A laceration is a deep cut or tear in the skin caused by sharp objects, accidents, or trauma, requiring proper cleaning and sometimes stitches to prevent infection and promote healing. Recognizing the signs of severity and appropriate first aid can significantly reduce complications and scarring. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective treatment methods and when to seek medical help for your laceration.
Table of Comparison
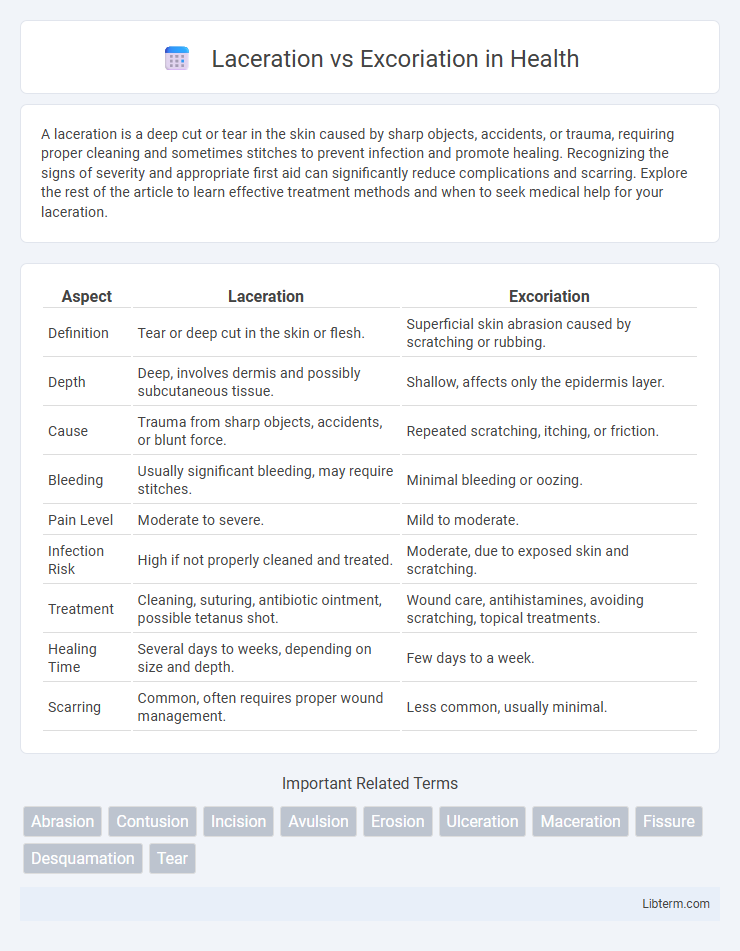
| Aspect | Laceration | Excoriation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tear or deep cut in the skin or flesh. | Superficial skin abrasion caused by scratching or rubbing. |
| Depth | Deep, involves dermis and possibly subcutaneous tissue. | Shallow, affects only the epidermis layer. |
| Cause | Trauma from sharp objects, accidents, or blunt force. | Repeated scratching, itching, or friction. |
| Bleeding | Usually significant bleeding, may require stitches. | Minimal bleeding or oozing. |
| Pain Level | Moderate to severe. | Mild to moderate. |
| Infection Risk | High if not properly cleaned and treated. | Moderate, due to exposed skin and scratching. |
| Treatment | Cleaning, suturing, antibiotic ointment, possible tetanus shot. | Wound care, antihistamines, avoiding scratching, topical treatments. |
| Healing Time | Several days to weeks, depending on size and depth. | Few days to a week. |
| Scarring | Common, often requires proper wound management. | Less common, usually minimal. |
Understanding Laceration and Excoriation
Lacerations are deep cuts or tears in the skin or flesh caused by blunt trauma, often resulting in irregular wound edges, while excoriations are superficial skin abrasions typically caused by scratching or rubbing, leading to linear or punctate lesions. Lacerations generally require medical intervention such as suturing due to their depth and potential for significant bleeding, whereas excoriations usually heal with minimal treatment but require management to prevent infection. Understanding the distinction aids healthcare providers in accurate diagnosis, appropriate wound care, and optimized healing outcomes.
Definition of Laceration
Laceration is a deep cut or tear in the skin or flesh, typically caused by blunt trauma that results in irregular, jagged wound edges. Unlike an excoriation, which is a superficial abrasion caused by scratching or scraping, lacerations often penetrate multiple skin layers and may involve underlying tissues. Proper assessment of the depth and severity of lacerations is critical for effective wound management and healing.
Definition of Excoriation
Excoriation is a superficial skin lesion caused by mechanical scratching or abrasion that removes the epidermis, often leading to visible redness and sometimes minor bleeding. Unlike lacerations, which are deeper, irregular tears in the skin typically caused by trauma, excoriations are more superficial and result from repetitive scratching or rubbing. Excoriations are commonly associated with conditions like eczema or pruritus, where persistent itching leads to skin damage.
Key Differences Between Laceration and Excoriation
Lacerations are deep cuts or tears in the skin or flesh caused by blunt trauma, typically resulting in jagged, irregular wound edges, whereas excoriations are superficial skin abrasions caused by scratching or irritation, affecting only the epidermis. Lacerations often require sutures or medical intervention to promote healing and prevent infection, while excoriations usually heal spontaneously without severe scarring. The key differences lie in depth, causative mechanisms, and treatment approaches, with lacerations being more severe and involving deeper tissue damage compared to the surface-level injury of excoriations.
Causes of Laceration
Lacerations are primarily caused by blunt trauma that results in irregular, jagged wound edges as the skin and underlying tissues tear, often from accidents involving sharp or heavy objects. Common causes include falls, machinery-related injuries, and vehicle collisions where the skin is forcefully split. Unlike excoriations, which are superficial abrasions typically caused by scratching or friction, lacerations penetrate deeper, potentially damaging muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
Causes of Excoriation
Excoriations are superficial skin abrasions caused primarily by repetitive scratching or rubbing, often linked to underlying conditions such as eczema, acne, or insect bites. Unlike lacerations, which result from blunt force trauma causing irregular tears in the skin, excoriations typically arise from compulsive behaviors or dermatologic diseases that induce persistent itching. Understanding the differentiation in causes is critical for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies.
Clinical Features and Symptoms
Lacerations present as deep, irregular wounds with jagged edges caused by blunt trauma, often accompanied by bleeding and pain. Excoriations are superficial skin abrasions resulting from scratching or friction, characterized by linear or irregular erosions with minimal bleeding but significant itching or discomfort. Both conditions display inflammation, but lacerations have a higher risk of infection and scarring due to tissue damage depth.
Diagnostic Criteria and Examination
Lacerations present as deep cuts or tears in the skin with irregular, jagged edges, identifiable through inspection showing disrupted dermal continuity often caused by blunt trauma, whereas excoriations appear as superficial linear abrasions resulting from scratching or rubbing. Diagnostic criteria for lacerations include depth assessment, involvement of underlying structures, and potential contamination, while excoriations are primarily evaluated based on lesion shape, distribution, and history of pruritus. Examination involves careful inspection for bleeding, tissue loss, and foreign bodies in lacerations, contrasting with excoriations which reveal erythematous, eroded skin without deep tissue injury.
Treatment and Management Options
Laceration treatment involves cleaning the wound to prevent infection, followed by suturing or adhesive strips for proper closure and faster healing. Excoriation management primarily focuses on maintaining skin hygiene, applying topical antibiotics to reduce infection risk, and addressing underlying causes such as itching or compulsive scratching. Both conditions benefit from pain control, wound monitoring, and preventive measures to avoid recurrence or complications.
Prevention Strategies for Skin Injuries
Effective prevention strategies for lacerations and excoriations emphasize maintaining skin integrity through protective measures such as wearing appropriate clothing and using barrier creams. Regular moisturizing and gentle skin care routines reduce vulnerability to tears and abrasions by preserving skin elasticity and hydration. Minimizing exposure to irritants and sharp objects further decreases the risk of these common skin injuries.
Laceration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com