Centrifugal force is an apparent force experienced in a rotating reference frame, acting outwardly away from the center of rotation. It plays a crucial role in the dynamics of rotating systems such as centrifuges, vehicle turns, and amusement park rides. Discover how understanding centrifugal force can enhance your grasp of motion and stability in various applications by reading the full article.
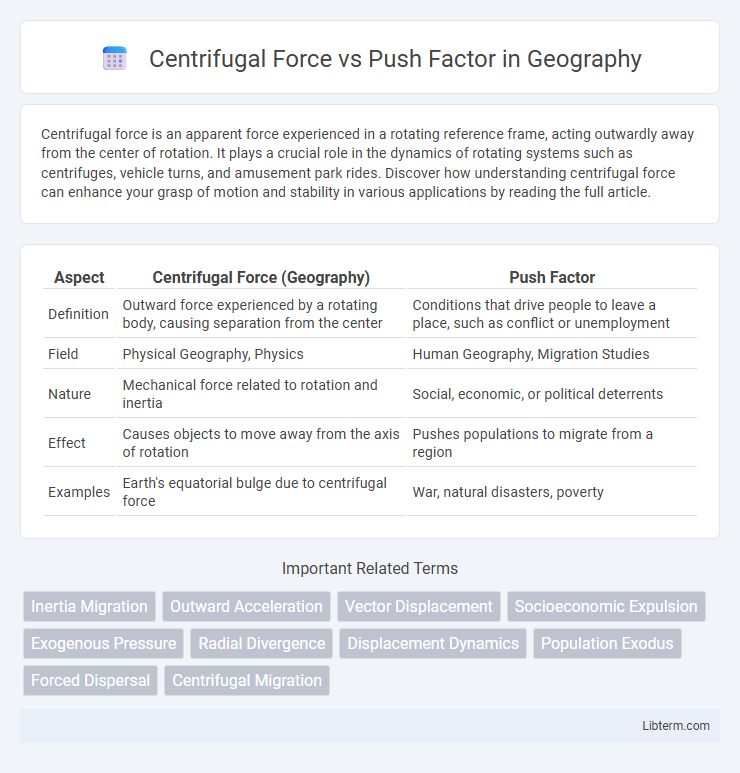
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Centrifugal Force (Geography) | Push Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outward force experienced by a rotating body, causing separation from the center | Conditions that drive people to leave a place, such as conflict or unemployment |
| Field | Physical Geography, Physics | Human Geography, Migration Studies |
| Nature | Mechanical force related to rotation and inertia | Social, economic, or political deterrents |
| Effect | Causes objects to move away from the axis of rotation | Pushes populations to migrate from a region |
| Examples | Earth's equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force | War, natural disasters, poverty |
Introduction to Centrifugal Force and Push Factor
Centrifugal force refers to the apparent outward force experienced by an object moving in a circular path, driving it away from the center of rotation. Push factors are conditions or circumstances that compel individuals or groups to leave their current location, often including economic hardship, political instability, or environmental challenges. Understanding centrifugal force in a physical context helps illustrate the concept of push factors as forces that push populations away from their origin.
Defining Centrifugal Force: Key Concepts
Centrifugal force refers to the apparent force that acts outward on a body moving around a center, arising from the body's inertia. It plays a crucial role in understanding dynamics in rotating systems, where it balances the centripetal force directed toward the center. Unlike push factors in migration studies, which represent external pressures driving people to move, centrifugal force is a physical concept explaining motion and equilibrium in circular movement.
Understanding Push Factor: Meaning and Context
Push factors refer to adverse conditions or negative influences that compel individuals to leave their current location, such as unemployment, political instability, or natural disasters. These factors create pressure to migrate or move away, contrasting with centrifugal forces which function broadly to disperse or separate groups within a society or region. Understanding push factors is crucial in migration studies as they directly drive people to seek better opportunities or safer environments elsewhere.
Physics Behind Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is an apparent force experienced in a rotating reference frame, directed outward from the axis of rotation, caused by inertia resisting the centripetal acceleration. This pseudo force arises because an object moving in a circular path tends to move in a straight line due to Newton's first law, creating the sensation of being pushed outward. In contrast, push factors in social sciences refer to conditions driving individuals away from a location, which are unrelated to the physical principles underlying centrifugal force.
Push Factors in Social and Economic Contexts
Push factors in social and economic contexts drive individuals to migrate due to adverse conditions such as unemployment, poverty, political instability, and lack of access to education or healthcare. These negative influences compel populations to leave their origin areas in search of better opportunities and improved living standards. Understanding push factors is crucial for policymakers addressing migration patterns and designing interventions to mitigate root causes.
Comparing Centrifugal Force and Push Factor
Centrifugal force in physics refers to the apparent force that pushes an object moving in a circular path away from the center of rotation, caused by inertia. Push factors, in contrast, are sociological drivers such as economic hardship or political instability that compel individuals to leave their current location. While centrifugal force is a physical phenomenon explained by Newtonian mechanics, push factors describe underlying reasons in human migration patterns.
Real-World Applications of Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force plays a crucial role in various real-world applications, such as in centrifuges used for separating substances of different densities in medical laboratories and industrial processes. It is also essential in automotive engineering, particularly in designing curved roadways and turning vehicles where the outward force affects vehicle stability and passenger safety. Furthermore, centrifugal force is applied in amusement park rides, like spinning rides and roller coasters, creating thrilling experiences by simulating outward forces on riders.
Examples of Push Factors in Migration and Sociology
Examples of push factors in migration and sociology include economic hardship, political instability, and environmental disasters. These forces drive individuals to leave their home regions in search of better opportunities, safety, and living conditions. Centrifugal forces, such as ethnic conflicts or social fragmentation, further exacerbate migration by weakening community cohesion and increasing the desire to relocate.
Misconceptions Between Centrifugal Force and Push Factor
Centrifugal force is a perceived force that acts outward on a body moving in a circular path, often misinterpreted as a real force rather than a fictitious force arising from an accelerating reference frame. Push factors, in migration studies, refer to negative conditions that drive individuals to leave their home regions, such as economic hardship or political instability. Confusion arises when centrifugal force, a physics concept, is mistakenly equated with push factors in social sciences, though they belong to entirely different contexts and disciplines.
Conclusion: Distinguishing Force from Factor
Centrifugal force is a physical phenomenon experienced in rotating reference frames, characterized by an apparent outward force acting on objects, whereas push factors refer to socioeconomic or environmental conditions that drive individuals or populations to migrate. Understanding the distinction is crucial: centrifugal force belongs strictly to physics and mechanics, while push factors are components of human behavioral and geographic studies. Clear differentiation enhances interdisciplinary clarity and prevents conflation of physical forces with motivational causes.
Centrifugal Force Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com