A cuspate delta forms when sediment deposits protrude outward from the shoreline in a pointed, tooth-like shape due to the convergence of opposing longshore currents. This type of delta creates unique coastal landforms that influence marine ecosystems and human activities. Discover how cuspate deltas affect your local environment and their significance by reading the full article.
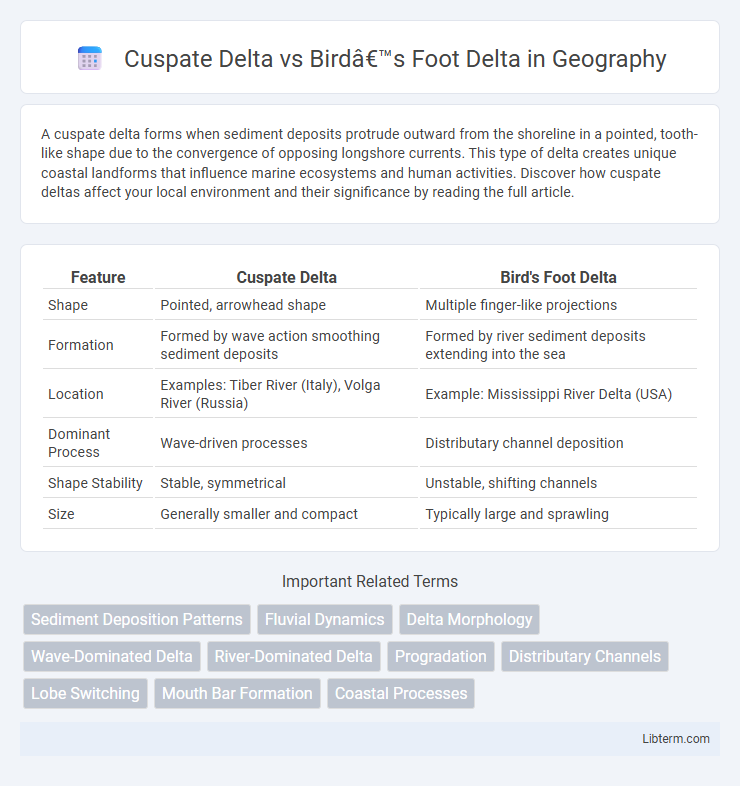
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cuspate Delta | Bird's Foot Delta |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Pointed, arrowhead shape | Multiple finger-like projections |
| Formation | Formed by wave action smoothing sediment deposits | Formed by river sediment deposits extending into the sea |
| Location | Examples: Tiber River (Italy), Volga River (Russia) | Example: Mississippi River Delta (USA) |
| Dominant Process | Wave-driven processes | Distributary channel deposition |
| Shape Stability | Stable, symmetrical | Unstable, shifting channels |
| Size | Generally smaller and compact | Typically large and sprawling |
Introduction to Delta Formations
Cuspate deltas form where sediment accumulates in a pointed, triangular shape due to the balanced action of waves and tidal currents, commonly found along coasts with moderate wave energy. Bird's foot deltas develop when river sediment is deposited in distributary channels extending into calm, low-energy marine environments, resulting in finger-like projections resembling a bird's foot. The contrasting shapes of these deltas are directly influenced by the interplay of fluvial sediment supply, wave energy, and tidal dynamics.
Defining Cuspate Deltas
Cuspate deltas feature a pointed, triangular shape formed where sediment deposits extend outward in a cusp-like pattern due to wave action and longshore currents. These deltas develop in coastal environments with moderate wave energy and minimal river sediment supply, resulting in a smooth, symmetrical shoreline protrusion. Unlike bird's foot deltas, cuspate deltas lack prominent distributary channels and instead exhibit a broad, rounded apex pointing seaward.
Characteristics of Bird’s Foot Deltas
Bird's Foot Deltas are characterized by their distinct protruding distributary channels that extend far into the open water, resembling a bird's foot. These deltas form predominantly in environments with strong riverine sediment supply and weak wave or tidal activity, which allows the channels to maintain their course. Sediment deposition creates elongated, finger-like projections of land separated by deep, navigable channels, making them highly dynamic and conducive to navigation and sediment trapping.
Geological Formation Processes
Cuspate deltas form through the balanced deposition of sediments by wave action, creating a pointed or tooth-like shape due to the lateral spreading of sediments along the shoreline. Bird's foot deltas develop where river sediment deposition extends far into a body of water, often a gulf or sea, forming multiple distributary channels that protrude into the water. The geological formation of cuspate deltas relies heavily on strong wave energy reshaping sediments, while bird's foot deltas result from dominant fluvial processes with minimal wave reworking and sediment dispersal.
Sediment Deposition Patterns
A cuspate delta features a pointed, triangular shape formed by evenly distributed sediment deposition from multiple directions, resulting in symmetrical landform growth. In contrast, a bird's foot delta exhibits elongated distributary channels that extend far into the body of water, with sediment primarily deposited along these narrow protrusions creating a finger-like pattern. The sediment deposition in cuspate deltas is more centralized and compact, while bird's foot deltas show dispersed deposition aligned with strong river currents transporting sediments downstream.
River Dynamics and Water Flow
Cuspate deltas form where river flow meets strong wave or tidal action, creating a pointed, triangular shape as sediment is evenly distributed along the coast. Bird's foot deltas develop when river discharge is dominant over marine forces, causing multiple distributary channels to extend outward like bird's toes, with sediment deposition concentrated at these channels' mouths. River dynamics in cuspate deltas involve balanced sediment transport and wave redistribution, while bird's foot deltas exhibit channel-dominated sediment deposition with less influence from wave or tidal currents.
Examples of Cuspate Deltas Worldwide
Cuspate deltas, characterized by their pointed, tooth-like projections, are exemplified by the Tiber River Delta in Italy, the Nile Delta in Egypt, and the Po River Delta in the Adriatic Sea. These deltas form where sediment supply is balanced by wave action, creating a triangular shape that extends into the body of water. Contrasting with bird's foot deltas like the Mississippi River Delta, cuspate deltas exhibit more symmetric, broad-fronted landforms shaped by even wave and tidal forces.
Notable Bird’s Foot Delta Locations
The Bird's Foot Delta, characterized by its distinct finger-like projections, is notably exemplified by the Mississippi River Delta in the United States, which extends far into the Gulf of Mexico. Other significant Bird's Foot Deltas include the Nile Delta in Egypt, though more classically arcuate, it occasionally exhibits slight protrusions resembling a bird's foot due to sediment deposition patterns. These deltas differ from cuspate deltas, such as the Tiber Delta in Italy, which display a triangular, pointed shape formed by the direct convergence of sediment-laden currents and wave action.
Ecological and Environmental Impact
Cuspate deltas, like the Tiber River delta in Italy, create broad, triangular landforms that support diverse wetland ecosystems with abundant vegetation and provide crucial habitats for migratory birds and aquatic species. Bird's foot deltas, exemplified by the Mississippi River delta, extend layered distributary channels into the sea, promoting rich sediment deposition that fosters extensive marshlands and serves as vital buffers against storms and coastal erosion. Both delta types influence nutrient cycling and sediment dynamics, but bird's foot deltas typically exhibit more complex hydrological patterns essential for sustaining fisheries and maintaining coastal resilience.
Human Influence and Future Outlook
Cuspate deltas, characterized by their triangular shape formed through wave action, often experience moderate human influence due to their accessibility and stable coastline, supporting port development and agriculture. Bird's foot deltas, such as the Mississippi River delta, face significant human impact from extensive river management, levee construction, and sediment diversion, leading to reduced sediment supply and heightened vulnerability to subsidence and sea-level rise. Future outlook for cuspate deltas includes potential resilience through managed sediment replenishment, while bird's foot deltas require integrated restoration strategies to mitigate land loss and adapt to climate change effects.
Cuspate Delta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com