Desertification is the degradation of land in arid and semi-arid areas due to factors like climate change and unsustainable agricultural practices. It leads to reduced soil fertility, loss of vegetation, and increased vulnerability to drought, threatening ecosystems and human livelihoods. Discover how desertification impacts your environment and what strategies can help combat this pressing issue in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
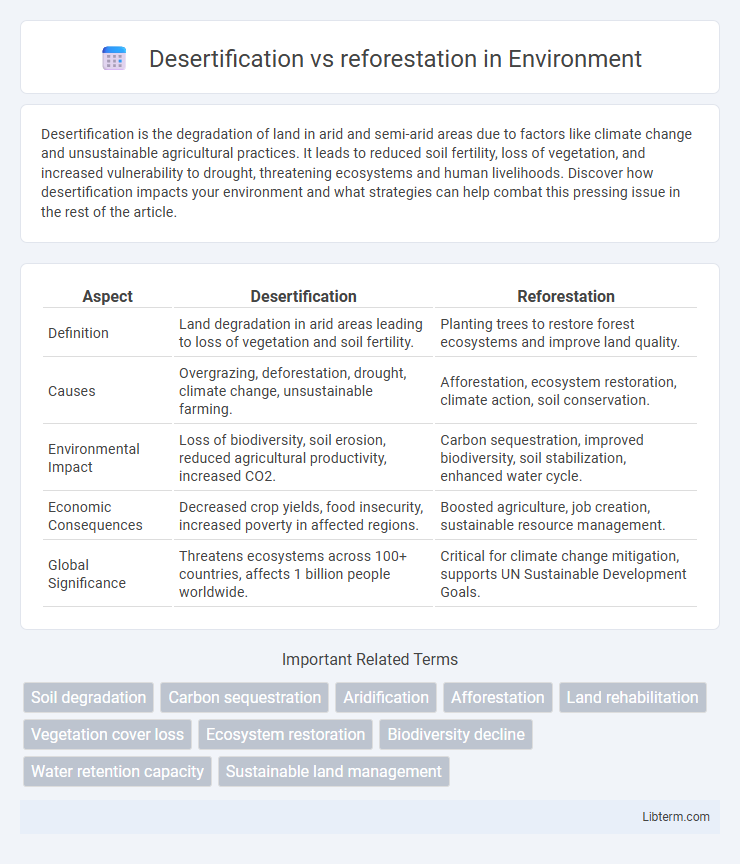
| Aspect | Desertification | Reforestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Land degradation in arid areas leading to loss of vegetation and soil fertility. | Planting trees to restore forest ecosystems and improve land quality. |
| Causes | Overgrazing, deforestation, drought, climate change, unsustainable farming. | Afforestation, ecosystem restoration, climate action, soil conservation. |
| Environmental Impact | Loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, reduced agricultural productivity, increased CO2. | Carbon sequestration, improved biodiversity, soil stabilization, enhanced water cycle. |
| Economic Consequences | Decreased crop yields, food insecurity, increased poverty in affected regions. | Boosted agriculture, job creation, sustainable resource management. |
| Global Significance | Threatens ecosystems across 100+ countries, affects 1 billion people worldwide. | Critical for climate change mitigation, supports UN Sustainable Development Goals. |
Understanding Desertification: Causes and Consequences
Desertification is primarily caused by factors such as deforestation, overgrazing, climate change, and unsustainable agricultural practices, leading to the degradation of once fertile land into arid desert. Consequences include loss of biodiversity, reduced agricultural productivity, soil erosion, and increased vulnerability to drought, which threaten food security and livelihoods. Reforestation combats desertification by restoring vegetation cover, improving soil quality, and enhancing water retention, thereby reversing land degradation and supporting ecosystem resilience.
The Science Behind Reforestation
Reforestation involves the systematic planting and restoration of trees to combat the effects of desertification, a process where fertile land becomes desert due to factors like deforestation, drought, and soil erosion. Scientific studies reveal that trees play a critical role in stabilizing soil, enhancing water retention, and increasing local humidity, which counteracts desertification's degradation processes. By restoring vegetation cover through reforestation, ecosystems regain biodiversity and carbon sequestration capacity, ultimately improving soil health and reversing land degradation trends.
Key Differences: Desertification vs. Reforestation
Desertification involves the degradation of fertile land into desert typically due to drought, deforestation, and inappropriate agricultural practices, resulting in lost vegetation and diminished soil quality. Reforestation is the process of restoring trees and vegetation to deforested or degraded lands, enhancing biodiversity, improving soil health, and increasing carbon sequestration. While desertification leads to ecosystem decline and reduced land productivity, reforestation promotes ecological recovery and sustainable land management.
Human Activities Accelerating Desertification
Human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable agricultural practices accelerate desertification by depleting soil nutrients and reducing vegetation cover. Intensive land use leads to soil erosion and decreased water retention, exacerbating land degradation and expanding desertified areas. Reforestation combats desertification by restoring vegetation, improving soil stability, and enhancing local microclimates, thereby reversing land degradation trends.
Ecological Benefits of Reforestation
Reforestation plays a pivotal role in reversing desertification by restoring soil fertility, enhancing biodiversity, and stabilizing local climates through increased carbon sequestration. Trees improve water retention in the soil, reduce erosion, and create habitats that support various species, thereby boosting ecosystem resilience. This restoration of forested areas counteracts the degradation caused by desertification, promoting environmental sustainability and long-term ecological balance.
Socioeconomic Impacts of Land Degradation
Desertification reduces agricultural productivity, leading to food insecurity and increased poverty in rural communities reliant on land resources. Reforestation restores soil fertility and supports biodiversity, enhancing livelihoods through sustainable agriculture and ecotourism. Land degradation exacerbates migration pressures, while reforestation projects can create job opportunities and stabilize local economies.
Innovative Solutions in Reforestation
Innovative solutions in reforestation leverage drone technology for precision planting and real-time monitoring, significantly enhancing tree growth rates and ecosystem recovery in desertified areas. Bioengineering advances enable the development of drought-resistant tree species that improve soil quality and sequester carbon more efficiently, combating desertification effects. Community-based reforestation programs integrate traditional knowledge with modern techniques, promoting sustainable land management and long-term environmental resilience.
Global Success Stories in Combating Desertification
Global success stories in combating desertification highlight reforestation projects like the Great Green Wall in Africa, which aims to restore 100 million hectares of degraded land. China's Three-North Shelter Forest Program has also effectively reduced desertification by planting over 66 billion trees across 42 million hectares. These large-scale efforts demonstrate the potential of reforestation to improve soil quality, increase biodiversity, and reverse land degradation worldwide.
Policy Frameworks: Supporting Reforestation Efforts
Policy frameworks supporting reforestation efforts prioritize sustainable land management practices, funding incentives, and community engagement to combat desertification effectively. Governments implement regulations that promote afforestation, protect existing forests, and integrate reforestation into national climate action plans, ensuring alignment with goals such as the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD). International cooperation and transparent monitoring systems enhance accountability and optimize the long-term restoration of degraded ecosystems.
Future Pathways: Balancing Restoration and Prevention
Future pathways to address desertification and promote reforestation emphasize integrating sustainable land management practices with advanced afforestation technologies. Balancing restoration efforts with preventive measures requires leveraging satellite monitoring and AI-driven soil analysis to optimize tree planting in vulnerable areas. Policies prioritizing community engagement and climate-resilient species selection enhance the long-term success of both desertification control and reforestation initiatives.
Desertification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com