Naturopathy emphasizes natural healing methods such as herbal medicine, nutrition, and lifestyle changes to support your body's inherent ability to heal itself. This holistic approach focuses on treating the root cause of illness rather than just alleviating symptoms, promoting overall well-being. Explore the rest of the article to discover how naturopathy can enhance your health naturally.
Table of Comparison
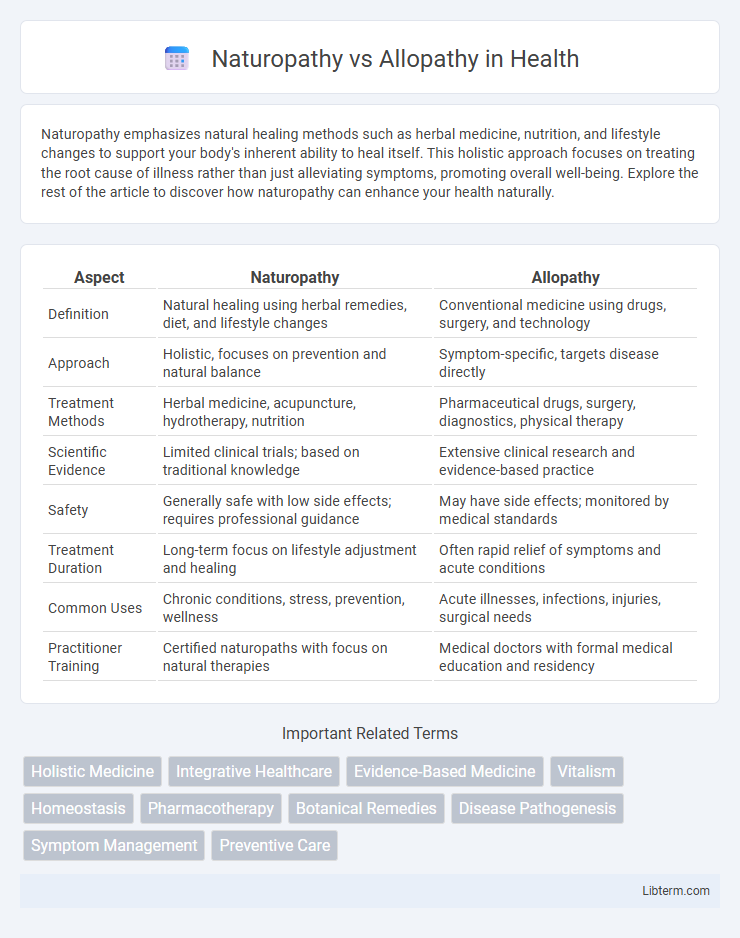
| Aspect | Naturopathy | Allopathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural healing using herbal remedies, diet, and lifestyle changes | Conventional medicine using drugs, surgery, and technology |
| Approach | Holistic, focuses on prevention and natural balance | Symptom-specific, targets disease directly |
| Treatment Methods | Herbal medicine, acupuncture, hydrotherapy, nutrition | Pharmaceutical drugs, surgery, diagnostics, physical therapy |
| Scientific Evidence | Limited clinical trials; based on traditional knowledge | Extensive clinical research and evidence-based practice |
| Safety | Generally safe with low side effects; requires professional guidance | May have side effects; monitored by medical standards |
| Treatment Duration | Long-term focus on lifestyle adjustment and healing | Often rapid relief of symptoms and acute conditions |
| Common Uses | Chronic conditions, stress, prevention, wellness | Acute illnesses, infections, injuries, surgical needs |
| Practitioner Training | Certified naturopaths with focus on natural therapies | Medical doctors with formal medical education and residency |
Introduction to Naturopathy and Allopathy
Naturopathy emphasizes natural healing methods such as herbal medicine, nutrition, and lifestyle changes to promote the body's inherent ability to heal itself, rooted in holistic care and preventive practices. Allopathy, also known as conventional medicine, relies on pharmacological treatments, surgery, and evidence-based interventions to diagnose and treat specific diseases or symptoms. Both systems aim to improve health outcomes but differ fundamentally in approach, with naturopathy focusing on treating the root cause through natural therapies, while allopathy targets symptom management and acute medical conditions.
Historical Origins and Development
Naturopathy originated in the late 19th century, rooted in European natural healing traditions emphasizing diet, exercise, and herbal remedies, with figures like Benedict Lust pioneering its development in the United States. Allopathy, or modern Western medicine, traces its origins to ancient Greek practices and was systematized in the 19th century through scientific advances, clinical research, and pharmaceutical development. The evolution of allopathy focused on evidence-based interventions and technological innovations, contrasting with naturopathy's holistic and preventive approach.
Core Philosophies and Principles
Naturopathy emphasizes holistic healing, prioritizing the body's innate ability to self-repair through natural therapies such as nutrition, herbal medicine, and lifestyle changes. Allopathy, or conventional medicine, relies on evidence-based interventions including pharmaceuticals and surgery to directly target and eliminate symptoms or underlying disease processes. Naturopathy advocates prevention and root cause treatment, whereas allopathy focuses on acute care and symptom management.
Diagnostic Approaches
Naturopathy emphasizes holistic diagnostic approaches such as detailed patient history, physical examinations, and assessment of lifestyle factors to identify root causes of illness. Allopathy relies heavily on advanced diagnostic tools including blood tests, imaging technologies like MRI and CT scans, and biochemical analyses to detect specific disease markers. While naturopathy focuses on wellness and prevention through natural methods, allopathy prioritizes symptom management and targeted medical interventions based on standardized diagnostic protocols.
Treatment Methods and Modalities
Naturopathy emphasizes natural treatment methods such as herbal medicine, acupuncture, nutrition, and hydrotherapy to stimulate the body's self-healing processes, focusing on holistic and preventive care. Allopathy relies on pharmaceutical drugs, surgery, and other conventional medical interventions aimed at directly targeting symptoms and diseases for rapid relief and control. Both modalities offer distinct approaches, with naturopathy prioritizing non-invasive, natural therapies and allopathy focusing on evidence-based conventional treatments.
Effectiveness and Evidence-Based Outcomes
Naturopathy emphasizes holistic treatments using natural remedies and lifestyle changes, with varying levels of scientific support depending on the condition treated. Allopathy, or conventional medicine, relies heavily on evidence-based protocols and clinical trials to ensure effectiveness and safety in disease management. Comparative studies often show allopathy delivers more consistent outcomes in acute and critical care, while naturopathy may provide complementary benefits in chronic disease prevention and wellness maintenance.
Common Conditions Treated
Naturopathy commonly addresses chronic conditions such as allergies, digestive disorders, and stress-related illnesses through natural therapies like herbal medicine and lifestyle counseling. Allopathy primarily treats acute and severe conditions including infections, injuries, and chronic diseases with pharmaceuticals and surgical interventions. Both approaches overlap in managing common ailments like hypertension, diabetes, and arthritis, but differ significantly in treatment methodologies and emphasis on holistic care.
Safety, Risks, and Side Effects
Naturopathy emphasizes natural remedies and minimal invasive techniques, often resulting in fewer side effects but carries risks if used as a sole treatment for serious conditions. Allopathy relies on scientifically tested drugs and surgical procedures, which provide rapid symptom relief but may involve significant side effects and potential drug interactions. Safety in both approaches depends on accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment selection, and professional supervision to minimize adverse effects and health risks.
Patient Experience and Accessibility
Naturopathy offers patients a holistic, personalized approach emphasizing natural remedies and lifestyle changes, often resulting in a more participatory and educational experience. Allopathy provides rapid symptom relief through standardized medical treatments, ensuring wide accessibility in hospitals and clinics globally. While allopathic care is typically covered by insurance and more widely available, naturopathy can face accessibility challenges due to variable practitioner availability and limited insurance support.
Integrative Approaches and Future Trends
Integrative approaches in healthcare combine naturopathy's emphasis on holistic, natural therapies with allopathy's reliance on evidence-based medical treatments to enhance patient outcomes and reduce side effects. Emerging trends include personalized medicine, where genetic and lifestyle data tailor integrative protocols, and increased research into combining herbal remedies with conventional drugs for chronic disease management. Future advancements focus on digital health technologies facilitating patient monitoring and the growing acceptance of integrative models within mainstream healthcare systems worldwide.
Naturopathy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com