Total Quality Management (TQM) focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction by integrating quality principles into every organizational process. Emphasizing employee involvement and data-driven decision-making ensures that products and services consistently meet or exceed quality standards. Explore the article to discover how TQM can transform Your business and drive sustainable success.
Table of Comparison
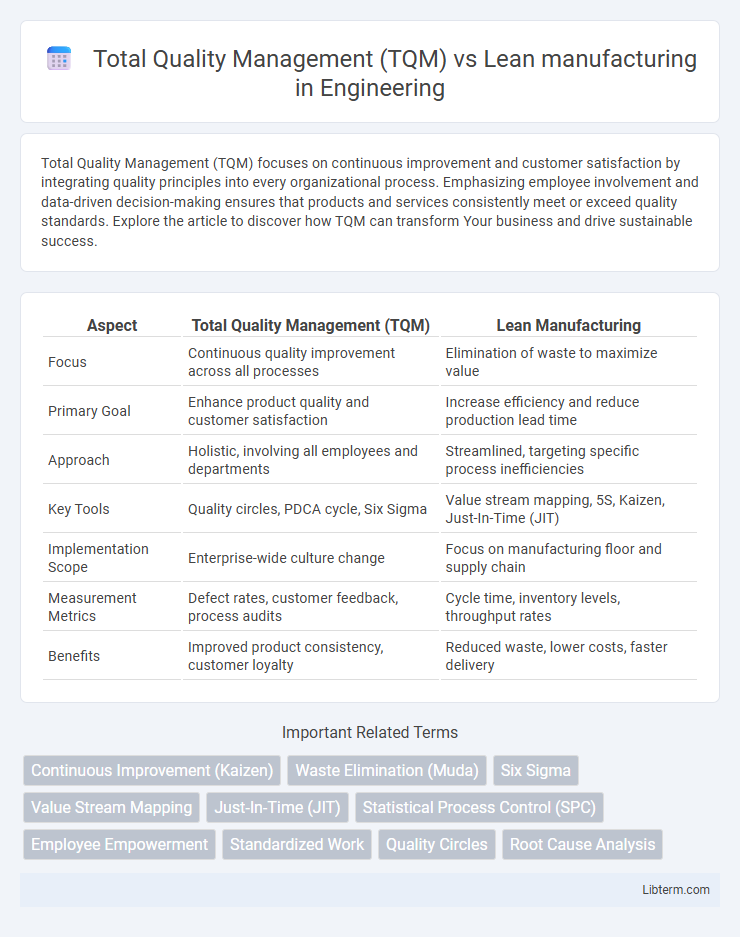
| Aspect | Total Quality Management (TQM) | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Continuous quality improvement across all processes | Elimination of waste to maximize value |
| Primary Goal | Enhance product quality and customer satisfaction | Increase efficiency and reduce production lead time |
| Approach | Holistic, involving all employees and departments | Streamlined, targeting specific process inefficiencies |
| Key Tools | Quality circles, PDCA cycle, Six Sigma | Value stream mapping, 5S, Kaizen, Just-In-Time (JIT) |
| Implementation Scope | Enterprise-wide culture change | Focus on manufacturing floor and supply chain |
| Measurement Metrics | Defect rates, customer feedback, process audits | Cycle time, inventory levels, throughput rates |
| Benefits | Improved product consistency, customer loyalty | Reduced waste, lower costs, faster delivery |
Introduction to TQM and Lean Manufacturing
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through employee involvement, customer focus, and process-centered strategies to enhance product quality and organizational performance. Lean Manufacturing targets waste reduction, streamlined workflows, and increased efficiency by identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities within production processes. Both methodologies aim to optimize operational excellence but differ in approach; TQM focuses broadly on quality improvement across all functions, while Lean concentrates specifically on process efficiency and waste minimization.
Core Principles of Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) centers on core principles like customer focus, continuous improvement, employee involvement, and process-centered approaches to enhance product quality and organizational performance. In contrast, Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, streamlining processes, and maximizing value by eliminating non-value-added activities. While TQM fosters a culture of quality and long-term commitment across all organizational levels, Lean targets operational efficiency through specific tools like Just-in-Time and Kaizen.
Key Concepts of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste through continuous improvement, just-in-time production, and value stream mapping to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Key concepts include focusing on customer value, minimizing inventory, streamlining workflows, and empowering employees to identify inefficiencies. Unlike Total Quality Management (TQM), which centers on overall quality improvement and customer satisfaction, Lean targets faster delivery and resource optimization by systematically removing non-value-added activities.
Historical Evolution: TQM vs Lean
Total Quality Management (TQM) emerged in the 1950s focusing on continuous quality improvement through employee involvement and customer satisfaction, shaped significantly by pioneers like W. Edwards Deming and Joseph Juran. Lean manufacturing originated in the late 1940s with the Toyota Production System, emphasizing waste elimination, just-in-time production, and maximizing value with minimal resources. Both methodologies evolved from post-World War II industrial challenges, but TQM centers on quality culture while Lean prioritizes process efficiency and flow.
Main Differences Between TQM and Lean
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous quality improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement across all organizational processes, focusing on defect prevention and systematic problem-solving. Lean manufacturing centers on waste elimination, value stream optimization, and enhancing flow efficiency through tools like Just-In-Time inventory and Kaizen events. The main differences lie in TQM's broad focus on quality culture versus Lean's targeted approach to operational efficiency and waste reduction.
Shared Goals and Overlapping Strategies
Total Quality Management (TQM) and Lean manufacturing both emphasize continuous improvement and waste reduction to enhance product quality and customer satisfaction. Shared goals include increasing operational efficiency, minimizing defects, and fostering a culture of employee involvement through techniques such as root cause analysis and standardized work processes. Overlapping strategies involve the use of tools like Kaizen, value stream mapping, and statistical process control to identify inefficiencies, streamline workflows, and sustain high performance levels across production systems.
Implementation Challenges: TQM vs Lean
Implementation challenges of Total Quality Management (TQM) often include resistance to cultural change, extensive training requirements, and the need for sustained top management commitment. Lean manufacturing implementation faces obstacles such as identifying value stream inefficiencies, overcoming employee pushback to process standardization, and maintaining continuous improvement momentum. Both methodologies demand cross-functional collaboration and persistent communication, but Lean emphasizes waste reduction while TQM focuses more on overall quality improvements.
Measuring Success: Metrics and Outcomes
Total Quality Management (TQM) measures success through comprehensive metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, defect rates, and overall quality improvement over time. Lean manufacturing focuses on key performance indicators including cycle time reduction, inventory turnover, and waste elimination to drive efficiency. Both approaches utilize data-driven outcomes but prioritize different metrics aligned with their strategic goals for operational excellence.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction across industries like automotive and healthcare, demonstrated by Toyota's enhanced quality standards and Mayo Clinic's patient care processes. Lean manufacturing concentrates on waste reduction and efficiency, prominently applied in manufacturing sectors such as Boeing's streamlined production lines and Intel's semiconductor fabrication processes. Case studies reveal TQM's strength in holistic organizational culture transformation, while Lean excels in operational speed and cost savings.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through employee involvement, focusing on quality at every organizational level to reduce defects and enhance customer satisfaction. Lean manufacturing concentrates on eliminating waste and streamlining processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Selecting the right approach depends on organizational goals: TQM suits companies aiming for comprehensive quality enhancement, while Lean is ideal for those prioritizing operational efficiency and cost reduction.
Total Quality Management (TQM) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com