Statins effectively lower cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, reducing LDL levels and cardiovascular risk. Bile acid sequestrants bind bile acids in the gut, preventing their reabsorption and prompting the liver to use cholesterol to produce more bile acids, further decreasing LDL cholesterol. Discover how these medications work together and which might be best for your cholesterol management in the full article.
Table of Comparison
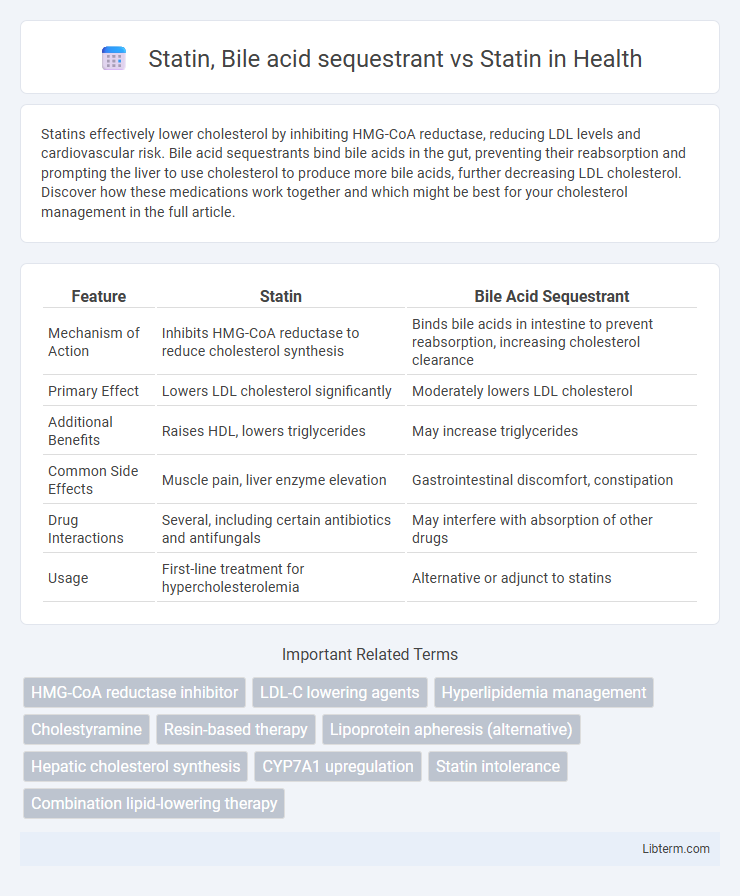
| Feature | Statin | Bile Acid Sequestrant |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase to reduce cholesterol synthesis | Binds bile acids in intestine to prevent reabsorption, increasing cholesterol clearance |
| Primary Effect | Lowers LDL cholesterol significantly | Moderately lowers LDL cholesterol |
| Additional Benefits | Raises HDL, lowers triglycerides | May increase triglycerides |
| Common Side Effects | Muscle pain, liver enzyme elevation | Gastrointestinal discomfort, constipation |
| Drug Interactions | Several, including certain antibiotics and antifungals | May interfere with absorption of other drugs |
| Usage | First-line treatment for hypercholesterolemia | Alternative or adjunct to statins |
Understanding Statins: Mechanism of Action
Statins lower cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, a key enzyme in hepatic cholesterol synthesis, resulting in increased LDL receptor expression and enhanced clearance of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. Bile acid sequestrants reduce cholesterol by binding bile acids in the intestine, preventing their reabsorption, which stimulates hepatic conversion of cholesterol into bile acids and upregulates LDL receptors. Statins provide a more direct and potent mechanism for reducing LDL cholesterol compared to bile acid sequestrants, which act indirectly through bile acid metabolism.
Overview of Bile Acid Sequestrants
Bile acid sequestrants are non-absorbable resins that lower LDL cholesterol by binding bile acids in the intestine, preventing their reabsorption and promoting cholesterol conversion to bile acids in the liver. Unlike statins, which inhibit HMG-CoA reductase to reduce cholesterol synthesis, bile acid sequestrants work through a different mechanism targeting cholesterol elimination. These agents are often used as adjunct therapy with statins to enhance lipid-lowering effects, especially in patients intolerant to statins or requiring additional LDL reduction.
Statins vs. Bile Acid Sequestrants: Key Differences
Statins primarily reduce LDL cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, leading to decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver, whereas bile acid sequestrants lower LDL cholesterol by binding bile acids in the intestine and promoting their excretion. Statins generally provide more potent LDL reduction and have demonstrated cardiovascular outcome benefits, while bile acid sequestrants may cause gastrointestinal side effects but are useful in combination therapy or for patients intolerant to statins. Statins also improve endothelial function and reduce inflammation, effects not observed with bile acid sequestrants, highlighting their broader therapeutic role in cardiovascular risk management.
Efficacy in Lowering LDL Cholesterol
Statins consistently demonstrate superior efficacy in lowering LDL cholesterol compared to bile acid sequestrants, achieving reductions typically ranging from 20% to 55%. Bile acid sequestrants lower LDL cholesterol by 15% to 30% but often require combination with statins for optimal lipid control. Clinical trials show statins not only reduce LDL levels more effectively but also provide significant cardiovascular risk reduction beyond cholesterol lowering.
Safety Profiles and Side Effects
Statins primarily lower LDL cholesterol and are generally well-tolerated, but common side effects include muscle pain, elevated liver enzymes, and a slight risk of diabetes. Bile acid sequestrants also reduce LDL cholesterol but often cause gastrointestinal issues such as constipation, bloating, and nausea, with minimal systemic absorption reducing systemic side effects. In combination therapy, statins and bile acid sequestrants offer enhanced lipid control, but monitoring for muscle symptoms and gastro-intestinal tolerance is essential to optimize safety profiles.
Clinical Indications: When to Use Statins or Bile Acid Sequestrants
Statins are primarily indicated for patients with hypercholesterolemia, especially those with elevated LDL cholesterol and high cardiovascular risk, including individuals with a history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or diabetes. Bile acid sequestrants are typically used as adjunct therapy in patients who cannot tolerate statins or require additional LDL cholesterol reduction, particularly in cases of familial hypercholesterolemia or mild to moderate hyperlipidemia. Statins are preferred for their potent LDL-lowering effect and proven cardiovascular benefit, while bile acid sequestrants serve as alternative or complementary agents when statins are contraindicated or insufficient.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Statins primarily interact with CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole and erythromycin, increasing the risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, while bile acid sequestrants can reduce the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and interfere with drugs like warfarin and thyroxine by binding them in the gut. Contraindications for statins include active liver disease and pregnancy due to hepatotoxicity and teratogenic risk, whereas bile acid sequestrants are contraindicated in patients with complete biliary obstruction and severe hypertriglyceridemia. Monitoring liver function tests is essential during statin therapy, and careful timing of medication administration is required with bile acid sequestrants to minimize drug interaction risks.
Patient Compliance and Tolerability
Statin therapy generally offers higher patient compliance due to once-daily dosing and well-established efficacy in lowering LDL cholesterol. Bile acid sequestrants often present challenges in tolerability, including gastrointestinal side effects like constipation and bloating, which can reduce adherence. Combining statins with bile acid sequestrants may improve lipid control but requires careful management to maintain patient tolerability and compliance.
Impact on Cardiovascular Outcomes
Statins effectively lower LDL cholesterol and significantly reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Bile acid sequestrants also reduce LDL cholesterol by binding bile acids in the intestine, but their impact on cardiovascular outcomes is less pronounced compared to statins. Combining statins with bile acid sequestrants can provide additive LDL reduction and further cardiovascular risk improvement in patients intolerant to high-dose statins.
Choosing the Right Therapy: Statin or Bile Acid Sequestrant?
Statins effectively lower LDL cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, providing significant cardiovascular risk reduction, making them the first-line therapy for hyperlipidemia. Bile acid sequestrants reduce LDL cholesterol by binding bile acids in the intestine, serving as alternative or adjunct treatments for patients intolerant to statins or needing additional lipid lowering. Choosing between statin monotherapy or combining with bile acid sequestrants depends on patient-specific factors such as statin tolerance, baseline LDL levels, and comorbidities to optimize lipid control and minimize adverse effects.
Statin, Bile acid sequestrant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com