Eczema and dermatitis are common inflammatory skin conditions characterized by red, itchy, and irritated patches. Managing these disorders involves identifying triggers, moisturizing regularly, and using prescribed treatments to reduce inflammation and discomfort. Discover effective strategies to soothe your skin and prevent flare-ups by reading further.
Table of Comparison
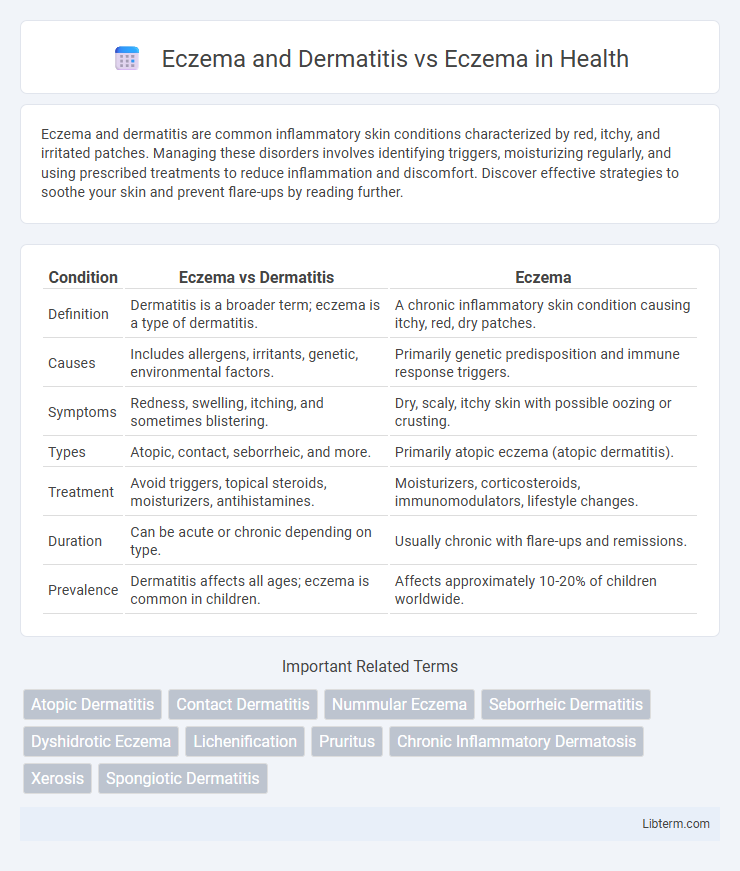
| Condition | Eczema vs Dermatitis | Eczema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dermatitis is a broader term; eczema is a type of dermatitis. | A chronic inflammatory skin condition causing itchy, red, dry patches. |
| Causes | Includes allergens, irritants, genetic, environmental factors. | Primarily genetic predisposition and immune response triggers. |
| Symptoms | Redness, swelling, itching, and sometimes blistering. | Dry, scaly, itchy skin with possible oozing or crusting. |
| Types | Atopic, contact, seborrheic, and more. | Primarily atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis). |
| Treatment | Avoid triggers, topical steroids, moisturizers, antihistamines. | Moisturizers, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, lifestyle changes. |
| Duration | Can be acute or chronic depending on type. | Usually chronic with flare-ups and remissions. |
| Prevalence | Dermatitis affects all ages; eczema is common in children. | Affects approximately 10-20% of children worldwide. |
Understanding Eczema and Dermatitis: Key Differences
Eczema and dermatitis are often used interchangeably but differ in scope and specificity; eczema is a broader term encompassing various inflammatory skin conditions, while dermatitis specifically refers to skin inflammation caused by external irritants or allergens. Understanding eczema involves recognizing it as a chronic condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, including types like atopic eczema, which has a genetic component. Dermatitis highlights the role of environmental triggers and irritants, such as contact dermatitis caused by exposure to chemicals or allergens, emphasizing diagnosis and targeted treatment based on the underlying cause.
What is Eczema? Causes and Symptoms
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and dryness. Common causes of eczema include genetic factors, environmental triggers like allergens and irritants, and immune system dysfunction. Symptoms often present as patches of itchy, inflamed skin that may blister, ooze, or become scaly, distinguishing it from other forms of dermatitis with varied causes and presentations.
What is Dermatitis? Types and Triggers
Dermatitis, a common inflammatory skin condition, encompasses various types such as atopic, contact, and seborrheic dermatitis, each characterized by redness, itching, and swelling. Triggers for dermatitis vary widely, including allergens, irritants, stress, and environmental factors like temperature changes or pollution. Understanding these triggers helps differentiate dermatitis from eczema, though eczema is often used interchangeably with atopic dermatitis, a specific subtype of dermatitis.
Eczema vs Dermatitis: Clinical Presentation
Eczema and dermatitis often describe similar inflammatory skin conditions, but eczema refers more broadly to a group of disorders characterized by itchy, red, and dry skin, such as atopic eczema. Dermatitis specifically denotes inflammation caused by irritation or allergic reactions, presenting with redness, swelling, and sometimes vesicles or oozing. Clinically, eczema often shows chronic, recurring patches with lichenification, whereas dermatitis may present acutely with localized inflammation linked to identifiable triggers.
Common Causes of Eczema and Dermatitis
Eczema and dermatitis both refer to inflammatory skin conditions characterized by redness, itching, and irritation, with common causes including genetic predisposition, environmental allergens, irritants like soaps and detergents, and immune system dysfunction. Atopic eczema often arises from a combination of hereditary factors and triggers such as pollen, pet dander, and stress, while contact dermatitis is primarily caused by direct exposure to irritants or allergens. Understanding these causative factors is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of eczema and dermatitis symptoms.
Diagnosis: Distinguishing Eczema from Dermatitis
Accurate diagnosis of Eczema versus Dermatitis relies on identifying specific clinical features and patient history, as both conditions share overlapping symptoms such as redness, itching, and inflammation. Dermatitis often refers broadly to inflammation of the skin caused by external irritants or allergens, while Eczema, particularly Atopic Eczema, is chronic, with a genetic predisposition and distinct flare-ups. Diagnostic tools include patch testing for allergic contact dermatitis and skin biopsy when necessary, enabling targeted treatment strategies for each condition.
Treatment Options for Eczema and Dermatitis
Treatment options for eczema and dermatitis primarily include topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and moisturizers to restore skin barrier function. Antihistamines can alleviate itching, while severe cases may require immunosuppressants or phototherapy. Identifying and avoiding triggers also plays a crucial role in managing symptoms effectively.
Managing Flare-Ups: Prevention Tips
Managing eczema and dermatitis flare-ups involves consistent skin hydration using fragrance-free moisturizers and avoiding known triggers such as allergens, irritants, and extreme temperatures. Wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and maintaining a gentle skincare routine with mild, soap-free cleansers reduces skin irritation significantly. Regular use of prescribed topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors helps control inflammation and prevent severe outbreaks.
Complications and Long-Term Outlook
Eczema and dermatitis encompass inflammatory skin conditions that often have overlapping symptoms, but eczema typically refers to a group of conditions including atopic dermatitis, which can lead to chronic inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction. Complications such as secondary bacterial infections, thickened skin (lichenification), and increased risk of allergic sensitization are common in chronic eczema cases, impacting quality of life and requiring ongoing management. The long-term outlook varies with severity and treatment adherence; many individuals experience symptom fluctuations with potential remission, though some may develop persistent skin issues or complications without proper care.
When to Seek Professional Help for Skin Conditions
Seek professional help for eczema or dermatitis when symptoms worsen, such as intense itching, persistent redness, or swelling that disrupts daily activities. Consult a dermatologist if over-the-counter treatments fail to alleviate flare-ups within two weeks or if signs of infection like oozing, crusting, or increased pain appear. Early diagnosis ensures appropriate management, preventing complications and improving skin health outcomes.
Eczema and Dermatitis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com