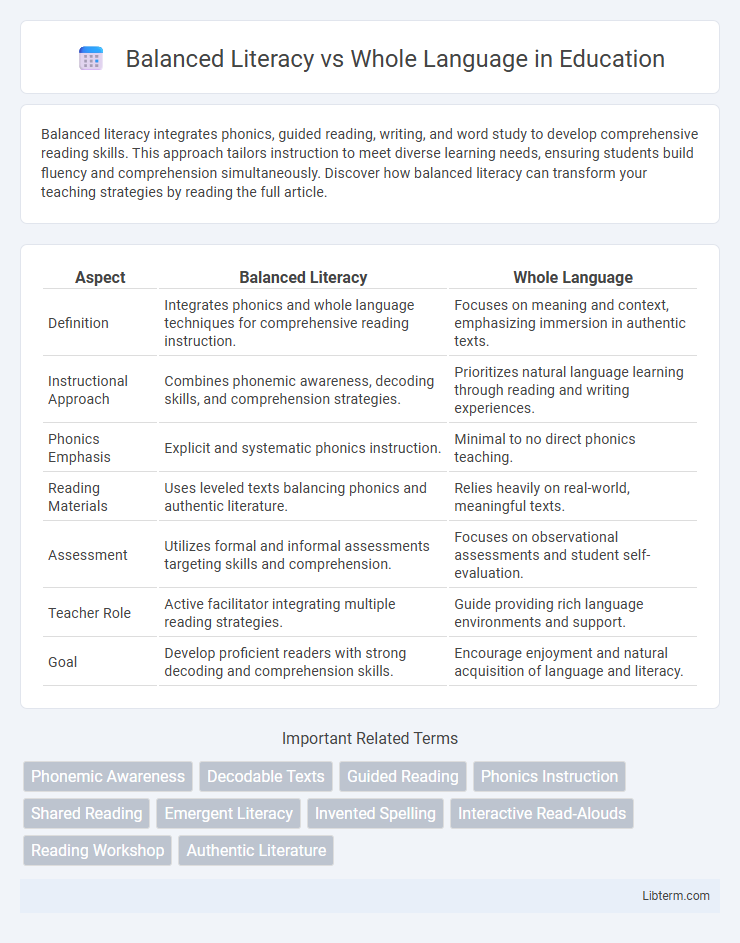
| Aspect | Balanced Literacy | Whole Language |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates phonics and whole language techniques for comprehensive reading instruction. | Focuses on meaning and context, emphasizing immersion in authentic texts. |
| Instructional Approach | Combines phonemic awareness, decoding skills, and comprehension strategies. | Prioritizes natural language learning through reading and writing experiences. |
| Phonics Emphasis | Explicit and systematic phonics instruction. | Minimal to no direct phonics teaching. |
| Reading Materials | Uses leveled texts balancing phonics and authentic literature. | Relies heavily on real-world, meaningful texts. |
| Assessment | Utilizes formal and informal assessments targeting skills and comprehension. | Focuses on observational assessments and student self-evaluation. |
| Teacher Role | Active facilitator integrating multiple reading strategies. | Guide providing rich language environments and support. |
| Goal | Develop proficient readers with strong decoding and comprehension skills. | Encourage enjoyment and natural acquisition of language and literacy. |
Introduction to Balanced Literacy and Whole Language
Balanced Literacy integrates phonics, vocabulary, comprehension, and writing strategies to support diverse learning styles, emphasizing explicit instruction alongside authentic reading and writing experiences. Whole Language prioritizes immersion in rich, meaningful texts to foster natural language acquisition, encouraging readers to derive meaning using context, syntax, and semantics rather than isolated phonics skills. Both approaches aim to develop proficient readers but differ in instructional focus and methodology, with Balanced Literacy providing structured skills practice and Whole Language promoting holistic language engagement.
Defining Balanced Literacy
Balanced Literacy combines phonics and whole language approaches to provide a comprehensive reading instruction framework. It emphasizes decoding skills through systematic phonics alongside meaning-making strategies from whole language, supporting both fluency and comprehension. This approach integrates guided reading, shared reading, and writing to create a well-rounded literacy experience.
Understanding the Whole Language Approach
The Whole Language approach emphasizes immersion in authentic literature and the integration of reading, writing, speaking, and listening skills to foster a natural, meaningful learning experience. It prioritizes context and comprehension over phonics instruction, encouraging students to deduce meaning through exposure to rich, engaging texts. This approach contrasts with Balanced Literacy by minimizing isolated skill drills and promoting holistic language acquisition through student-centered, literature-rich environments.
Core Principles of Balanced Literacy
Balanced Literacy integrates phonics instruction with whole language strategies, emphasizing reading, writing, speaking, and listening skills to develop comprehensive literacy. Core principles include explicit phonemic awareness, guided reading, shared reading, and independent reading to accommodate diverse learning styles. This approach supports vocabulary development and comprehension through meaningful context while reinforcing foundational decoding skills.
Key Features of Whole Language Instruction
Whole Language instruction emphasizes meaning and context by integrating reading, writing, speaking, and listening naturally. It prioritizes authentic literature and student choice, encouraging learners to construct meaning through real-world texts. This approach fosters a holistic literacy environment where phonics is taught in context rather than through isolated drills.
Phonics in Balanced Literacy vs Whole Language
Balanced Literacy emphasizes systematic phonics instruction, integrating explicit teaching of sound-letter relationships to support decoding skills. In contrast, Whole Language de-emphasizes direct phonics, promoting context and meaning-based learning through exposure to authentic texts. Research shows that balanced literacy's phonics approach enhances early reading proficiency and word recognition accuracy more effectively than whole language methods.
Student Engagement and Reading Motivation
Balanced Literacy integrates phonics and whole language strategies, enhancing student engagement through diverse reading activities that cater to various learning styles. Whole Language emphasizes context and meaning, fostering intrinsic reading motivation by encouraging students to connect personally with texts. Research indicates that combining explicit skill instruction with meaningful interaction boosts overall reading motivation and sustained student involvement.
Assessment Strategies: Balanced Literacy vs Whole Language
Balanced Literacy employs diverse assessment strategies including formative assessments, running records, and standardized tests to monitor reading progress and inform instructional adjustments. Whole Language relies more heavily on qualitative assessments such as anecdotal records, portfolios, and observations to gauge comprehension and holistic language development. The data-driven approach in Balanced Literacy contrasts with the interpretive, student-centered assessment methods common in Whole Language instruction.
Research Findings and Effectiveness
Research findings indicate that Balanced Literacy, which integrates phonics and whole language strategies, consistently improves reading fluency and comprehension by addressing diverse learner needs. Studies show that Whole Language alone may lead to uneven decoding skills and poorer word recognition in early readers. Effectiveness data favor Balanced Literacy for fostering foundational literacy skills while maintaining motivation and engagement with meaningful text.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Balanced Literacy integrates phonics and whole language techniques, offering a flexible framework that addresses the varied needs of diverse learners by combining explicit decoding instruction with meaningful, context-rich reading experiences. Whole Language emphasizes immersion in authentic texts to promote natural literacy development but may be less effective for students requiring structured phonemic awareness and decoding support. Selecting the appropriate approach involves assessing individual learner profiles, including language proficiency, learning styles, and literacy backgrounds, to ensure instruction aligns with their unique strengths and challenges.
Balanced Literacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com