Hypergalactia refers to an excessive production of breast milk, often caused by hormonal imbalances, certain medications, or underlying health conditions. Managing hypergalactia involves identifying the root cause and implementing appropriate treatments, which may include medication adjustments or lifestyle changes. Discover effective approaches to control hypergalactia and support your health by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
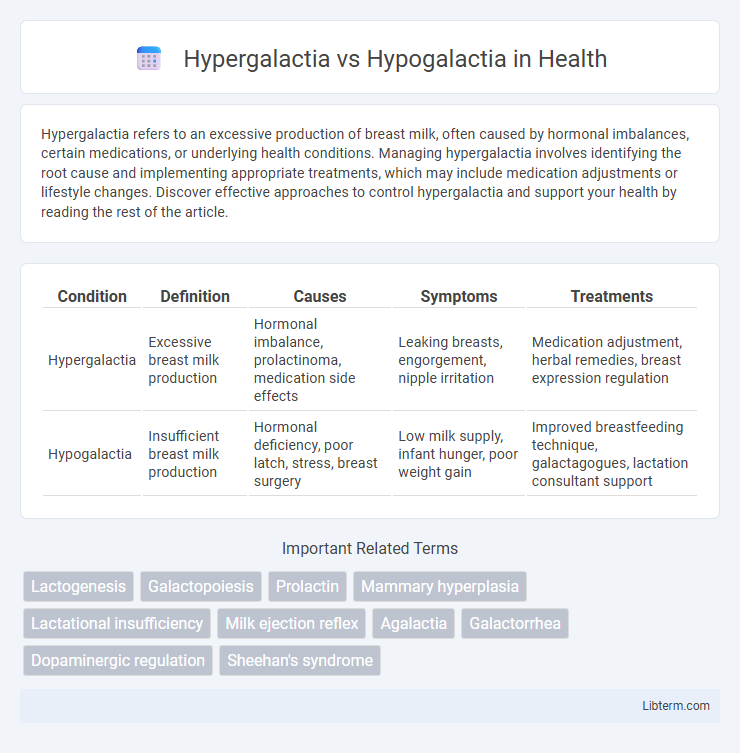
| Condition | Definition | Causes | Symptoms | Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypergalactia | Excessive breast milk production | Hormonal imbalance, prolactinoma, medication side effects | Leaking breasts, engorgement, nipple irritation | Medication adjustment, herbal remedies, breast expression regulation |
| Hypogalactia | Insufficient breast milk production | Hormonal deficiency, poor latch, stress, breast surgery | Low milk supply, infant hunger, poor weight gain | Improved breastfeeding technique, galactagogues, lactation consultant support |
Understanding Hypergalactia: Definition and Causes
Hypergalactia refers to the excessive production of breast milk, often caused by hormonal imbalances such as elevated prolactin levels or overstimulation of the breasts. This condition may result from factors including frequent breastfeeding, certain medications like domperidone, or endocrine disorders. Understanding hypergalactia involves recognizing symptoms such as breast engorgement and milk leakage, alongside differentiating it from hypogalactia, which is characterized by insufficient milk supply.
What is Hypogalactia? Overview and Contributing Factors
Hypogalactia refers to insufficient milk production in lactating women, often causing challenges in breastfeeding and infant nutrition. Common contributing factors include hormonal imbalances such as low prolactin levels, maternal stress, inadequate glandular tissue, and certain medical conditions like hypothyroidism or diabetes. Effective management requires identifying underlying causes and may involve lactation support, hormonal treatments, and addressing maternal health issues to improve milk supply.
Key Differences Between Hypergalactia and Hypogalactia
Hypergalactia is characterized by excessive milk production, often caused by hormonal imbalances or overstimulation of the breasts, while hypogalactia involves insufficient milk supply due to factors like poor latch, hormonal deficiencies, or breast tissue anomalies. The main clinical concerns differ: hypergalactia can lead to engorgement, mastitis, and nipple trauma, whereas hypogalactia results in inadequate infant nutrition and poor weight gain. Effective management depends on accurate diagnosis; treatments for hypergalactia may include breast drainage techniques and hormonal therapy, whereas hypogalactia often requires lactation support and supplementation strategies.
Signs and Symptoms: How to Recognize Each Condition
Hypergalactia presents with excessive milk production, leading to symptoms such as breast engorgement, frequent leaking, and a forceful let-down reflex, which may cause discomfort or nipple pain. Hypogalactia is characterized by insufficient milk supply, with signs including difficulty in infant latching, reduced baby weight gain, and infrequent or short breastfeeding sessions. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for appropriate interventions to manage milk flow effectively in nursing mothers.
Risk Factors for Developing Hypergalactia vs Hypogalactia
Hypergalactia risk factors include excessive prolactin secretion often caused by pituitary adenomas, hypothyroidism, or certain medications like antipsychotics and antidepressants. In contrast, hypogalactia is commonly linked to inadequate milk production due to insufficient glandular tissue, hormonal imbalances such as low prolactin or thyroid hormones, as well as conditions like breast surgery, diabetes, and stress. Both conditions are influenced by underlying endocrine disorders, but hypergalactia primarily involves prolactin excess, whereas hypogalactia stems from prolactin deficiency or impaired breast tissue response.
Diagnostic Approaches: Identifying Milk Production Disorders
Diagnostic approaches for hypergalactia and hypogalactia involve evaluating milk output through clinical assessment and lactation history review. Quantitative measurement of milk volume using standardized breast pumps or weighing pre- and post-feed can help differentiate excessive milk production from insufficient supply. Imaging techniques like breast ultrasound and biochemical analysis of milk composition provide further insights into underlying glandular function and possible pathological causes.
Management Strategies for Hypergalactia
Management of hypergalactia involves regulating excessive milk production through effective strategies such as reducing breast stimulation and milk expression frequency while utilizing cold compresses to alleviate engorgement. Herbal remedies like sage and dopamine agonists like bromocriptine can be considered to suppress lactation, combined with monitoring for complications like mastitis. Patient education on gradual weaning and maintaining proper hydration supports successful control of hypergalactia symptoms and prevents discomfort.
Treatment Options for Hypogalactia
Hypogalactia, characterized by insufficient breast milk production, requires targeted treatment options such as lactation consulting, frequent breastfeeding or pumping, and galactagogues like fenugreek or domperidone. Optimizing maternal nutrition, hydration, and addressing underlying medical conditions also play critical roles in enhancing milk supply. In contrast, hypergalactia involves excessive milk production and often necessitates management strategies to reduce milk output and alleviate symptoms.
Impact on Mother and Infant Health
Hypergalactia results in excessive milk production, which can cause breast engorgement, nipple pain, and infant gastrointestinal discomfort due to overfeeding, potentially leading to inadequate weight gain or colic. Hypogalactia, or low milk supply, often results in insufficient infant nutrition, poor weight gain, and increased risk of infections, while causing maternal stress, anxiety, and risk of postpartum depression. Effective management of these lactation disorders is critical for ensuring optimal growth, immune protection in infants, and maternal well-being.
Prevention Tips and When to Seek Medical Help
Hypergalactia, characterized by excessive milk production, and hypogalactia, marked by insufficient milk supply, both require careful management to ensure maternal and infant health. Prevention tips for hypergalactia include avoiding excessive breast stimulation and maintaining regular feeding schedules, while hypogalactia can be prevented by ensuring proper latch techniques, frequent breastfeeding, and adequate maternal hydration and nutrition. Seek medical help if hypergalactia leads to breast engorgement, mastitis, or significant discomfort, or if hypogalactia results in poor infant weight gain, dehydration, or persistent feeding difficulties.
Hypergalactia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com