Palpitations are sensations of a rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeat that can be caused by stress, exercise, or underlying medical conditions such as arrhythmias. Understanding the triggers and symptoms of palpitations is crucial for identifying when to seek medical attention. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to manage and recognize the significance of your palpitations.
Table of Comparison
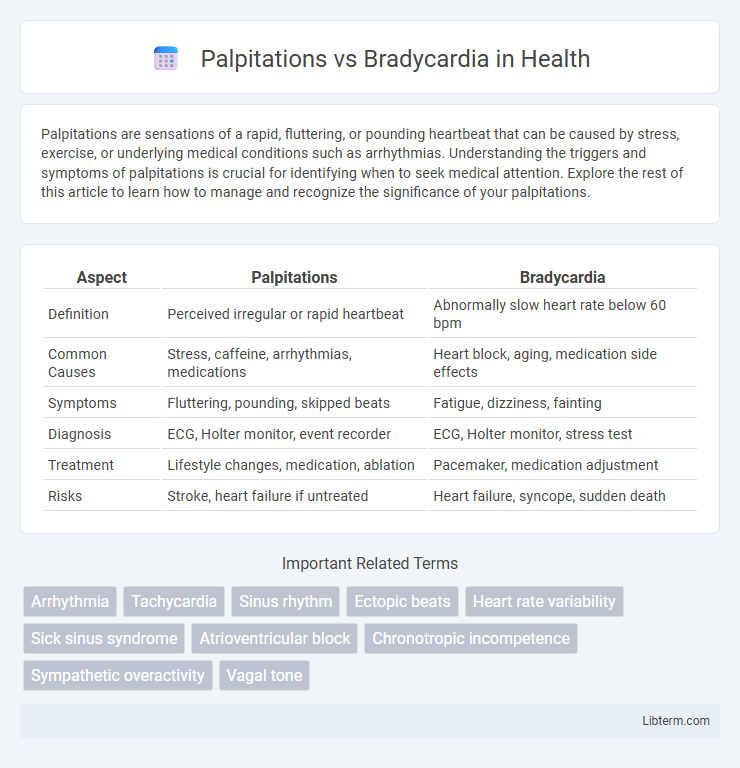
| Aspect | Palpitations | Bradycardia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Perceived irregular or rapid heartbeat | Abnormally slow heart rate below 60 bpm |
| Common Causes | Stress, caffeine, arrhythmias, medications | Heart block, aging, medication side effects |
| Symptoms | Fluttering, pounding, skipped beats | Fatigue, dizziness, fainting |
| Diagnosis | ECG, Holter monitor, event recorder | ECG, Holter monitor, stress test |
| Treatment | Lifestyle changes, medication, ablation | Pacemaker, medication adjustment |
| Risks | Stroke, heart failure if untreated | Heart failure, syncope, sudden death |
Introduction to Palpitations and Bradycardia
Palpitations refer to the sensation of rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeats often caused by stress, caffeine, or arrhythmias, signaling irregular heart rhythm. Bradycardia is characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute, potentially resulting from aging, heart tissue damage, or underlying medical conditions. Both conditions affect cardiac rhythm but differ significantly in their causes, symptoms, and clinical implications.
Defining Palpitations: Causes and Symptoms
Palpitations are sensations of rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeats often caused by stress, anxiety, excessive caffeine, or arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Common symptoms include irregular heartbeat, chest discomfort, dizziness, and a feeling of the heart skipping beats or racing. Unlike bradycardia, which is characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate below 60 beats per minute, palpitations reflect abnormal heart rhythm intensity or speed rather than a reduced pulse rate.
Understanding Bradycardia: Causes and Symptoms
Bradycardia is a slower-than-normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute, caused by factors such as aging, heart tissue damage, or underlying medical conditions like hypothyroidism and electrolyte imbalances. Symptoms often include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fainting spells due to insufficient blood flow to organs. Understanding these causes and manifestations helps differentiate bradycardia from palpitations, which involve a sensation of rapid or irregular heartbeat.
Key Differences Between Palpitations and Bradycardia
Palpitations are sensations of rapid, irregular, or forceful heartbeats often caused by stress, caffeine, or arrhythmias, while bradycardia refers to an abnormally slow heart rate below 60 beats per minute, frequently linked to aging, heart disease, or medications. Palpitations manifest as fluttering or pounding in the chest, signaling possible underlying cardiovascular conditions, whereas bradycardia may cause fatigue, dizziness, or fainting due to insufficient blood flow. Key differences include heart rate variation, symptom presentation, and underlying causes, which are critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Common Risk Factors for Palpitations and Bradycardia
Common risk factors for palpitations include stress, anxiety, caffeine consumption, and underlying heart conditions such as arrhythmias or valve disorders. Bradycardia risk factors often involve aging, hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalances, and medications like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers. Both conditions may be influenced by lifestyle factors and structural heart abnormalities impacting cardiac electrical activity.
Diagnostic Methods for Heart Rhythm Abnormalities
Electrocardiography (ECG) is the primary diagnostic tool for differentiating palpitations from bradycardia by recording heart rhythm abnormalities in real time. Holter monitors provide continuous ECG data over 24 to 48 hours, capturing intermittent arrhythmias that may not appear during a standard ECG. In selected cases, electrophysiological studies offer invasive mapping of cardiac electrical activity to precisely identify conduction defects causing bradycardia or symptomatic palpitations.
Treatment Options for Palpitations
Treatment options for palpitations include lifestyle modifications such as reducing caffeine and stress, as well as medical interventions like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to regulate heart rhythm. In cases related to arrhythmias, antiarrhythmic medications or catheter ablation may be recommended by cardiologists. Monitoring through Holter monitors or event recorders assists in tailoring treatment plans to address the underlying causes effectively.
Treatment Strategies for Bradycardia
Treatment strategies for bradycardia focus on underlying causes such as medication adjustments, management of metabolic disorders, or addressing heart conduction system abnormalities. In symptomatic cases, pacemaker implantation remains the definitive treatment to maintain adequate heart rate and prevent complications like syncope or heart failure. Continuous monitoring and tailored pharmacologic interventions, including atropine or isoproterenol, may be used transiently to stabilize patients before more permanent solutions are implemented.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for palpitations if they are accompanied by chest pain, dizziness, shortness of breath, or fainting, as these may indicate underlying heart conditions requiring urgent evaluation. In cases of bradycardia, medical assessment is critical if heart rates consistently fall below 60 beats per minute with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, confusion, or syncope, potentially signaling problems like heart block or sick sinus syndrome. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications such as heart failure, stroke, or cardiac arrest.
Preventive Tips and Lifestyle Modifications
Managing palpitations and bradycardia effectively involves regular cardiovascular monitoring and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle. Engaging in moderate aerobic exercise, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, and managing stress through mindfulness or yoga can help stabilize heart rhythm and prevent arrhythmias. Avoiding smoking, adhering to prescribed medications, and scheduling routine ECG evaluations are essential preventive measures to minimize complications linked to abnormal heart rates.
Palpitations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com