A plateau is an elevated flatland that rises sharply above the surrounding area, often formed by volcanic activity or erosion. These geographical features influence climate, vegetation, and human settlement patterns in significant ways. Explore the rest of the article to understand how plateaus impact your environment and lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
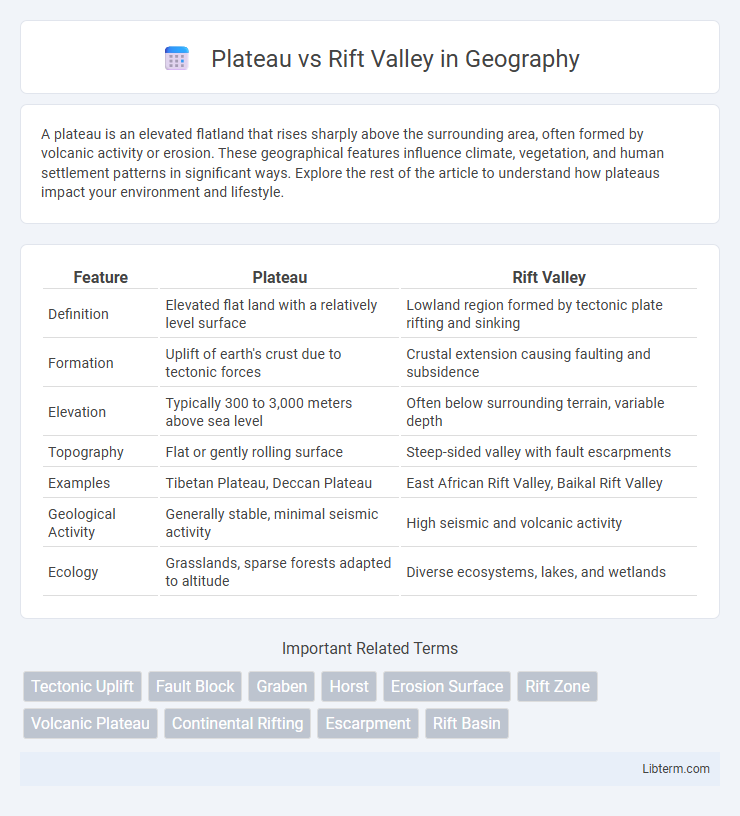
| Feature | Plateau | Rift Valley |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated flat land with a relatively level surface | Lowland region formed by tectonic plate rifting and sinking |
| Formation | Uplift of earth's crust due to tectonic forces | Crustal extension causing faulting and subsidence |
| Elevation | Typically 300 to 3,000 meters above sea level | Often below surrounding terrain, variable depth |
| Topography | Flat or gently rolling surface | Steep-sided valley with fault escarpments |
| Examples | Tibetan Plateau, Deccan Plateau | East African Rift Valley, Baikal Rift Valley |
| Geological Activity | Generally stable, minimal seismic activity | High seismic and volcanic activity |
| Ecology | Grasslands, sparse forests adapted to altitude | Diverse ecosystems, lakes, and wetlands |
Introduction to Plateaus and Rift Valleys
Plateaus are elevated flatlands formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity, characterized by relatively stable surfaces and significant altitude above sea level. Rift valleys occur where tectonic plates diverge, creating long, deep depressions bordered by fault lines and often associated with seismic activity. Both landforms result from distinct geological processes that shape the Earth's crust, influencing regional ecosystems and human settlement patterns.
Defining a Plateau
A plateau is a flat or gently sloping elevated landform that rises sharply above the surrounding area, often formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity. Unlike a rift valley, which is a low-lying region created by the divergence of tectonic plates causing the Earth's crust to thin and sink, a plateau maintains a high elevation and extensive flat surfaces. Plateaus are commonly composed of sedimentary rock layers and can cover large geographic areas, supporting diverse ecosystems and human settlements.
Defining a Rift Valley
A rift valley is a linear-shaped lowland between highlands or mountain ranges created by tectonic plate movements pulling apart the Earth's crust, often accompanied by volcanic activity and earthquakes. Unlike plateaus, which are elevated flatlands formed through uplift or volcanic processes, rift valleys represent areas of crustal extension and subsidence. The East African Rift Valley exemplifies this geological phenomenon, characterized by deep valleys flanked by steep escarpments.
Geological Formation of Plateaus
Plateaus form mainly through volcanic activity, tectonic uplift, or the erosion of surrounding land, resulting in elevated flat regions with steep sides. Unlike rift valleys, which are created by tectonic plates pulling apart and causing land to sink, plateaus emerge from the upward movement of the Earth's crust or accumulation of lava flows. Geological formations such as the Deccan Plateau in India exemplify volcanic origin, while the Colorado Plateau in the USA showcases uplift processes.
Geological Formation of Rift Valleys
Rift valleys form through the process of tectonic plate divergence where the Earth's lithosphere is pulled apart, causing the crust to thin and create a deep valley bordered by fault lines. The geological formation involves extensional forces that lead to subsidence and volcanic activity, often resulting in elongated depressions filled with sediment and water. Unlike plateaus, which are elevated flatlands formed by uplifting or volcanic activity, rift valleys signify zones of crustal instability and active geological transformation.
Key Differences Between Plateaus and Rift Valleys
Plateaus are elevated flat terrains that cover extensive areas with relatively uniform height, often formed by volcanic activity or uplift of the earth's crust. Rift valleys are elongated depressions formed by tectonic plates pulling apart, characterized by steep sides and a linear trench-like shape. While plateaus exhibit broad, flat surfaces at high elevations, rift valleys are notable for their deep, narrow, and often tectonically active valleys.
Global Examples of Major Plateaus
Major plateaus such as the Tibetan Plateau in Asia, the Colorado Plateau in North America, and the Altiplano in South America exemplify the diverse geological formations found worldwide. These elevated flat regions contrast sharply with rift valleys like the East African Rift Valley, which are characterized by significant tectonic activity and crustal extension. Understanding the global distribution of plateaus highlights their formation through processes like uplift and volcanic activity, distinguishing them from the subsidence and faulting typical of rift valleys.
Notable Rift Valleys Around the World
Notable rift valleys around the world include the East African Rift Valley, which stretches over 3,000 kilometers across Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tanzania, showcasing active tectonic plate divergence. The Baikal Rift Valley in Siberia is the world's deepest continental rift, featuring Lake Baikal, the oldest and deepest freshwater lake. The Rio Grande Rift in North America extends from Colorado to Mexico, representing a significant geological feature formed by crustal extension.
Ecological and Economic Importance
Plateaus support diverse ecosystems with unique flora and fauna adapted to elevated environments, contributing to biodiversity conservation and providing grazing lands essential for livestock economies. Rift Valleys, characterized by fertile soils and abundant water sources from freshwater lakes and rivers, enhance agricultural productivity and support fishing industries crucial for local livelihoods. Both landforms play vital roles in sustaining ecological balance and underpinning economic activities such as agriculture, tourism, and natural resource extraction.
Conclusion: Plateau vs Rift Valley Comparison
Plateaus and Rift Valleys represent distinct geological landforms shaped by tectonic activities; plateaus are elevated flat terrains formed primarily through volcanic or tectonic uplifts, while rift valleys are elongated lowlands created by the diverging movement of tectonic plates. The East African Rift Valley exemplifies active rifting characterized by seismic activity and volcanic formations, contrasting with the stable, expansive Deccan Plateau known for its basaltic composition and minimal seismic disturbances. Understanding these differences is crucial for geological studies, ecosystem diversity, and resource management in regions dominated by either plateaus or rift valleys.
Plateau Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com