Noninvasive procedures minimize physical intrusion by avoiding cuts or needles, reducing pain and recovery time while enhancing patient comfort. These techniques are widely used in diagnostics and treatments, such as imaging tests and laser therapies, offering effective alternatives to traditional surgery. Discover how noninvasive methods can benefit your health and what options might suit your needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
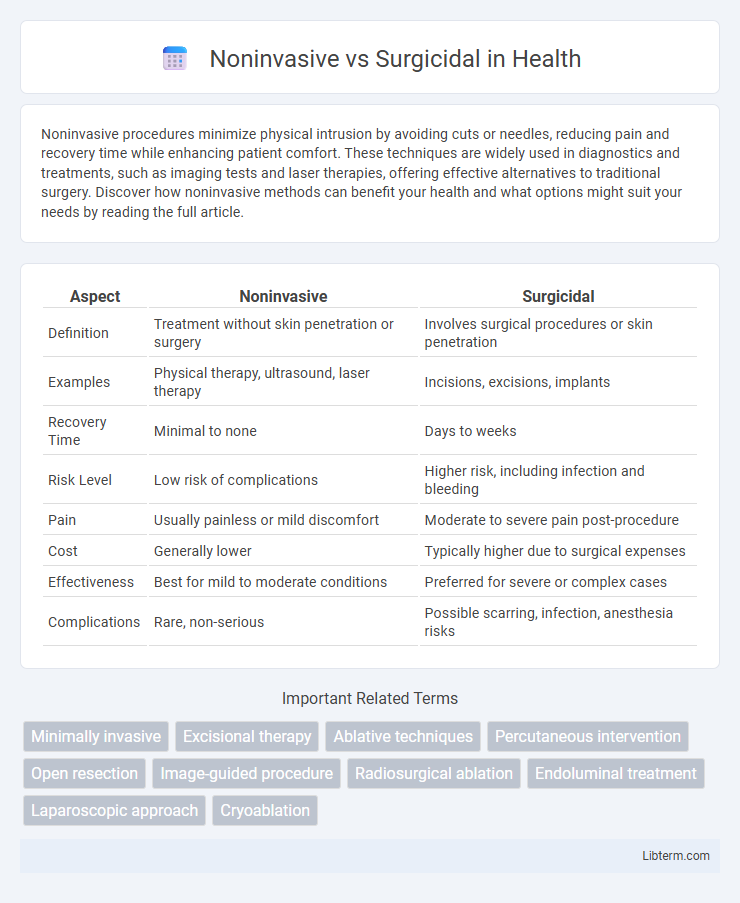
| Aspect | Noninvasive | Surgicidal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Treatment without skin penetration or surgery | Involves surgical procedures or skin penetration |
| Examples | Physical therapy, ultrasound, laser therapy | Incisions, excisions, implants |
| Recovery Time | Minimal to none | Days to weeks |
| Risk Level | Low risk of complications | Higher risk, including infection and bleeding |
| Pain | Usually painless or mild discomfort | Moderate to severe pain post-procedure |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to surgical expenses |
| Effectiveness | Best for mild to moderate conditions | Preferred for severe or complex cases |
| Complications | Rare, non-serious | Possible scarring, infection, anesthesia risks |
Introduction to Noninvasive and Surgicidal Treatments
Noninvasive treatments refer to medical procedures that do not require incisions or penetration into the body, minimizing risk and promoting faster recovery. Surgicidal treatments involve surgical intervention aimed at removing or destroying targeted tissues, typically requiring anesthesia and longer healing times. Understanding the fundamental differences between noninvasive modalities, such as laser therapy or ultrasound, and surgicidal options is essential for optimizing patient outcomes in clinical practice.
Defining Noninvasive Procedures
Noninvasive procedures involve techniques that do not require incisions into the body or removal of tissue, prioritizing minimal physical disruption and reduced recovery time. These methods often use external devices or imaging technology to diagnose or treat conditions, such as ultrasound, MRI-guided therapies, or transcutaneous electrical stimulation. By avoiding surgical entry, noninvasive procedures significantly lower the risk of infection and complications compared to surgicidal interventions that involve cutting or destroying tissue.
Understanding Surgicidal Interventions
Surgicidal interventions involve procedures that directly remove or destroy tissue to treat medical conditions, offering definitive solutions especially in cases of malignant tumors or severe infections. These interventions often require anesthesia, sterile environments, and postoperative care to ensure healing and prevent complications. Understanding surgicidal methods is crucial in determining the balance between effective disease eradication and minimizing patient risk compared to noninvasive approaches.
Key Differences Between Noninvasive and Surgicidal Methods
Noninvasive methods target pathogens without physically breaching the skin, using techniques such as ultraviolet light, chemical agents, or heat to neutralize or remove microbes. Surgicidal methods involve surgical intervention or tissue destruction to eliminate infection, often requiring precision and sterile environments to prevent complications. Key differences include the level of tissue disruption, recovery time, and risk profile, with noninvasive approaches generally offering faster healing and less discomfort compared to surgicidal techniques.
Benefits of Noninvasive Treatments
Noninvasive treatments offer significant benefits by minimizing tissue damage, reducing recovery time, and lowering the risk of complications compared to surgicidal procedures. Patients experience less pain and scarring, enabling quicker returns to daily activities and work. These treatments also often result in cost savings due to shorter hospital stays and fewer postoperative interventions.
Advantages of Surgicidal Procedures
Surgicidal procedures offer the advantage of definitively removing or destroying targeted tissue, leading to potentially permanent resolution of conditions such as tumors or abnormal growths. These methods often provide faster recovery times compared to repeated noninvasive treatments, reducing the likelihood of recurrence. Enhanced precision in surgicidal techniques minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue, improving overall treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
Common Noninvasive Techniques
Common noninvasive techniques like laser therapy, cryotherapy, and radiofrequency ablation target abnormal tissues without penetrating the skin, minimizing pain and recovery time compared to surgicidal methods. These procedures leverage advanced energy sources to destroy or alter cells at the surface or just below it, preserving surrounding healthy tissues and reducing infection risk. Noninvasive treatments are widely favored for their efficiency in managing skin lesions, varicose veins, and certain cancers while avoiding surgical complications.
Typical Surgicidal Approaches
Typical surgicidal approaches involve direct physical or chemical methods to eliminate pathogens, commonly used in clinical settings for sterilization and infection control. These methods include surgical excision, chemical cauterization, and the use of antimicrobial implants that destroy infectious agents at the targeted site. Compared to noninvasive techniques, surgicidal interventions provide immediate pathogen eradication but carry risks such as tissue damage and longer recovery times.
Choosing the Right Treatment: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right treatment between noninvasive and surgicidal methods depends on factors such as the severity of the condition, patient health status, and recovery time. Noninvasive treatments offer minimal risk and quicker recovery but may have limited effectiveness for advanced cases. Surgicidal options provide definitive results for severe conditions but involve higher risks and longer healing periods.
Conclusion: Noninvasive vs Surgicidal – Which Is Better?
Noninvasive treatments offer reduced recovery times and minimal risk of complications, making them ideal for patients seeking less aggressive interventions. Surgicidal methods provide definitive removal of affected tissue, often necessary for advanced or resistant conditions. Choosing between noninvasive and surgicidal approaches depends on the severity of the condition, patient health status, and long-term treatment goals.
Noninvasive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com