Urticaria, commonly known as hives, manifests as red, itchy welts on the skin caused by an allergic reaction or other triggers such as stress or infections. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options can help you manage and alleviate discomfort quickly. Discover more about how to identify and treat urticaria in the following article.
Table of Comparison
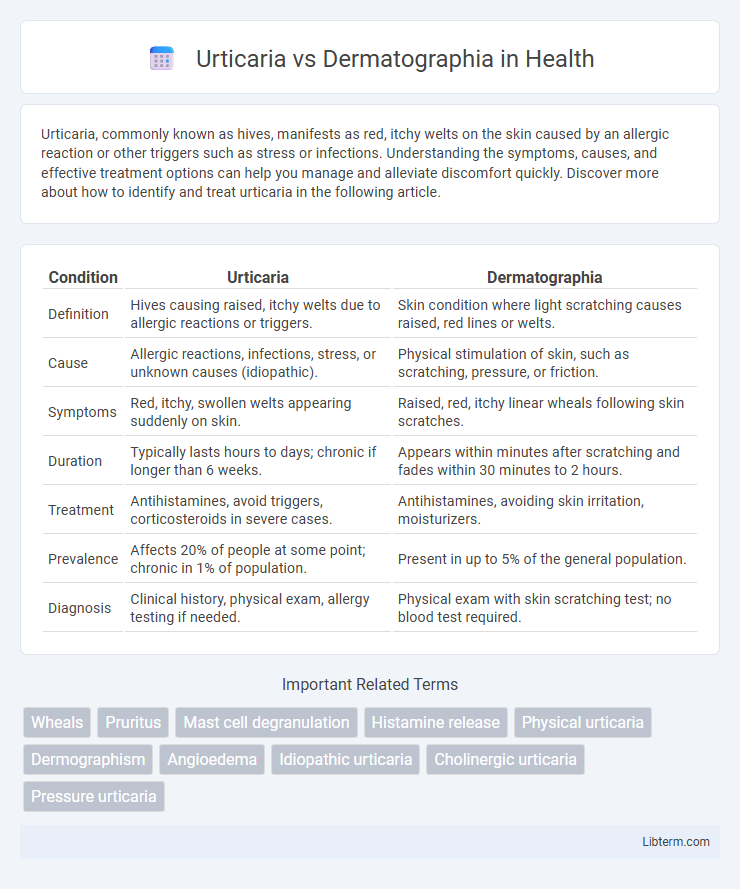
| Condition | Urticaria | Dermatographia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hives causing raised, itchy welts due to allergic reactions or triggers. | Skin condition where light scratching causes raised, red lines or welts. |
| Cause | Allergic reactions, infections, stress, or unknown causes (idiopathic). | Physical stimulation of skin, such as scratching, pressure, or friction. |
| Symptoms | Red, itchy, swollen welts appearing suddenly on skin. | Raised, red, itchy linear wheals following skin scratches. |
| Duration | Typically lasts hours to days; chronic if longer than 6 weeks. | Appears within minutes after scratching and fades within 30 minutes to 2 hours. |
| Treatment | Antihistamines, avoid triggers, corticosteroids in severe cases. | Antihistamines, avoiding skin irritation, moisturizers. |
| Prevalence | Affects 20% of people at some point; chronic in 1% of population. | Present in up to 5% of the general population. |
| Diagnosis | Clinical history, physical exam, allergy testing if needed. | Physical exam with skin scratching test; no blood test required. |
Understanding Urticaria: Definition and Causes
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts caused by the release of histamine and other chemicals in response to allergens, stress, infections, or medications. It results from an immune system reaction that triggers the dilation of blood vessels and fluid leakage into the skin, leading to swelling and irritation. Understanding the difference from dermatographia, which specifically involves skin writing caused by physical pressure, highlights the diverse triggers and mechanisms behind urticaria.
What Is Dermatographia? Key Facts
Dermatographia, also known as skin writing, is a common form of physical urticaria characterized by raised, red welts that develop after the skin is scratched or rubbed. It affects approximately 5% of the population and is triggered by minor physical pressure, resulting in an exaggerated histamine response. Unlike general urticaria, which can be caused by allergies or infections, dermatographia specifically involves hypersensitivity to mechanical stimuli on the skin.
Symptoms Comparison: Urticaria vs Dermatographia
Urticaria presents with widespread, itchy, raised welts that vary in size and shape, often appearing rapidly and fading within 24 hours. Dermatographia is characterized by localized, linear wheals or red lines triggered by minor skin trauma or scratching, usually lasting 30 minutes to an hour. Both conditions cause itching and skin swelling, but urticaria's lesions are more transient and widespread, while dermatographia exhibits persistent, pattern-specific skin markings.
Triggers: Identifying What Sets Each Condition Off
Urticaria, commonly triggered by allergens such as foods, medications, infections, or insect bites, involves immune system responses that release histamines causing hives and itching. Dermatographia, also known as "skin writing," is primarily triggered by physical stimuli like scratching, pressure, or friction, leading to raised, red lines on the skin without an allergic basis. Understanding these distinct triggers is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment of each condition.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Distinguish Urticaria and Dermatographia
Doctors distinguish urticaria from dermatographia primarily through clinical evaluation and patient history, noting that urticaria involves spontaneous wheals triggered by allergens or physical stimuli, while dermatographia manifests as wheals triggered specifically by mechanical pressure or scratching. Diagnostic tests include the application of a blunt object to the skin to elicit dermatographia's characteristic linear wheals, whereas urticaria may require allergy testing or blood work to identify underlying causes. Skin biopsy is rarely needed but can assist in distinguishing chronic urticaria from other dermatologic conditions when diagnosis is uncertain.
Treatment Options for Urticaria
Treatment options for urticaria primarily include non-sedating antihistamines such as cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine to reduce histamine-induced itching and swelling. For chronic or refractory cases, leukotriene receptor antagonists, corticosteroids, or omalizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IgE, may be prescribed to control symptoms. Avoidance of known triggers and maintaining a symptom diary can help optimize management and prevent flare-ups.
Treatment Approaches for Dermatographia
Treatment approaches for dermatographia primarily involve the use of antihistamines such as cetirizine or loratadine to reduce histamine release and alleviate symptoms. Avoiding skin trauma and irritants is crucial to prevent flare-ups, alongside applying soothing topical agents like calamine lotion. In more severe cases, doctors may recommend stronger medications such as leukotriene receptor antagonists or corticosteroids to manage inflammation and itching.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Both Conditions
Maintaining a cool environment and wearing loose, breathable clothing helps reduce flare-ups in both urticaria and dermatographia by minimizing skin irritation. Avoiding known triggers such as stress, allergens, and harsh soaps can significantly decrease symptom severity and frequency. Regular moisturizing with fragrance-free lotions supports the skin barrier, preventing dryness and itching associated with these conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for urticaria when hives persist for more than six weeks, are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or severe pain, as these symptoms may indicate a serious allergic reaction or an underlying condition. In dermatographia, consult a healthcare provider if skin markings worsen, become painful, or if swelling spreads rapidly, which could suggest an infection or a more complex dermatological issue. Prompt evaluation by a dermatologist or allergist is essential to determine appropriate treatment and prevent complications in both conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions: Urticaria vs Dermatographia
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is characterized by red, itchy welts caused by an allergic reaction, while dermatographia, or skin writing, results in raised, red lines triggered by minor skin scratching. Both conditions involve histamine release, but urticaria often has systemic triggers like foods or medications, whereas dermatographia is typically a physical response to skin pressure. Frequently asked questions focus on symptom differentiation, treatment options such as antihistamines, and whether either condition indicates a serious underlying health issue.
Urticaria Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com