Monitoring enables real-time tracking and analysis of systems to ensure optimal performance and early detection of issues. Effective monitoring tools collect and interpret data that help prevent downtime and enhance security. Discover how monitoring can transform your operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
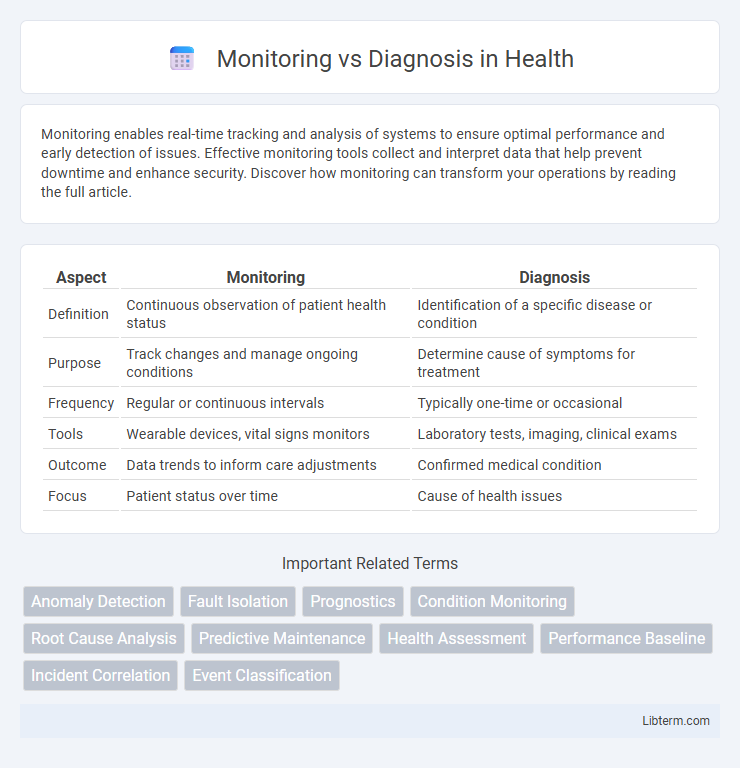
| Aspect | Monitoring | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous observation of patient health status | Identification of a specific disease or condition |
| Purpose | Track changes and manage ongoing conditions | Determine cause of symptoms for treatment |
| Frequency | Regular or continuous intervals | Typically one-time or occasional |
| Tools | Wearable devices, vital signs monitors | Laboratory tests, imaging, clinical exams |
| Outcome | Data trends to inform care adjustments | Confirmed medical condition |
| Focus | Patient status over time | Cause of health issues |
Introduction to Monitoring and Diagnosis
Monitoring involves the continuous observation and tracking of system performance and health metrics to detect anomalies and ensure operational stability. Diagnosis refers to the systematic process of identifying the root cause of detected issues through data analysis and fault isolation techniques. Effective implementation of monitoring and diagnosis enhances system reliability, reduces downtime, and optimizes maintenance strategies.
Defining Monitoring in Healthcare
Monitoring in healthcare involves the continuous and systematic collection of patient data, such as vital signs, symptoms, and laboratory results, to track health status and detect changes over time. It supports early identification of potential issues, enabling timely interventions that can prevent complications and improve outcomes. Unlike diagnosis, which determines the cause of symptoms at a specific point, monitoring emphasizes ongoing assessment to manage chronic conditions and guide treatment adjustments.
Understanding Diagnosis: Key Concepts
Diagnosis involves identifying the root cause of a problem through systematic analysis of data collected during monitoring. It requires interpreting symptoms and patterns to distinguish between similar issues, facilitating accurate resolution. Effective diagnosis relies on integrating real-time monitoring data with historical information and expert knowledge to ensure precise problem identification.
Major Differences Between Monitoring and Diagnosis
Monitoring involves continuous observation and data collection to track the status or performance of a system or process, while diagnosis focuses on identifying the root cause of a specific problem or failure based on collected data. Monitoring provides real-time or periodic information to detect anomalies early, whereas diagnosis interprets symptoms and patterns to determine underlying issues. The primary difference lies in monitoring's preventive role versus diagnosis's problem-solving objective.
When to Monitor vs When to Diagnose
Monitoring is essential for ongoing observation of system performance or patient health to detect early signs of change or deterioration, typically used in stable conditions or routine check-ups. Diagnosis is necessary when specific symptoms or anomalies arise, requiring detailed analysis to identify the root cause of a problem or disease. Timely monitoring helps inform the need for diagnosis by highlighting deviations from normal parameters that warrant further investigation.
Importance of Monitoring in Early Detection
Continuous monitoring plays a crucial role in the early detection of health conditions by capturing real-time data and subtle changes that might be missed during periodic diagnostic tests. Advanced monitoring technologies, such as wearable devices and remote sensors, enable timely intervention before symptoms escalate into severe stages. Early detection through consistent monitoring significantly improves treatment outcomes and reduces healthcare costs by preventing complications.
Role of Diagnosis in Treatment Planning
Diagnosis plays a crucial role in treatment planning by identifying the specific nature and cause of a medical condition, enabling personalized and targeted therapeutic interventions. Accurate diagnosis informs the selection of appropriate medications, procedures, or lifestyle modifications, thereby improving patient outcomes and minimizing risks. Continuous monitoring complements diagnosis by tracking treatment effectiveness and facilitating timely adjustments to the care plan.
Tools and Technologies for Monitoring and Diagnosis
Monitoring tools such as Prometheus, Nagios, and Zabbix provide real-time data collection and alerting for system performance and availability, enabling proactive system health tracking. Diagnostic technologies include advanced log analyzers, like Splunk and ELK Stack, and AI-driven root cause analysis platforms, which facilitate deep problem identification and resolution. Integration of these tools maximizes operational efficiency by correlating monitoring insights with diagnostic findings to address issues promptly.
Challenges in Differentiating Monitoring and Diagnosis
Challenges in differentiating monitoring and diagnosis arise from overlapping data interpretation and similar clinical assessments, making it difficult to distinctly categorize ongoing observation versus the identification of a condition. Monitoring requires continuous data collection to track progression or response to treatment, while diagnosis involves a conclusive evaluation to determine the presence of a specific disease or condition. The ambiguity in symptom presentation and variability in patient responses further complicate the boundary between monitoring and diagnostic processes.
Future Trends in Monitoring and Diagnosis
Future trends in monitoring and diagnosis emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance predictive analytics and personalized healthcare. Wearable sensors and continuous health monitoring devices are evolving to provide real-time data, improving early detection and management of diseases. Advances in telemedicine and remote diagnostic tools enable more accurate, accessible, and timely intervention, transforming patient care models globally.
Monitoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com