Pharmacoepidemiology examines the use and effects of medications in large populations, focusing on drug safety, efficacy, and patterns of use. It integrates principles of pharmacology and epidemiology to better understand how drugs impact public health outcomes and inform regulatory decisions. Discover more about how pharmacoepidemiology can enhance your knowledge of drug safety and improve healthcare practices in the full article.
Table of Comparison
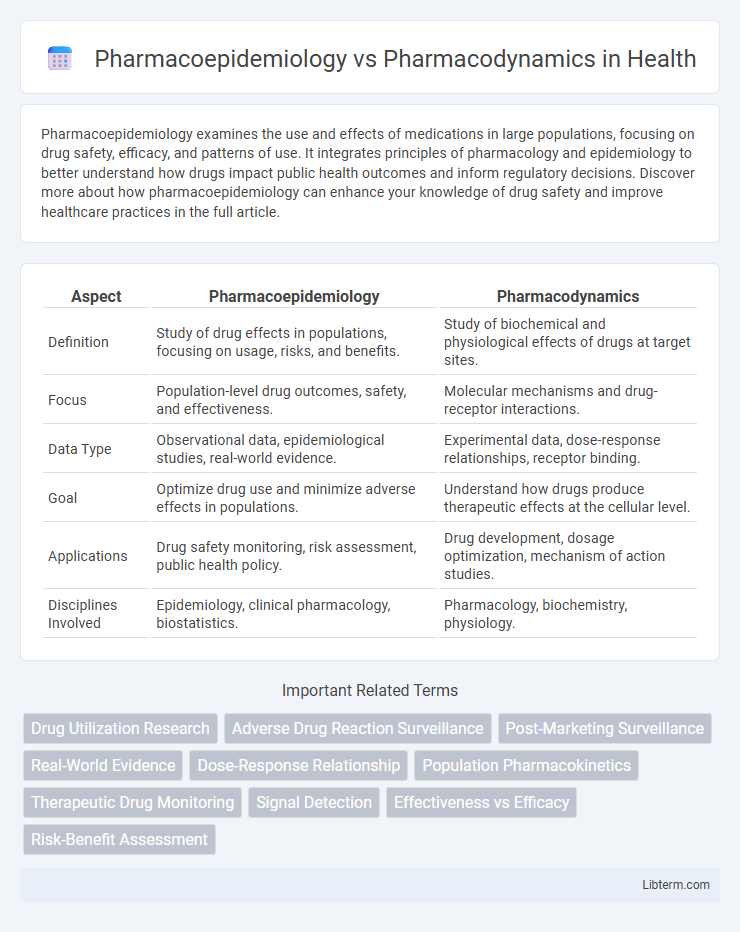
| Aspect | Pharmacoepidemiology | Pharmacodynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of drug effects in populations, focusing on usage, risks, and benefits. | Study of biochemical and physiological effects of drugs at target sites. |
| Focus | Population-level drug outcomes, safety, and effectiveness. | Molecular mechanisms and drug-receptor interactions. |
| Data Type | Observational data, epidemiological studies, real-world evidence. | Experimental data, dose-response relationships, receptor binding. |
| Goal | Optimize drug use and minimize adverse effects in populations. | Understand how drugs produce therapeutic effects at the cellular level. |
| Applications | Drug safety monitoring, risk assessment, public health policy. | Drug development, dosage optimization, mechanism of action studies. |
| Disciplines Involved | Epidemiology, clinical pharmacology, biostatistics. | Pharmacology, biochemistry, physiology. |
Introduction to Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacoepidemiology studies the use and effects of drugs in large populations, focusing on patterns, causes, and outcomes of medication usage to optimize therapeutic efficacy and safety. Pharmacodynamics examines the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, analyzing drug-receptor interactions to determine mechanisms of action and dose-response relationships. Integrating pharmacoepidemiology with pharmacodynamics enhances drug development, risk assessment, and personalized medicine by linking population-based data with molecular drug effects.
Defining Pharmacoepidemiology
Pharmacoepidemiology studies the distribution, patterns, and effects of drugs in large populations, analyzing drug usage, safety, and outcomes to inform public health decisions. Unlike pharmacodynamics, which examines the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on individual organisms and their mechanisms of action, pharmacoepidemiology focuses on real-world drug utilization and adverse events across diverse demographics. Key data in pharmacoepidemiology include population-based drug exposure, incidence rates of side effects, and factors affecting drug efficacy in varied patient groups.
Understanding Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics explores the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, detailing mechanisms of action, receptor interactions, dose-response relationships, and therapeutic outcomes. This field provides insights into drug efficacy, potency, and toxicity by examining how drugs influence cellular pathways and receptor activity. Understanding pharmacodynamics is crucial for optimizing drug dosage, predicting therapeutic effects, and minimizing adverse reactions in clinical pharmacology.
Core Objectives: Pharmacoepidemiology vs Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacoepidemiology focuses on studying drug effects in large populations to understand usage patterns, safety, and effectiveness, aiming to optimize public health outcomes. Pharmacodynamics investigates the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, particularly the mechanisms of drug action at the receptor or cellular level. Core objectives of pharmacoepidemiology center on monitoring adverse drug reactions and treatment efficacy in real-world settings, while pharmacodynamics targets understanding dose-response relationships and drug-receptor interactions.
Methodological Approaches in Pharmacoepidemiology
Pharmacoepidemiology employs observational study designs such as cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies to assess drug effects and safety in large populations, utilizing data from electronic health records, insurance claims, and registries. Advanced statistical methods including propensity score matching, instrumental variable analysis, and time-to-event analysis address confounding and bias inherent in real-world data. In contrast, pharmacodynamics focuses on experimental and mechanistic approaches at the molecular or cellular level to quantify drug-receptor interactions, dose-response relationships, and physiological effects.
Key Mechanisms Explored by Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics investigates the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs, focusing on receptor binding, signal transduction, and dose-response relationships to understand drug efficacy and toxicity. This field explores mechanisms such as agonist and antagonist interactions, enzyme inhibition, and modulation of ion channels that directly influence drug action at target sites. Understanding these key mechanisms enables precise predictions of therapeutic outcomes and guides drug design for improved clinical effectiveness.
Data Sources and Analysis Techniques
Pharmacoepidemiology utilizes large-scale real-world data sources such as electronic health records, insurance claims databases, and patient registries to analyze drug use patterns and population-level safety, employing advanced statistical methods like cohort studies, case-control studies, and survival analysis. Pharmacodynamics relies heavily on experimental data from in vitro assays, animal models, and clinical trial biomarker measurements to evaluate drug-receptor interactions and dose-response relationships using mechanistic modeling and nonlinear regression techniques. Both fields integrate bioinformatics tools and machine learning algorithms to enhance data interpretation and support precision medicine initiatives.
Clinical and Public Health Impact
Pharmacoepidemiology assesses the effects and patterns of drug use in populations, providing critical data to improve drug safety and effectiveness on a public health scale. Pharmacodynamics focuses on the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs at the cellular level, guiding personalized medicine by understanding the mechanisms of drug action. Integrating pharmacoepidemiological trends with pharmacodynamic insights enhances clinical decision-making and optimizes therapeutic outcomes in diverse patient populations.
Integration of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacodynamics in Research
Integrating pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacodynamics in research enhances understanding of drug effects in real-world populations by linking drug action mechanisms with population-level outcomes. This approach enables identification of variability in drug response due to genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors, contributing to personalized medicine. Advanced data analytics and modeling techniques facilitate combining pharmacodynamic biomarkers with pharmacoepidemiological data to optimize therapeutic strategies and improve drug safety profiles.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
Pharmacoepidemiology is advancing through the integration of big data analytics and real-world evidence to enhance drug safety monitoring and personalized medicine. Pharmacodynamics research is increasingly leveraging molecular modeling and AI-driven simulations to predict drug-receptor interactions and optimize dosage regimens. Emerging trends in both fields emphasize the convergence of computational tools and genomic data to facilitate precision pharmacotherapy and reduce adverse drug reactions.
Pharmacoepidemiology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com