Heart block occurs when the electrical signals that control your heartbeat are partially or completely blocked, disrupting the normal rhythm. This condition can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and fainting, and may require medical intervention like a pacemaker. Explore the rest of the article to understand the types, causes, and treatment options for heart block.
Table of Comparison
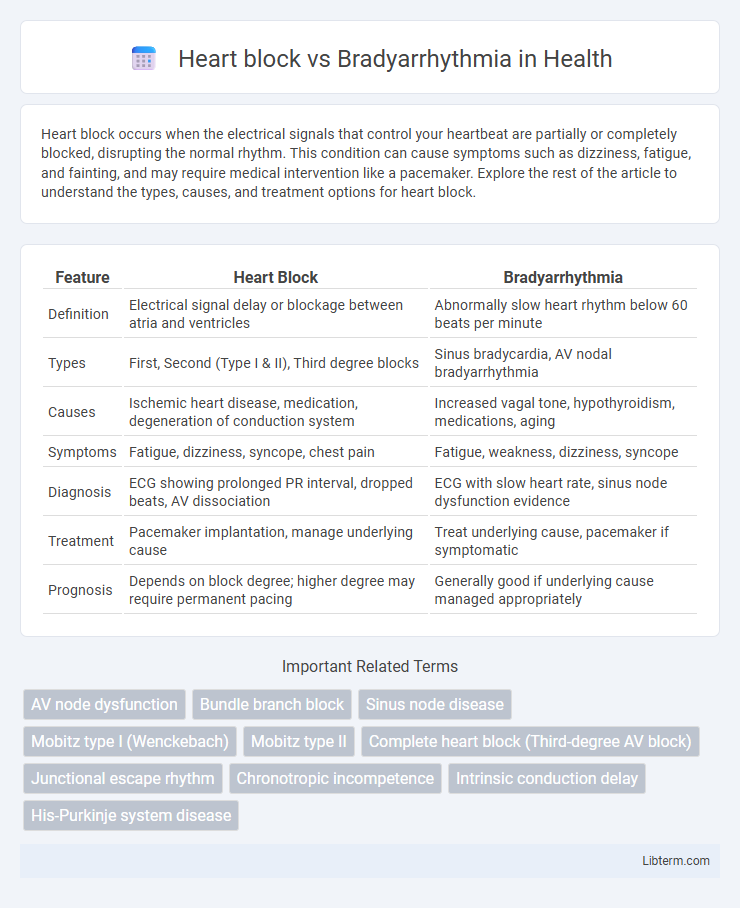
| Feature | Heart Block | Bradyarrhythmia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electrical signal delay or blockage between atria and ventricles | Abnormally slow heart rhythm below 60 beats per minute |
| Types | First, Second (Type I & II), Third degree blocks | Sinus bradycardia, AV nodal bradyarrhythmia |
| Causes | Ischemic heart disease, medication, degeneration of conduction system | Increased vagal tone, hypothyroidism, medications, aging |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, dizziness, syncope, chest pain | Fatigue, weakness, dizziness, syncope |
| Diagnosis | ECG showing prolonged PR interval, dropped beats, AV dissociation | ECG with slow heart rate, sinus node dysfunction evidence |
| Treatment | Pacemaker implantation, manage underlying cause | Treat underlying cause, pacemaker if symptomatic |
| Prognosis | Depends on block degree; higher degree may require permanent pacing | Generally good if underlying cause managed appropriately |
Understanding Heart Block: Definition and Types
Heart block is a cardiac conduction disorder characterized by delayed or interrupted electrical signals between the atria and ventricles, resulting in abnormal heart rhythms. There are three main types: first-degree heart block, where signals are slowed but still reach the ventricles; second-degree heart block, which involves intermittent failure of signal conduction; and third-degree heart block, where no signals pass from the atria to the ventricles, causing complete dissociation. Differentiating heart block from bradyarrhythmia, which is a slow heart rhythm often caused by sinus node dysfunction or other conditions, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What is Bradyarrhythmia? Key Features
Bradyarrhythmia is a cardiac rhythm disorder characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate, typically less than 60 beats per minute, caused by impaired electrical conduction in the sinoatrial node or atrioventricular node. Key features include symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, syncope, and possible heart failure due to inefficient cardiac output. Unlike heart block, which specifically refers to impaired conduction between the atria and ventricles, bradyarrhythmia encompasses a broader range of slow heart rhythms including sinus bradycardia and junctional rhythms.
Heart Block vs Bradyarrhythmia: Core Differences
Heart block is a condition characterized by impaired electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles, resulting in delayed or blocked signals, while bradyarrhythmia refers to any slow heart rhythm typically below 60 beats per minute. The core difference lies in the origin of the conduction delay; heart block specifically involves AV node or His-Purkinje system dysfunction, whereas bradyarrhythmia can arise from sinus node dysfunction or other pacemaker abnormalities. Diagnostic tools such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) differentiate these conditions by revealing distinctive patterns like PR interval prolongation in heart block or sinus pauses and slow rates in bradyarrhythmias.
Causes and Risk Factors: Heart Block vs Bradyarrhythmia
Heart block is primarily caused by damage to the heart's electrical conduction system due to conditions like ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, or degenerative fibrosis, while bradyarrhythmia results from dysfunction in the sinus node or atrioventricular node often linked to aging, electrolyte imbalances, or medication effects such as beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers. Risk factors for heart block include coronary artery disease, previous heart surgery, and autoimmune diseases, whereas bradyarrhythmia is commonly associated with hypothyroidism, sleep apnea, and increased vagal tone. Both conditions share overlapping risk elements like underlying cardiac pathology and electrolyte disturbances but differ fundamentally in their pathophysiological mechanisms affecting heart rate regulation.
Symptoms Comparison: Heart Block and Bradyarrhythmia
Heart block symptoms often include fatigue, dizziness, syncope, and palpitations due to impaired electrical conduction between atria and ventricles, varying by degree (first, second, or third-degree block). Bradyarrhythmia presents with similar symptoms such as weakness, chest pain, and exercise intolerance resulting from abnormally slow heart rhythms caused by sinus node dysfunction or atrioventricular conduction delays. Differentiating symptoms relies on clinical assessment and ECG findings showing distinct conduction abnormalities in heart block versus generalized slow heart rate in bradyarrhythmias.
Diagnostic Approaches for Both Conditions
Diagnostic approaches for heart block primarily include electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis, which identifies the type and severity by detecting delayed or blocked electrical signals between the atria and ventricles. Bradyarrhythmia diagnosis involves continuous cardiac monitoring, such as Holter monitoring or event recorders, to capture intermittent slow heart rates often missed on standard ECGs. Both conditions may require electrophysiological studies for precise localization and assessment of conduction system abnormalities.
Treatment Options: Heart Block vs Bradyarrhythmia
Treatment options for heart block primarily involve pacemaker implantation to regulate heart rhythm and prevent symptoms. Bradyarrhythmia management depends on the underlying cause and severity, with medications like atropine or temporary pacing used in acute cases and permanent pacemakers for persistent or symptomatic bradycardia. Both conditions require careful diagnosis and individualized therapy to restore adequate heart rate and improve cardiac output.
Prognosis and Outcomes
Heart block, particularly third-degree or complete heart block, often necessitates pacemaker implantation to prevent potentially fatal outcomes, while first-degree heart block usually has a benign prognosis. Bradyarrhythmias, including sinus bradycardia and junctional rhythms, generally have variable outcomes depending on underlying causes such as ischemic heart disease or medication effects. Long-term prognosis improves significantly with timely diagnosis and appropriate interventions, especially when reversible factors are addressed and device therapy is employed.
Prevention Strategies and Patient Education
Effective prevention strategies for heart block and bradyarrhythmia include controlling underlying risk factors such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, and electrolyte imbalances through medication adherence and lifestyle modification. Patient education should emphasize recognizing symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and syncope, while encouraging regular cardiac monitoring and timely medical consultations to manage arrhythmia progression. Understanding the importance of avoiding medications that may exacerbate conduction abnormalities also supports better clinical outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention for symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, chest pain, or severe shortness of breath, as these may indicate advanced heart block or bradyarrhythmia requiring urgent intervention. Persistent fatigue, unexplained palpitations, or episodes of near-syncope should prompt evaluation by a cardiologist to assess the need for diagnostic testing like ECG or Holter monitoring. Early medical assessment is critical to prevent complications like cardiac arrest or heart failure associated with untreated conduction abnormalities.
Heart block Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com