Lipolysis is the metabolic process that breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, providing energy for the body. Understanding how lipolysis works can enhance your approach to weight management and metabolic health. Explore the detailed mechanisms and benefits of lipolysis in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
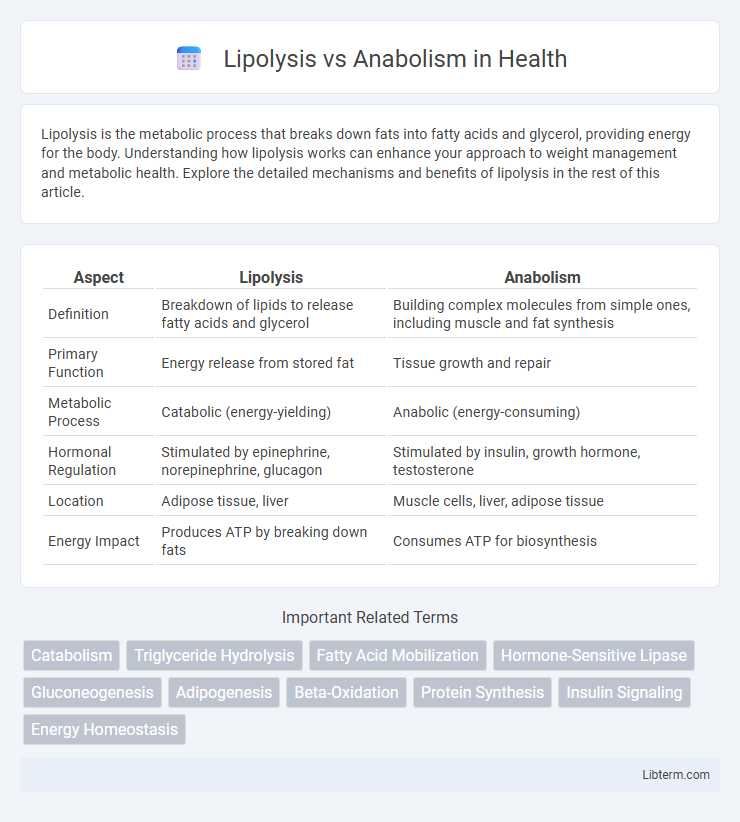
| Aspect | Lipolysis | Anabolism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breakdown of lipids to release fatty acids and glycerol | Building complex molecules from simple ones, including muscle and fat synthesis |
| Primary Function | Energy release from stored fat | Tissue growth and repair |
| Metabolic Process | Catabolic (energy-yielding) | Anabolic (energy-consuming) |
| Hormonal Regulation | Stimulated by epinephrine, norepinephrine, glucagon | Stimulated by insulin, growth hormone, testosterone |
| Location | Adipose tissue, liver | Muscle cells, liver, adipose tissue |
| Energy Impact | Produces ATP by breaking down fats | Consumes ATP for biosynthesis |
Understanding Lipolysis: The Fat Breakdown Process
Lipolysis is the metabolic process where triglycerides stored in fat cells are broken down into glycerol and free fatty acids, providing energy for the body during periods of fasting or exercise. Hormones such as adrenaline and glucagon activate enzymes like hormone-sensitive lipase, which catalyze the breakdown of fat stores. Understanding lipolysis is crucial for optimizing fat loss strategies and managing energy balance in metabolic health.
Exploring Anabolism: Building Up the Body
Anabolism is the metabolic process responsible for synthesizing complex molecules from simpler ones, crucial for muscle growth, tissue repair, and energy storage. This process involves the formation of proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, supporting cellular regeneration and overall body development. Enhancing anabolic pathways through nutrition and resistance training promotes increased muscle mass and improved metabolic health.
Key Differences Between Lipolysis and Anabolism
Lipolysis is the metabolic process that breaks down triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids to release energy, while anabolism refers to the synthesis of complex molecules like lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids from simpler ones, supporting growth and repair. Lipolysis primarily occurs in adipose tissue and liver cells during energy demand, whereas anabolism occurs in nearly all cells during periods of nutrient abundance to build cellular structures. The key difference lies in their roles: lipolysis is catabolic and energy-releasing, whereas anabolism is biosynthetic and energy-consuming.
Hormonal Regulation: Lipolysis vs. Anabolic Pathways
Hormonal regulation of lipolysis primarily involves catecholamines like adrenaline and noradrenaline, which activate hormone-sensitive lipase to break down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol. Insulin plays a crucial role in anabolic pathways by promoting glucose uptake, glycogen synthesis, and lipid storage through activating lipoprotein lipase and inhibiting lipolysis. Glucagon and cortisol favor catabolic processes by stimulating lipolysis and gluconeogenesis, balancing energy homeostasis during fasting and stress.
Impact on Energy Balance and Metabolism
Lipolysis breaks down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol, providing a vital energy source during fasting or exercise by increasing fatty acid availability for beta-oxidation. Anabolism, conversely, consumes energy to synthesize macromolecules like lipids and proteins, supporting tissue growth and repair while storing excess nutrients. The dynamic balance between lipolysis and anabolism regulates overall energy homeostasis and metabolic rate, influencing body weight maintenance and metabolic health.
Role in Weight Loss and Muscle Gain
Lipolysis plays a critical role in weight loss by breaking down stored triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol, which the body uses for energy, facilitating fat reduction. Anabolism supports muscle gain by synthesizing proteins and building cellular structures, increasing muscle mass and strength. Efficient weight management and muscle growth depend on balancing lipolytic activity for fat loss and anabolic processes for tissue repair and growth.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Influences
Lipolysis, the metabolic process of breaking down stored fats into free fatty acids for energy, is significantly influenced by nutritional intake such as low-carbohydrate diets and intermittent fasting, which promote fat mobilization. In contrast, anabolism, the synthesis of complex molecules like muscle proteins and lipids, is stimulated by nutrient-rich diets high in protein and carbohydrates, along with regular resistance training that enhances muscle growth and repair. Lifestyle factors including sleep quality, stress management, and physical activity levels critically regulate the balance between lipolysis and anabolism, thereby affecting body composition and metabolic health.
Exercise Effects: Cardio vs. Resistance Training
Cardio primarily stimulates lipolysis by increasing the breakdown of triglycerides into free fatty acids for energy, promoting fat loss and improved metabolic efficiency. Resistance training enhances anabolism by triggering muscle protein synthesis and promoting muscle hypertrophy, leading to increased lean muscle mass and resting metabolic rate. Combining both exercise types maximizes fat reduction and muscle growth, optimizing overall body composition and metabolic health.
Health Implications of Lipolytic and Anabolic States
Lipolysis involves the breakdown of fats into fatty acids, enabling energy release during fasting or exercise, whereas anabolism focuses on building and storing molecules like proteins and fats for growth and repair. A lipolytic state enhances fat burning and improves insulin sensitivity, reducing risks of obesity and type 2 diabetes, while an anabolic state supports muscle growth and tissue regeneration but may contribute to fat accumulation if energy intake exceeds expenditure. Balancing lipolysis and anabolism is crucial for metabolic health, weight management, and preventing chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases.
Optimizing Lipolysis and Anabolism for Fitness Goals
Optimizing lipolysis involves enhancing the breakdown of stored fats into free fatty acids for energy, which can be achieved through high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and maintaining a calorie deficit. Anabolism focuses on muscle growth and repair by promoting protein synthesis through resistance training and sufficient dietary protein intake, particularly branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs). Balancing lipolysis and anabolism effectively improves body composition by reducing fat mass while increasing lean muscle, essential for achieving optimal fitness goals.
Lipolysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com