Ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes, posing serious health risks. Early detection and timely medical intervention are crucial to prevent complications such as rupture and internal bleeding. Discover more about symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options to protect your health in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
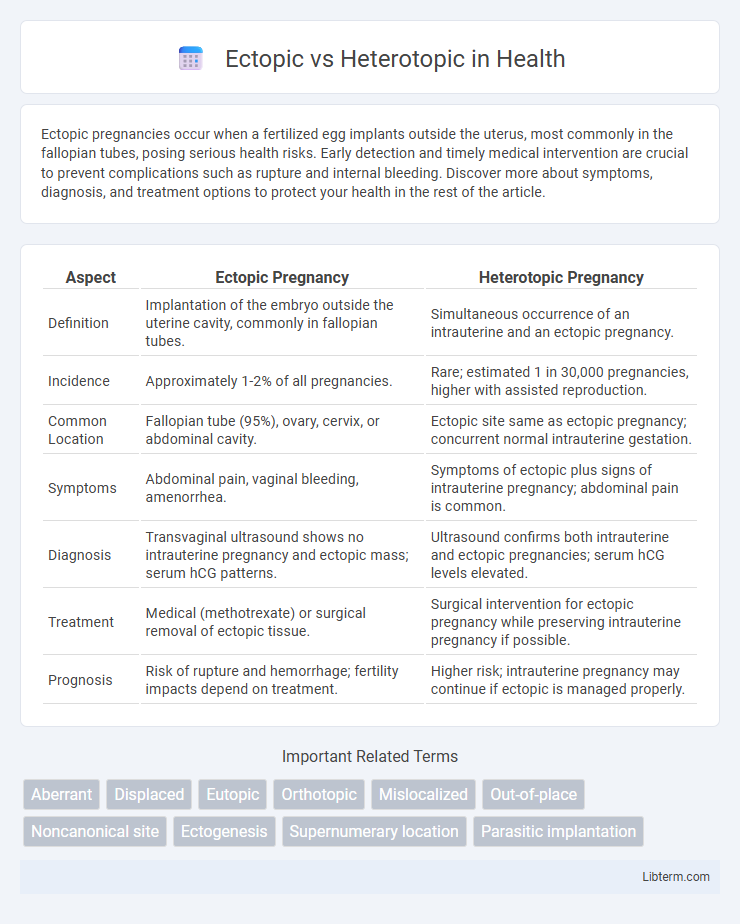
| Aspect | Ectopic Pregnancy | Heterotopic Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Implantation of the embryo outside the uterine cavity, commonly in fallopian tubes. | Simultaneous occurrence of an intrauterine and an ectopic pregnancy. |
| Incidence | Approximately 1-2% of all pregnancies. | Rare; estimated 1 in 30,000 pregnancies, higher with assisted reproduction. |
| Common Location | Fallopian tube (95%), ovary, cervix, or abdominal cavity. | Ectopic site same as ectopic pregnancy; concurrent normal intrauterine gestation. |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, amenorrhea. | Symptoms of ectopic plus signs of intrauterine pregnancy; abdominal pain is common. |
| Diagnosis | Transvaginal ultrasound shows no intrauterine pregnancy and ectopic mass; serum hCG patterns. | Ultrasound confirms both intrauterine and ectopic pregnancies; serum hCG levels elevated. |
| Treatment | Medical (methotrexate) or surgical removal of ectopic tissue. | Surgical intervention for ectopic pregnancy while preserving intrauterine pregnancy if possible. |
| Prognosis | Risk of rupture and hemorrhage; fertility impacts depend on treatment. | Higher risk; intrauterine pregnancy may continue if ectopic is managed properly. |
Introduction to Ectopic and Heterotopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, most commonly in the fallopian tubes, posing significant health risks due to potential rupture and internal bleeding. Heterotopic pregnancy involves simultaneous intrauterine and ectopic gestations, complicating diagnosis and management because the presence of a normal pregnancy can mask symptoms of the ectopic component. Early detection through transvaginal ultrasound and beta-hCG level monitoring is crucial for differentiating these conditions and preventing severe maternal complications.
Definition and Differences Between Ectopic and Heterotopic
Ectopic refers to the abnormal location of an organ or tissue outside its normal anatomical site, commonly seen in ectopic pregnancies where the embryo implants outside the uterus. Heterotopic, on the other hand, involves the presence of two different types of tissue or organs in an abnormal arrangement or location, such as heterotopic ossification where bone forms in soft tissue. The key difference lies in ectopic describing misplaced single tissue or organ, while heterotopic highlights the coexistence or abnormal displacement of different tissue types.
Causes and Risk Factors
Ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, commonly in the fallopian tubes, due to factors like previous pelvic infections, tubal surgery, or assisted reproductive techniques. Heterotopic pregnancies involve simultaneous intrauterine and ectopic implantations, with risks increasing significantly in cases of in vitro fertilization and other fertility treatments. Both conditions share risk factors such as pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, and a history of ectopic pregnancy, which compromise normal embryo implantation and tubal function.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
Ectopic pregnancy typically presents with unilateral pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, and a missed menstrual period, often accompanied by signs of early pregnancy such as breast tenderness and nausea. Heterotopic pregnancy, a rare occurrence of simultaneous intrauterine and ectopic pregnancies, presents with symptoms similar to ectopic pregnancy, including abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but may also show a viable intrauterine pregnancy on ultrasound. Diagnosis relies on transvaginal ultrasound and serum beta-hCG levels to distinguish between these conditions and to guide urgent management.
Diagnostic Approaches and Imaging
Ectopic and heterotopic tissue localization require precise diagnostic approaches to differentiate between abnormal tissue placement. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans play critical roles in identifying ectopic pregnancies or heterotopic ossifications by providing detailed visualization of tissue location and characteristics. Advanced methods like Doppler ultrasound and contrast-enhanced MRI enhance sensitivity and specificity, aiding in accurate diagnosis and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Complications and Potential Outcomes
Ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, commonly in the fallopian tubes, leading to risks such as tubal rupture, severe hemorrhage, and infertility if untreated. Heterotopic pregnancies involve simultaneous intrauterine and extrauterine implantation, complicating diagnosis and increasing the risk of miscarriage, preterm labor, and maternal morbidity. Both conditions require prompt medical intervention to minimize life-threatening complications and improve reproductive outcomes.
Ectopic Pregnancy: Types and Locations
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, most commonly in the fallopian tubes, accounting for over 90% of cases. Other locations include the cervical, ovarian, abdominal, and interstitial regions, each presenting unique clinical challenges and risks. Early diagnosis through transvaginal ultrasound and serum hCG levels is crucial to manage these potentially life-threatening pregnancies effectively.
Heterotopic Pregnancy: Incidence and Unique Challenges
Heterotopic pregnancy, the simultaneous occurrence of intrauterine and ectopic pregnancies, has an incidence of approximately 1 in 30,000 natural conceptions but increases significantly to about 1 in 100 to 1 in 500 with assisted reproductive technologies. This condition poses unique diagnostic challenges due to overlapping symptoms with ectopic pregnancy while maintaining a viable intrauterine gestation. Early detection through transvaginal ultrasound and careful monitoring is critical to manage the risks of rupture and ensure the viability of the intrauterine pregnancy.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Treatment of ectopic pregnancies primarily involves medical management with methotrexate or surgical intervention such as laparoscopy to remove the embryo and preserve fertility, while close monitoring of hCG levels is critical for assessing treatment success. Heterotopic pregnancy management requires a more complex approach, often combining surgical removal of the ectopic component with preservation strategies for the intrauterine pregnancy, necessitating multidisciplinary care and individualized treatment plans. Both conditions demand prompt diagnosis and tailored intervention to minimize complications and optimize reproductive outcomes.
Prognosis, Prevention, and Patient Counseling
Ectopic pregnancies involve implantation outside the uterine cavity, often posing significant risks such as tubal rupture, which requires prompt diagnosis and intervention to improve prognosis. Heterotopic pregnancy, characterized by simultaneous intrauterine and ectopic gestations, demands careful management to preserve the intrauterine embryo while preventing complications from the ectopic site. Effective patient counseling emphasizes early symptom recognition, risk factor modification including avoiding assisted reproductive technologies when unnecessary, and close monitoring through transvaginal ultrasound and beta-hCG levels to optimize outcomes and guide timely treatment.
Ectopic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com