Map symbols serve as visual representations of various geographic features and landmarks, making it easier to interpret maps quickly and accurately. These icons convey critical information such as terrain types, roads, water bodies, and man-made structures with minimal text. Explore the rest of this article to better understand how to read and use map symbols effectively for your navigation needs.
Table of Comparison
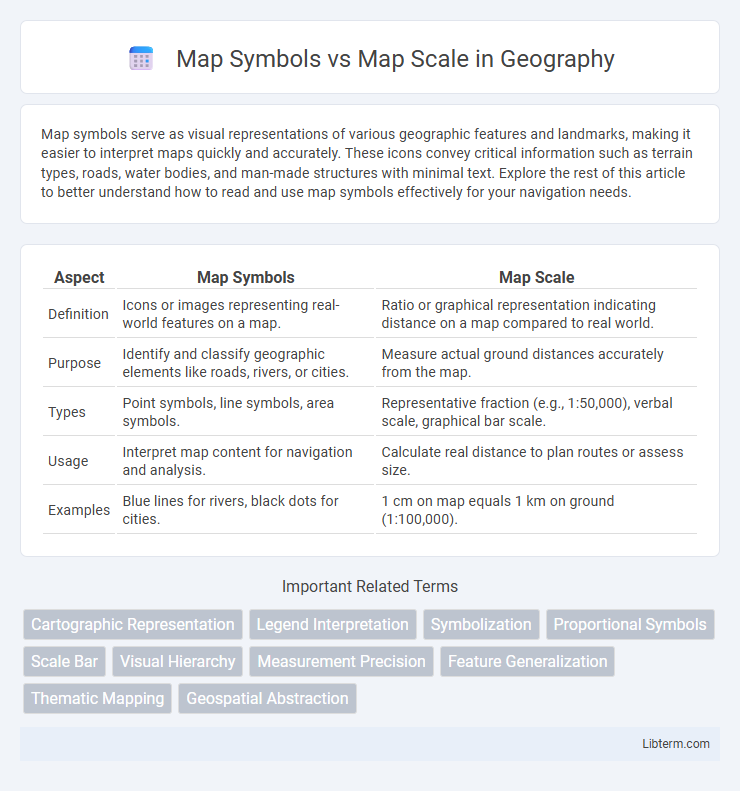
| Aspect | Map Symbols | Map Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Icons or images representing real-world features on a map. | Ratio or graphical representation indicating distance on a map compared to real world. |
| Purpose | Identify and classify geographic elements like roads, rivers, or cities. | Measure actual ground distances accurately from the map. |
| Types | Point symbols, line symbols, area symbols. | Representative fraction (e.g., 1:50,000), verbal scale, graphical bar scale. |
| Usage | Interpret map content for navigation and analysis. | Calculate real distance to plan routes or assess size. |
| Examples | Blue lines for rivers, black dots for cities. | 1 cm on map equals 1 km on ground (1:100,000). |
Introduction to Map Symbols and Map Scale
Map symbols serve as visual representations of geographic features, landmarks, and data points, allowing users to easily interpret complex spatial information on a map. Map scale defines the relationship between distances on the map and the corresponding real-world distances, crucial for accurately measuring and understanding the size and distance of mapped areas. Understanding both map symbols and scale is essential for effective map reading, navigation, and spatial analysis.
Defining Map Symbols
Map symbols represent real-world features like roads, rivers, and landmarks using standardized icons or shapes to convey spatial information efficiently. These symbols enable quick recognition and interpretation of geographic data without relying on extensive text. Properly understanding map symbols is essential for accurately reading and analyzing maps, as they provide a visual shorthand for complex information.
Understanding Map Scale
Understanding map scale is crucial for interpreting distances and spatial relationships accurately on any map. Map scale, expressed as a ratio or graphic bar, defines the relationship between a unit of length on the map and the actual ground distance, such as 1:50,000 meaning 1 unit on the map equals 50,000 units on the earth. While map symbols represent specific features like roads, landmarks, or terrain types, map scale ensures these symbols are proportionally sized and correctly spaced to reflect real-world dimensions.
Types of Map Symbols
Map symbols are graphical representations on maps that convey information about geographic features, including points, lines, and areas, each designed to reflect the data's nature effectively. Types of map symbols include point symbols for specific locations such as cities or landmarks, line symbols representing linear features like roads and rivers, and area symbols indicating regions like forests or lakes. Effective map design ensures symbols are intuitive and consistent, facilitating accurate interpretation regardless of map scale, which determines the ratio between distances on the map and actual ground distances.
Types of Map Scales
Map scales are essential for interpreting distances on a map, with common types including verbal scales, graphic scales, and representative fraction scales. Verbal scales describe distances in words, such as "one inch equals one mile," while graphic scales use a visual bar to represent distance units. Representative fraction scales use ratios like 1:50,000 to show the relationship between a unit on the map and the actual ground distance.
Importance of Map Symbols in Navigation
Map symbols play a crucial role in navigation by providing clear, immediate information about terrain features, landmarks, and routes, which enhances user comprehension and reduces the risk of errors. Unlike map scale, which determines the level of detail and distance representation, map symbols convey essential, standardized visual cues that enable quick decision-making in the field. Effective interpretation of map symbols ensures accurate orientation and safe navigation across diverse environments.
Role of Map Scale in Spatial Accuracy
Map scale defines the relationship between distances on a map and their real-world equivalents, directly impacting spatial accuracy by determining the level of detail that can be represented. Larger scales (e.g., 1:10,000) provide more precise spatial information, allowing for accurate placement of map symbols and features. Conversely, smaller scales (e.g., 1:1,000,000) reduce detail and spatial accuracy, often requiring generalized or simplified map symbols to represent extensive areas effectively.
Differences Between Map Symbols and Map Scale
Map symbols represent specific features or objects on a map, such as roads, rivers, or landmarks, using shapes, colors, and icons for easy identification. Map scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground, providing a measure of spatial extent and allowing users to calculate real-world distances. The primary difference lies in function: map symbols convey qualitative information about locations, while map scale quantifies spatial relationships and distance.
How Map Symbols and Scale Work Together
Map symbols represent real-world features such as roads, rivers, and landmarks, allowing users to interpret spatial information effectively. The map scale determines the proportional relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground, influencing the size and detail of symbols used. Together, map symbols and scale ensure accurate, meaningful representation of geographic data, enabling precise navigation and analysis.
Choosing the Right Map Symbols and Scale
Choosing the right map symbols and scale is essential for accurate geographic representation and user understanding. Map symbols must be clear, consistent, and universally recognizable to convey specific features effectively, while the map scale determines the level of detail and the spatial extent depicted. Balancing symbol size with the chosen scale ensures legibility and precision, enabling users to interpret distances and landmarks accurately on the map.
Map Symbols Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com