Abrasion is the process of scraping or wearing away a surface due to friction, often seen in skin injuries or material wear. Understanding how abrasion affects different surfaces can help in selecting protective measures and improving durability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how abrasion impacts your daily life and ways to prevent it effectively.
Table of Comparison
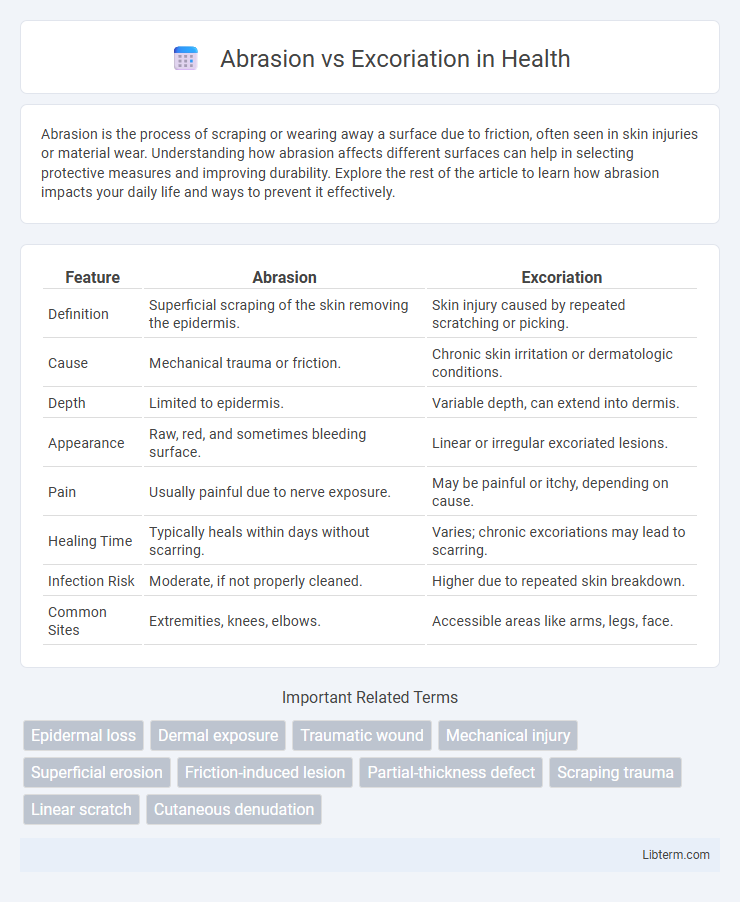
| Feature | Abrasion | Excoriation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Superficial scraping of the skin removing the epidermis. | Skin injury caused by repeated scratching or picking. |
| Cause | Mechanical trauma or friction. | Chronic skin irritation or dermatologic conditions. |
| Depth | Limited to epidermis. | Variable depth, can extend into dermis. |
| Appearance | Raw, red, and sometimes bleeding surface. | Linear or irregular excoriated lesions. |
| Pain | Usually painful due to nerve exposure. | May be painful or itchy, depending on cause. |
| Healing Time | Typically heals within days without scarring. | Varies; chronic excoriations may lead to scarring. |
| Infection Risk | Moderate, if not properly cleaned. | Higher due to repeated skin breakdown. |
| Common Sites | Extremities, knees, elbows. | Accessible areas like arms, legs, face. |
Understanding Abrasion and Excoriation
Abrasion refers to superficial skin damage caused by friction or scraping against a rough surface, typically affecting the epidermis with minor bleeding and rawness. Excoriation involves deeper skin trauma resulting from repetitive scratching or picking, often leading to open sores, redness, and potential scabbing. Recognizing the differences between abrasion and excoriation aids in appropriate wound care and prevention of infection.
Defining Abrasion: Causes and Characteristics
Abrasion is a superficial injury characterized by the removal of the epidermis due to friction or scrapping against a rough surface, commonly caused by falls, road rash, or contact sports injuries. These wounds typically present with raw, red, and sometimes bleeding skin, but usually do not penetrate beyond the outer skin layers. Healing of abrasions generally occurs quickly due to the preservation of the dermis, with minimal scarring unless complicated by infection or deeper tissue damage.
What Is Excoriation? Key Features Explained
Excoriation is a skin injury characterized by superficial abrasions caused by scratching or picking, often leading to raw, red, and inflamed areas. Unlike abrasion, which results from external mechanical forces like friction or scraping against a rough surface, excoriation primarily arises from repetitive trauma inflicted by the individual. Key features of excoriation include linear or irregular skin lesions, visible excoriated borders, and potential secondary infection due to skin barrier disruption.
Differences in Appearance: Abrasion vs Excoriation
Abrasion appears as a superficial wound with scraped or rubbed-off skin, often causing raw, red areas with minor bleeding, primarily affecting the epidermis. Excoriation displays as linear, scratch-like marks resulting from repetitive picking or scratching, often accompanied by crusts, scabs, or secondary infection, and may penetrate deeper skin layers. The key difference lies in abrasion's mechanical removal of skin surface versus excoriation's self-inflicted skin trauma with characteristic patterns and signs of chronic irritation.
Common Causes of Abrasion and Excoriation
Common causes of abrasion involve friction resulting from falls or scraping against rough surfaces, often affecting the skin's outer layer. Excoriation typically arises from repetitive scratching or picking due to skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or insect bites, leading to damage in deeper skin layers. Both conditions disrupt the skin barrier but differ primarily in origin--abrasions are externally caused by mechanical trauma, while excoriations are self-inflicted through habitual skin manipulation.
Clinical Diagnosis: Distinguishing Between the Two
Abrasion presents as superficial skin damage typically caused by friction, characterized by raw, red, and sometimes bleeding surfaces, often identifiable by the absence of deeper tissue involvement. Excoriation, however, involves more intense skin trauma resulting from repetitive scratching or picking, leading to linear or irregular wounds with possible secondary infection or scarring. Clinical diagnosis relies on patient history and lesion morphology, with abrasions usually linked to external mechanical forces and excoriations associated with dermatologic or psychological conditions causing self-inflicted injury.
Treatment Approaches for Abrasion
Treatment approaches for abrasion primarily involve thorough cleaning to prevent infection, typically using saline solution or mild antiseptics. Applying antibiotic ointments such as neomycin or bacitracin helps promote healing and reduce bacterial growth, while keeping the wound covered with a sterile dressing minimizes contamination and facilitates recovery. Pain management may include over-the-counter analgesics like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, and monitoring for signs of infection ensures timely intervention if complications arise.
Managing Excoriation: Best Practices
Managing excoriation involves keeping the affected skin clean and moisturized to prevent infection and promote healing. Use gentle cleansing agents and apply antibiotic ointments or barrier creams as recommended by healthcare professionals. Avoid scratching and consider behavioral therapies or medications if excoriation results from compulsive skin picking disorders.
Prevention Tips for Skin Abrasions and Excoriations
To prevent skin abrasions and excoriations, regularly moisturizing the skin helps maintain barrier integrity and reduces susceptibility to damage. Using protective clothing and gentle skin care products minimizes friction and irritation, lowering the risk of abrasions and excoriations. Avoiding harsh scrubbing and promptly treating minor skin injuries with antiseptics further prevents infection and promotes faster healing.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for abrasions if the wound is deep, excessively bleeding, or showing signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or pus. Excoriations require prompt evaluation when accompanied by intense pain, spreading redness, or if caused by underlying skin conditions like eczema or dermatitis. Persistent wounds not healing within a week should be assessed by a healthcare professional to prevent complications.
Abrasion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com