Pristine landscapes offer untouched beauty and serve as vital habitats for diverse wildlife, maintaining ecological balance and promoting natural sustainability. Exploring these areas can enhance your appreciation for nature's wonders and inspire conservation efforts. Discover more about the importance and preservation of pristine landscapes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
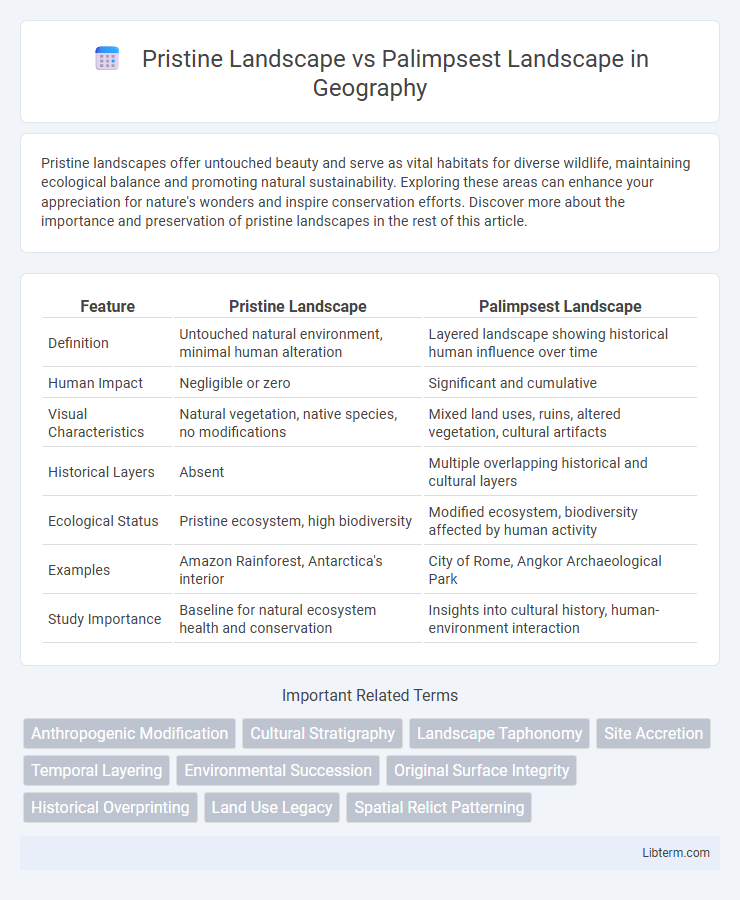
| Feature | Pristine Landscape | Palimpsest Landscape |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Untouched natural environment, minimal human alteration | Layered landscape showing historical human influence over time |
| Human Impact | Negligible or zero | Significant and cumulative |
| Visual Characteristics | Natural vegetation, native species, no modifications | Mixed land uses, ruins, altered vegetation, cultural artifacts |
| Historical Layers | Absent | Multiple overlapping historical and cultural layers |
| Ecological Status | Pristine ecosystem, high biodiversity | Modified ecosystem, biodiversity affected by human activity |
| Examples | Amazon Rainforest, Antarctica's interior | City of Rome, Angkor Archaeological Park |
| Study Importance | Baseline for natural ecosystem health and conservation | Insights into cultural history, human-environment interaction |
Introduction to Landscape Concepts
Pristine landscapes refer to natural environments largely untouched by human activity, maintaining original ecological processes and biodiversity. Palimpsest landscapes embody layers of historical and cultural modifications, reflecting successive human influences over time. Understanding these concepts aids in landscape conservation, emphasizing the interplay between natural integrity and cultural heritage.
Defining Pristine Landscapes
Pristine landscapes are natural environments largely untouched by human activity, retaining their original ecological processes and biodiversity. These landscapes serve as critical baselines for ecological research and conservation efforts due to their high levels of habitat integrity and minimal anthropogenic influence. In contrast, palimpsest landscapes display layers of historical human impact that have modified and reshaped the natural terrain over time.
Understanding Palimpsest Landscapes
Palimpsest landscapes reveal layered histories through visible traces of past human activities and natural processes, unlike pristine landscapes that remain largely untouched by significant alteration. Understanding palimpsest landscapes involves analyzing sediment deposits, archaeological artifacts, and vegetation patterns to decode environmental and cultural changes over time. This multidimensional approach helps reconstruct historical land use and guides sustainable landscape management by preserving a dynamic record of human-environment interaction.
Historical Context and Evolution
Pristine landscapes refer to natural environments that have remained largely untouched by human activity, embodying ecosystems in their original state prior to significant anthropogenic influence. In contrast, palimpsest landscapes reveal layers of human history and environmental modification, showcasing the cumulative impact of cultural, agricultural, and urban developments over time. The evolution of these landscapes highlights the dynamic interplay between natural processes and human interventions, which shapes ecological and historical narratives.
Human Influence on Landscape Transformation
Pristine landscapes represent natural environments largely untouched by human activities, maintaining original ecological processes and native biodiversity. Palimpsest landscapes exhibit layers of human influence where multiple periods of cultural or technological intervention have altered terrain, vegetation, and land use patterns. Human-driven transformations in palimpsest landscapes include urbanization, agriculture, and industrial development, which reshape ecosystems and create complex, historically contingent spatial mosaics.
Ecological Implications of Each Type
Pristine landscapes, characterized by minimal human disturbance, support high biodiversity and complex ecosystems that maintain natural processes such as nutrient cycling and habitat connectivity. Palimpsest landscapes exhibit a mosaic of past human influences layered over natural features, often leading to altered species compositions and ecosystem functions but can provide unique habitats and cultural ecosystem services. Ecologically, pristine landscapes promote resilience and stability, whereas palimpsest landscapes highlight the dynamic interaction between anthropogenic activities and ecological succession.
Cultural Significance and Heritage Value
Pristine landscapes represent untouched natural environments that hold intrinsic cultural significance as symbols of original ecosystems and indigenous heritage. Palimpsest landscapes embody layered histories where human activities, such as agriculture, settlement, and industrialization, have transformed and enriched the land, reflecting evolving cultural narratives and collective memory. The heritage value of palimpsest landscapes lies in their ability to illustrate the dynamic interaction between humans and nature over time, preserving diverse archaeological, architectural, and cultural artifacts within a single geographic area.
Challenges in Conservation and Management
Pristine landscapes face challenges in conservation due to their sensitivity to human disturbances and the difficulty of maintaining their original ecological conditions amid climate change and invasive species. Palimpsest landscapes, characterized by layered historical and cultural modifications, require complex management strategies that balance preservation of heritage values with ongoing land use and ecological restoration. Both demand adaptive approaches integrating scientific research, stakeholder involvement, and sustainable practices to mitigate degradation and ensure resilience.
Case Studies: Pristine vs Palimpsest Examples
Pristine landscapes, such as the Amazon Rainforest, showcase ecosystems minimally impacted by human activity, preserving original biodiversity and natural processes. Palimpsest landscapes, exemplified by urban areas like Rome, reveal layers of historical human modifications intertwined with natural features, reflecting cultural and environmental transformations over centuries. Comparative case studies highlight how pristine landscapes serve as baselines for ecological research, while palimpsest landscapes provide insights into human-environment interactions and adaptive land use.
Future Perspectives in Landscape Preservation
Pristine landscapes represent untouched natural environments, while palimpsest landscapes embody layers of human interaction and historical change, offering rich cultural narratives for preservation. Future perspectives in landscape preservation emphasize integrating advanced technologies such as GIS mapping and remote sensing to monitor ecological health and historical integrity simultaneously. Balancing conservation efforts between maintaining ecological purity and preserving cultural heritage will be crucial for sustainable landscape management.
Pristine Landscape Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com