Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by swelling due to the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, often affecting the arms or legs. Effective management includes specialized massage, compression therapy, and exercises to improve lymph flow and reduce discomfort. Discover more about treatment options and lifestyle tips to help manage your lymphedema throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
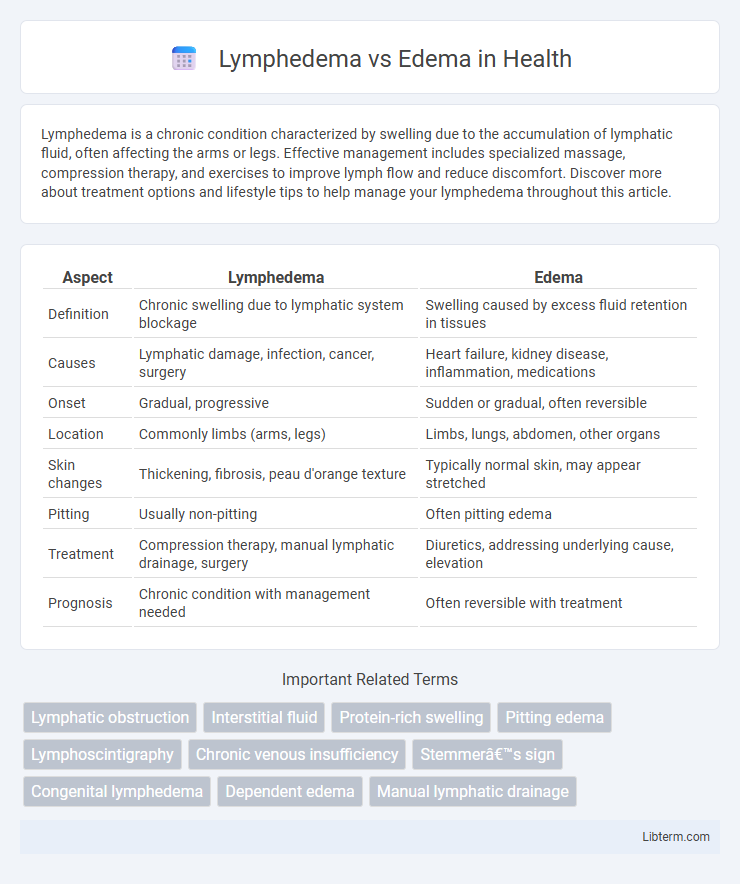
| Aspect | Lymphedema | Edema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic swelling due to lymphatic system blockage | Swelling caused by excess fluid retention in tissues |
| Causes | Lymphatic damage, infection, cancer, surgery | Heart failure, kidney disease, inflammation, medications |
| Onset | Gradual, progressive | Sudden or gradual, often reversible |
| Location | Commonly limbs (arms, legs) | Limbs, lungs, abdomen, other organs |
| Skin changes | Thickening, fibrosis, peau d'orange texture | Typically normal skin, may appear stretched |
| Pitting | Usually non-pitting | Often pitting edema |
| Treatment | Compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, surgery | Diuretics, addressing underlying cause, elevation |
| Prognosis | Chronic condition with management needed | Often reversible with treatment |
Understanding Lymphedema and Edema: Key Differences
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid due to impaired lymphatic system function, often resulting from surgery, infection, or congenital abnormalities. Edema refers to the general swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues, commonly due to inflammation, injury, or circulatory issues. Understanding the key differences, lymphedema involves protein-rich lymph fluid leading to tissue fibrosis, whereas edema typically involves protein-poor fluid and resolves with elevation or treatment of the underlying cause.
Causes: Why Do Lymphedema and Edema Happen?
Lymphedema occurs due to damage or blockage in the lymphatic system, often caused by surgery, radiation, infection, or congenital conditions, leading to impaired lymph fluid drainage. Edema results from fluid accumulation in tissues, typically caused by factors such as heart failure, kidney disease, liver cirrhosis, or localized inflammation and injury. Both conditions involve fluid retention, but lymphedema specifically stems from lymphatic dysfunction, while edema arises from diverse cardiovascular, renal, or inflammatory causes.
Symptoms Comparison: Lymphedema vs Edema
Lymphedema symptoms include persistent swelling primarily in the arms or legs, skin thickening, and a feeling of heaviness or tightness, often worsening over time without pitting when pressed. Edema symptoms involve swelling that may occur in multiple body areas such as the legs, feet, or abdomen, characterized by soft, pitting swelling that typically improves with elevation or rest. Unlike edema, lymphedema swelling is usually unilateral and associated with impaired lymphatic drainage leading to chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
Risk Factors Unique to Lymphedema and Edema
Lymphedema risk factors include lymphatic system damage from surgery, radiation therapy, or infection, particularly in cancer patients. Edema is commonly associated with systemic conditions such as heart failure, kidney disease, and chronic venous insufficiency. Unlike edema, lymphedema involves chronic swelling due to lymphatic flow obstruction rather than fluid imbalance alone.
Diagnostic Methods for Lymphedema and Edema
Lymphedema diagnosis primarily relies on clinical evaluation, patient history, and advanced imaging techniques such as lymphoscintigraphy, which assesses lymphatic flow and obstruction. Edema diagnosis involves identifying underlying causes using physical examination, blood tests, and imaging modalities like Doppler ultrasound to evaluate venous insufficiency or heart function. Both conditions benefit from bioimpedance spectroscopy for early detection and monitoring fluid accumulation in tissues.
Treatment Approaches: Managing Swelling
Lymphedema treatment emphasizes complete decongestive therapy (CDT), including manual lymphatic drainage, compression garments, and specialized exercises to improve lymphatic flow. In contrast, edema management often involves addressing the underlying cause, such as diuretics for heart or kidney-related fluid retention, along with elevation and compression techniques. Both conditions benefit from early intervention to prevent complications and enhance quality of life through tailored therapeutic plans.
Preventive Strategies for Lymphedema and Edema
Preventive strategies for lymphedema emphasize maintaining proper skin hygiene, avoiding trauma or infections, and using compression garments to support lymphatic drainage. For edema, prevention includes managing underlying causes such as heart, liver, or kidney conditions, reducing salt intake, and promoting regular physical activity to enhance circulation. Both conditions benefit from weight management and avoiding prolonged immobility to reduce fluid accumulation.
Complications Associated with Each Condition
Lymphedema, caused by lymphatic system dysfunction, can lead to chronic swelling, infections like cellulitis, and fibrosis due to impaired lymph drainage. Edema, resulting from fluid accumulation in tissues, often causes skin breakdown, increased risk of ulceration, and can signal underlying conditions such as heart failure or kidney disease. Both conditions require careful management to prevent severe complications including impaired mobility and recurrent infections.
Living with Lymphedema vs Edema: Quality of Life
Living with lymphedema significantly impacts quality of life due to chronic swelling, discomfort, and risk of infections, necessitating ongoing management such as compression therapy and meticulous skin care. In contrast, edema often resolves with treatment of the underlying cause, resulting in less long-term lifestyle disruption. Patients with lymphedema frequently face mobility limitations and emotional challenges, highlighting the importance of comprehensive support strategies to enhance daily functioning and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lymphedema and Edema
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by lymphatic system blockage, resulting in persistent swelling, primarily in the arms or legs, whereas edema is a temporary fluid buildup due to various causes like injury or infection. Frequently asked questions about lymphedema include its causes, symptoms such as swelling and skin changes, treatment options like compression therapy, and the risk of infection. Common inquiries about edema focus on identifying underlying conditions, duration of swelling, and effective management strategies to reduce fluid retention.
Lymphedema Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com