The Prime Meridian, located at 0 degrees longitude, serves as the starting point for measuring longitude and dividing the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. This imaginary line passes through Greenwich, London, and is essential for global navigation, timekeeping, and geographic information systems. Discover how the Prime Meridian impacts your understanding of time zones, navigation, and world geography by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
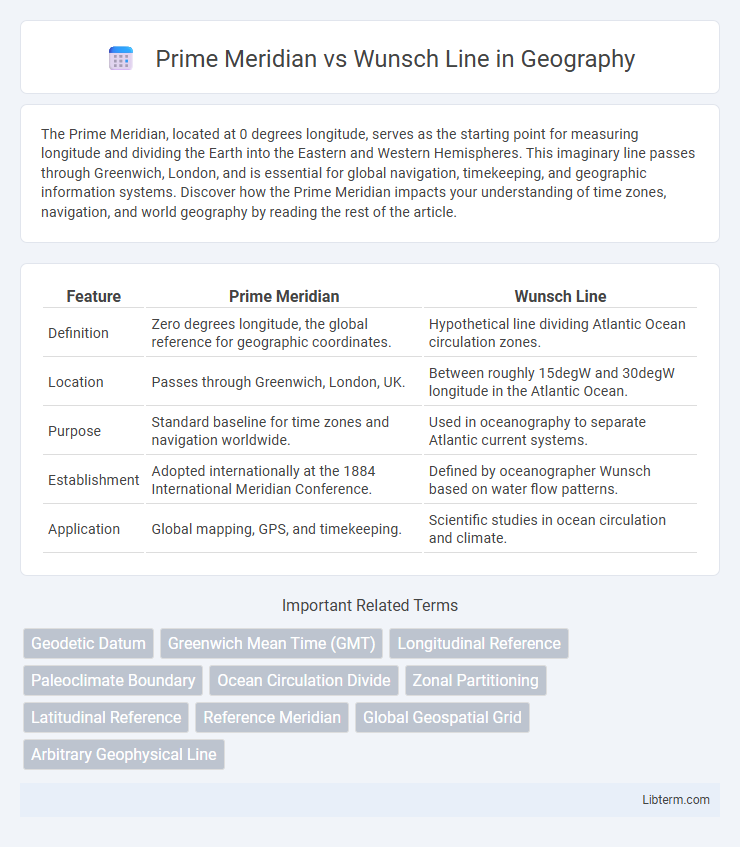
| Feature | Prime Meridian | Wunsch Line |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Zero degrees longitude, the global reference for geographic coordinates. | Hypothetical line dividing Atlantic Ocean circulation zones. |
| Location | Passes through Greenwich, London, UK. | Between roughly 15degW and 30degW longitude in the Atlantic Ocean. |
| Purpose | Standard baseline for time zones and navigation worldwide. | Used in oceanography to separate Atlantic current systems. |
| Establishment | Adopted internationally at the 1884 International Meridian Conference. | Defined by oceanographer Wunsch based on water flow patterns. |
| Application | Global mapping, GPS, and timekeeping. | Scientific studies in ocean circulation and climate. |
Introduction to Prime Meridian and Wunsch Line
The Prime Meridian serves as the zero-degree longitude line, running through Greenwich, England, and is the global standard for geographic coordinate systems and time zones. The Wunsch Line, less known, marks a boundary in oceanography between different water masses in the North Atlantic, influencing ocean circulation and climate patterns. Understanding both lines is crucial for navigation, mapping, and studying Earth's physical oceanographic processes.
Historical Background of the Prime Meridian
Established at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, the Prime Meridian was internationally adopted at the 1884 International Meridian Conference as the global standard for zero degrees longitude. This decision unified diverse longitudinal systems by providing a fixed, universally recognized reference line, crucial for navigation and timekeeping during the height of the British Empire's maritime dominance. In contrast, the Wunsch Line remains a less-known alternative meridian without widespread adoption or historical influence compared to the globally accepted Greenwich Prime Meridian.
The Origin and Purpose of the Wunsch Line
The Wunsch Line, developed by geophysicist Carl Wunsch, serves as a key demarcation in oceanography to study the Atlantic Ocean's circulation by tracing pathways of water masses. Unlike the Prime Meridian, which is an internationally recognized zero-longitude line established for global navigation and timekeeping, the Wunsch Line originates from scientific analysis of ocean currents and water mass exchanges. Its primary purpose is to provide a framework for understanding the complex transport processes and heat fluxes between the tropical and subtropical Atlantic.
Geographic Definitions: Prime Meridian vs Wunsch Line
The Prime Meridian is the zero-degree longitude line that serves as the global reference for geographic coordinate systems, passing through Greenwich, England. The Wunsch Line, by contrast, is a tectonic boundary within the Atlantic Ocean that separates different geological plates, specifically between the North American and Eurasian plates. While the Prime Meridian defines a standardized longitudinal position for navigation and mapping, the Wunsch Line represents a dynamic geological feature critical for understanding plate tectonics and oceanic crust formation.
Scientific Significance of Both Lines
The Prime Meridian, established at 0deg longitude, serves as the global reference point for timekeeping and navigation, enabling standardized geographic coordinate systems essential for cartography and GPS technology. The Wunsch Line, a scientifically derived boundary in the ocean, delineates distinct water masses and plays a crucial role in oceanographic studies by highlighting variations in temperature, salinity, and current patterns. Both lines facilitate precise scientific measurements, with the Prime Meridian underpinning terrestrial spatial orientation and the Wunsch Line enhancing understanding of marine environmental dynamics.
Role in Global Navigation and Mapping
The Prime Meridian at 0deg longitude serves as the primary reference line for global navigation and mapping, establishing the basis for time zones and geographic coordinate systems worldwide. The Wunsch Line, a more specialized and scientifically derived boundary in oceanography, plays a critical role in delineating water mass properties and circulation patterns rather than global positional referencing. Together, these lines contribute distinctly to the precision of cartographic representation and environmental data analysis in their respective domains.
Impact on Time Zones and Longitudinal Systems
The Prime Meridian, established at Greenwich, serves as the global reference point for longitudinal coordinates and the basis for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), standardizing time zones worldwide. In contrast, the Wunsch Line is a less recognized longitudinal demarcation, mainly used in specialized geophysical studies rather than global timekeeping. The adoption of the Prime Meridian facilitated international synchronization of time zones, while the Wunsch Line's impact remains limited to regional mapping and tectonic analysis.
Debates and Controversies Surrounding Their Adoption
The Prime Meridian, established at Greenwich in 1884, faced opposition from countries preferring other meridians such as Paris, reflecting geopolitical rivalries and scientific disagreements. The Wunsch Line, proposed as an alternative boundary for time zones or navigation, sparked debates over its practicality and global acceptance due to differing national interests and technological constraints. Controversies surrounding their adoption highlight the complexities of standardizing global navigation and timekeeping systems amid diverse political and cultural priorities.
Modern Applications in Geoscience and Climate Studies
The Prime Meridian, established at Greenwich, serves as the global standard for longitudinal reference, essential in satellite navigation, geospatial mapping, and climate modeling. In contrast, the Wunsch Line, identifying a major oceanographic boundary in the Southern Ocean, is vital for understanding ocean circulation patterns and their impact on global heat distribution and carbon cycling. Modern geoscience leverages these distinct but complementary references to improve accuracy in climate simulations and enhance predictions of environmental changes.
Conclusion: Comparing the Legacy and Utility
The Prime Meridian serves as the globally recognized zero-degree longitude line, establishing a standardized framework for navigation, timekeeping, and international coordination. The Wunsch Line, while valuable for particular geospatial analyses and regional mapping applications, lacks the universal acceptance and historical significance of the Prime Meridian. Evaluating their legacy and utility highlights the Prime Meridian's enduring role in global geography contrasted with the Wunsch Line's specialized, context-driven usage.
Prime Meridian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com