Idiopathic conditions are medical disorders with no identifiable cause despite thorough investigation, making diagnosis and treatment challenging. Understanding the nature of idiopathic diseases can help you better manage symptoms and explore targeted therapies. Discover more about idiopathic conditions and how they impact health in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
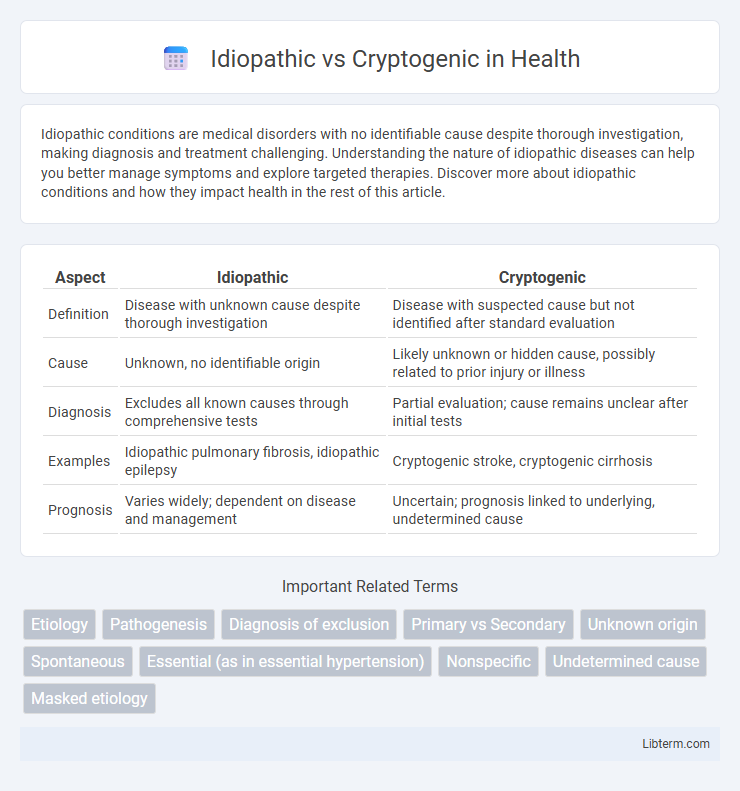
| Aspect | Idiopathic | Cryptogenic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disease with unknown cause despite thorough investigation | Disease with suspected cause but not identified after standard evaluation |
| Cause | Unknown, no identifiable origin | Likely unknown or hidden cause, possibly related to prior injury or illness |
| Diagnosis | Excludes all known causes through comprehensive tests | Partial evaluation; cause remains unclear after initial tests |
| Examples | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, idiopathic epilepsy | Cryptogenic stroke, cryptogenic cirrhosis |
| Prognosis | Varies widely; dependent on disease and management | Uncertain; prognosis linked to underlying, undetermined cause |
Understanding "Idiopathic" and "Cryptogenic": Definitions
Idiopathic refers to diseases or conditions with unknown causes despite thorough investigation, while cryptogenic denotes illnesses suspected to have hidden or unknown origins but with some identifiable features suggesting a specific etiology. Idiopathic conditions lack any identifiable underlying pathology, whereas cryptogenic cases imply an underlying cause remains undiagnosed after standard diagnostic testing. Understanding the nuances between idiopathic and cryptogenic helps guide clinical decision-making and research in unexplained medical disorders.
Origins of the Terms: Etymology and Historical Use
Idiopathic originates from the Greek words "idios," meaning "one's own," and "pathos," meaning "suffering," historically used in medicine to denote diseases with unknown causes intrinsic to the individual. Cryptogenic combines the Greek "kryptos," meaning "hidden," and "genesis," meaning "origin," describing conditions with concealed or obscure origins identified through clinical evaluation. Both terms emerged in the 19th and 20th centuries to classify diseases based on the knowledge gaps regarding their etiologies.
Key Differences Between Idiopathic and Cryptogenic
Idiopathic conditions arise without a known cause despite thorough investigation, whereas cryptogenic diseases have a suspected but unidentified origin based on limited clinical evidence. Idiopathic is a broader term often used when all known causes are ruled out, while cryptogenic implies an underlying cause that is currently hidden or undetectable. Diagnostic approaches for idiopathic disorders emphasize exclusion, whereas cryptogenic cases may require advanced testing to uncover elusive factors.
Common Medical Conditions Labeled as Idiopathic
Idiopathic conditions are medical disorders with unknown causes despite thorough investigation, commonly seen in diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, idiopathic epilepsy, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Cryptogenic conditions share a similar unknown origin but typically imply a suspected hidden or undetected cause, often applied to cryptogenic stroke or cryptogenic cirrhosis. Understanding the distinction aids clinicians in diagnostic approaches and tailoring treatment strategies for complex diseases with elusive etiologies.
Diseases Frequently Classified as Cryptogenic
Diseases frequently classified as cryptogenic include cryptogenic stroke, cryptogenic cirrhosis, and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, where the underlying cause remains unidentified despite extensive evaluation. Idiopathic diseases differ as they are characterized by unknown causes inherently, without suggesting a hidden or undiscovered origin. Accurate classification between idiopathic and cryptogenic conditions is crucial for guiding diagnostic strategies and tailored treatment plans.
Diagnostic Approaches: Identifying Idiopathic vs. Cryptogenic
Diagnostic approaches for distinguishing idiopathic from cryptogenic conditions largely depend on the extent of clinical investigation and the exclusion of identifiable causes. Idiopathic diagnoses arise after comprehensive testing fails to reveal an underlying etiology, while cryptogenic diagnoses indicate a suspected but unconfirmed cause despite targeted diagnostic tools such as imaging, serologic tests, and genetic screening. Advanced methodologies like next-generation sequencing and metabolic profiling increasingly aid in differentiating cryptogenic cases from truly idiopathic disorders by uncovering subtle or novel pathogenic factors.
Clinical Implications of Labeling a Condition Idiopathic or Cryptogenic
Labeling a condition as idiopathic implies an unknown cause despite extensive investigation, often guiding clinicians to focus on symptomatic management and ongoing research for potential etiology. Cryptogenic denotes a suspected but unproven origin, prompting targeted diagnostic reassessment and consideration of hidden pathologies or emerging diagnostic technologies. This distinction influences treatment decisions, prognosis estimations, and patient counseling by reflecting the certainty and scope of current medical knowledge.
Impact on Treatment Strategies
Idiopathic conditions lack a known cause, leading to treatment strategies that primarily focus on symptom management and supportive care. Cryptogenic diseases, suspected to have hidden etiologies, often prompt more extensive diagnostic evaluations to uncover underlying factors, enabling targeted therapies. Understanding the distinction influences clinical decisions, optimizing treatment efficacy by aligning interventions with the presumed pathogenesis.
Evolving Perspectives in Medical Research
Idiopathic conditions lack a known cause despite thorough investigation, while cryptogenic diseases have an unclear origin but show indirect evidence suggesting specific pathological mechanisms. Advances in medical research, including genomics and molecular diagnostics, are narrowing the gap between idiopathic and cryptogenic classifications by identifying previously undetectable biomarkers or genetic mutations. This evolving understanding enhances targeted therapies and personalized treatment strategies, transforming the approach to diseases once considered idiopathic or cryptogenic.
The Importance of Precise Terminology in Patient Care
Precise terminology in distinguishing idiopathic from cryptogenic conditions enhances diagnostic clarity by specifying whether a disease's origin is unknown or merely undetected after exhaustive evaluation. Accurate classification directly influences treatment decisions, risk stratification, and patient prognosis, ensuring tailored interventions and effective monitoring. Clear communication between healthcare providers and patients relies on these definitional distinctions to support informed consent and shared decision-making strategies.
Idiopathic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com