Refractive error occurs when the eye cannot properly focus light on the retina, leading to blurred vision, commonly caused by myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, or presbyopia. Corrective lenses or refractive surgery can effectively address these vision problems to improve clarity and comfort. Explore the rest of this article to understand how refractive errors affect your eyesight and learn about the best treatment options available.
Table of Comparison
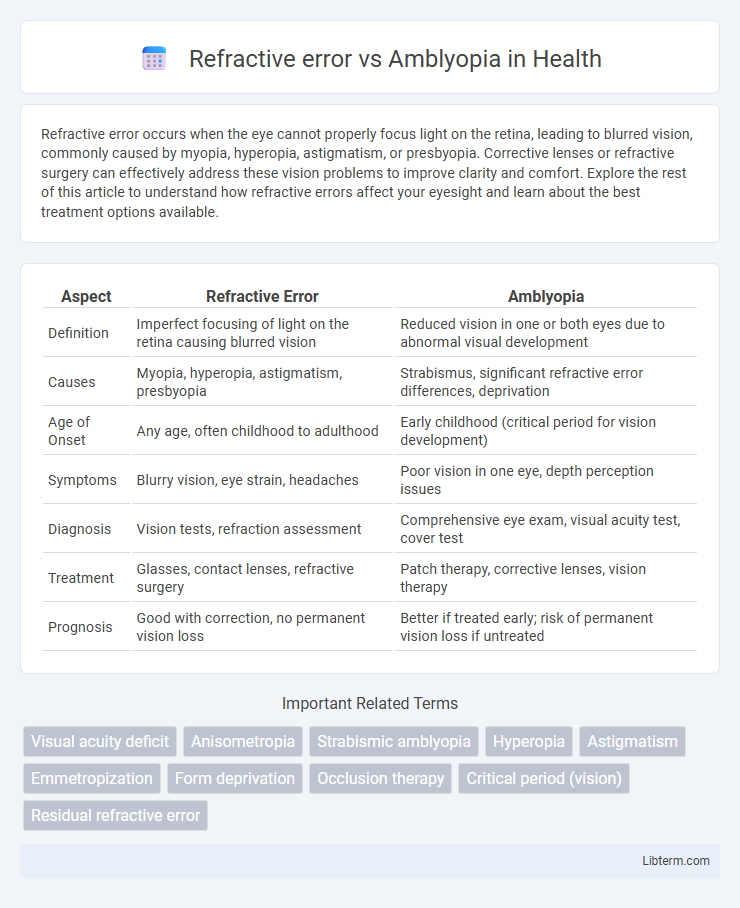
| Aspect | Refractive Error | Amblyopia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Imperfect focusing of light on the retina causing blurred vision | Reduced vision in one or both eyes due to abnormal visual development |
| Causes | Myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, presbyopia | Strabismus, significant refractive error differences, deprivation |
| Age of Onset | Any age, often childhood to adulthood | Early childhood (critical period for vision development) |
| Symptoms | Blurry vision, eye strain, headaches | Poor vision in one eye, depth perception issues |
| Diagnosis | Vision tests, refraction assessment | Comprehensive eye exam, visual acuity test, cover test |
| Treatment | Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery | Patch therapy, corrective lenses, vision therapy |
| Prognosis | Good with correction, no permanent vision loss | Better if treated early; risk of permanent vision loss if untreated |
Understanding Refractive Error
Refractive error occurs when the eye's shape prevents light from focusing directly on the retina, resulting in blurred vision; common types include myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. Unlike amblyopia, which is a developmental vision disorder leading to decreased visual acuity in one eye, refractive errors are primarily optical issues correctable with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery. Early detection and correction of refractive errors are crucial to prevent complications such as amblyopia in children.
Defining Amblyopia
Amblyopia, often called lazy eye, is a neurodevelopmental disorder where the brain favors one eye over the other, leading to decreased vision in the affected eye despite normal eye health. Unlike refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism that are caused by optical irregularities, amblyopia results from poor visual experience during critical periods of visual development. Effective treatment requires early diagnosis and interventions like patching or vision therapy to stimulate the weaker eye and improve neural connections.
Key Differences Between Refractive Error and Amblyopia
Refractive error involves the eye's inability to properly focus light on the retina, causing blurred vision due to conditions like myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism, whereas amblyopia, often called "lazy eye," is a neurodevelopmental disorder resulting in decreased vision in one or both eyes despite no structural eye abnormalities. Refractive error can typically be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery, whereas amblyopia requires early intervention through patching, atropine drops, or vision therapy to improve visual acuity. The key diagnostic difference is that refractive error affects visual clarity at all distances, and amblyopia results in reduced vision not fully correctable by lenses, emphasizing the neurological basis of amblyopia versus the optical focus issue in refractive errors.
Causes of Refractive Error
Refractive error occurs due to the irregular shape of the cornea, lens, or eyeball, causing light to focus improperly on the retina, leading to blurred vision. Common causes include myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism resulting from corneal curvature abnormalities or lens shape distortions. Amblyopia, also known as lazy eye, develops from poor visual stimulation during early childhood, often linked to untreated refractive errors, but it is primarily a neurological vision development issue rather than a structural refractive problem.
Causes of Amblyopia
Amblyopia, often called "lazy eye," arises primarily from abnormal visual experience during early childhood, unlike refractive error which is caused by the eye's inability to focus light correctly on the retina. The main causes of amblyopia include strabismus (misalignment of the eyes), anisometropia (significant differences in prescription between the two eyes), and deprivation (obstruction of vision due to cataracts or eyelid droop). Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent permanent vision loss.
Symptoms of Refractive Error vs Amblyopia
Refractive error symptoms include blurred vision, eye strain, headaches, and difficulty focusing on objects at various distances. Amblyopia symptoms often involve decreased vision in one eye, poor depth perception, and the affected eye may appear to wander or be misaligned. Unlike refractive errors, amblyopia does not typically cause both eyes to have blurred vision but rather a significant reduction in visual acuity in one eye.
Diagnosis: Refractive Error and Amblyopia
Refractive error diagnosis involves measuring visual acuity and performing retinoscopy or autorefractometry to detect focusing issues such as myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism. Amblyopia diagnosis requires comprehensive eye examination including visual acuity tests, cover-uncover test, and assessment of ocular alignment to identify reduced vision not correctable by lenses. Early detection through screening is critical for both conditions to prevent long-term visual impairment and ensure timely intervention.
Treatment Options for Refractive Error
Treatment options for refractive error primarily include corrective lenses such as eyeglasses and contact lenses, which adjust the focal point of the eye to improve vision affected by myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, or presbyopia. Refractive surgery, including LASIK and PRK, offers a permanent solution by reshaping the cornea to correct the eye's focusing ability. Regular eye examinations ensure proper prescription updates and monitor changes in refractive error to optimize visual outcomes.
Management and Therapy for Amblyopia
Management of amblyopia primarily involves corrective measures such as prescribing appropriate refractive lenses to address underlying refractive errors like myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism. Occlusion therapy, commonly using eye patches to cover the dominant eye, forces stimulation of the amblyopic eye and promotes visual development, especially effective in children under the age of 7. Supplementary treatments include atropine penalization to blur vision in the stronger eye, vision therapy exercises, and regular monitoring to adjust treatment as the child's visual acuity improves.
Prognosis and Long-term Outcomes
Refractive error and amblyopia differ significantly in prognosis and long-term outcomes, with refractive errors usually corrected effectively through glasses, contact lenses, or surgery, resulting in normal or near-normal vision. Amblyopia, if untreated during the critical period of visual development, often leads to permanent visual impairment despite subsequent corrective measures. Early diagnosis and intervention in amblyopia greatly improve visual prognosis and reduce the risk of long-term deficits compared to untreated cases.
Refractive error Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com