Prevalence measures how widespread a particular condition or characteristic is within a population at a specific time. Understanding prevalence helps identify the impact and scope of health issues or social trends. Explore the rest of the article to learn how prevalence data influences decision-making and resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
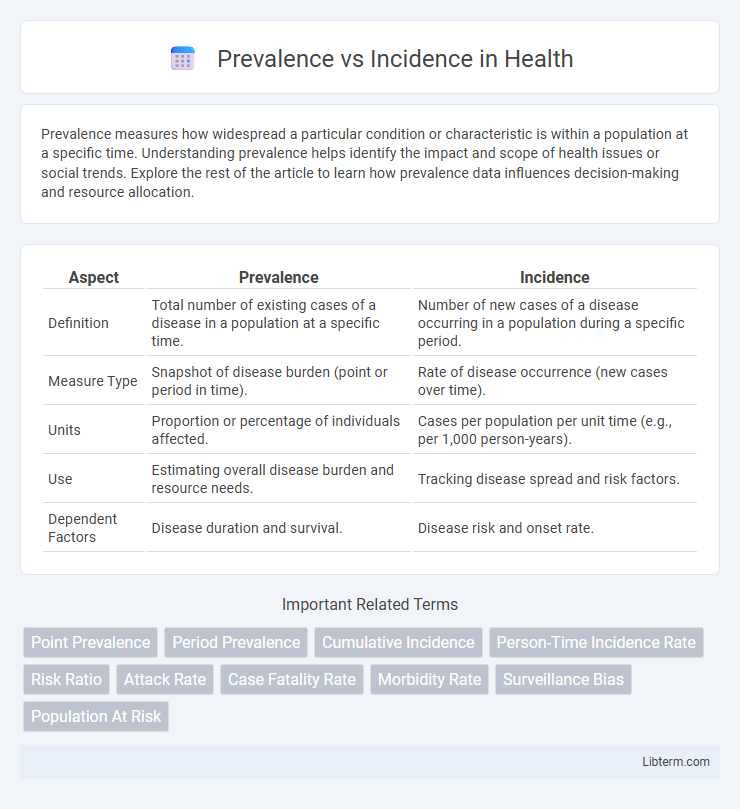
| Aspect | Prevalence | Incidence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a specific time. | Number of new cases of a disease occurring in a population during a specific period. |
| Measure Type | Snapshot of disease burden (point or period in time). | Rate of disease occurrence (new cases over time). |
| Units | Proportion or percentage of individuals affected. | Cases per population per unit time (e.g., per 1,000 person-years). |
| Use | Estimating overall disease burden and resource needs. | Tracking disease spread and risk factors. |
| Dependent Factors | Disease duration and survival. | Disease risk and onset rate. |
Introduction to Prevalence and Incidence
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease or condition in a population at a specific point or period, reflecting the disease burden. Incidence quantifies the number of new cases that develop in a population during a defined time frame, indicating the risk of developing the disease. Understanding prevalence and incidence is essential for epidemiological studies, healthcare planning, and resource allocation.
Defining Prevalence
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease or condition in a population at a specific point or over a period, reflecting the overall burden of the health issue. It includes both new and pre-existing cases, providing insight into how widespread the condition is. Prevalence is critical for healthcare planning and resource allocation due to its emphasis on the disease's continued impact on the community.
Understanding Incidence
Incidence measures the number of new cases of a disease or condition occurring in a specific population during a defined time period, offering critical insights into disease risk and causation. It is expressed as an incidence rate or incidence proportion, helping public health officials monitor outbreaks and evaluate intervention effectiveness. Understanding incidence enables targeted prevention strategies and resource allocation to reduce the disease burden effectively.
Key Differences Between Prevalence and Incidence
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease within a population at a specific point or period, reflecting the disease's overall burden. Incidence quantifies the number of new cases that develop in a population during a defined time frame, indicating the risk or rate of disease onset. The key difference lies in prevalence accounting for all current cases, whereas incidence strictly counts new occurrences, making prevalence useful for assessing chronic conditions and incidence critical for studying disease emergence and causation.
Importance in Epidemiological Studies
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a specific time, providing insights into the disease's burden and healthcare resource needs. Incidence captures the number of new cases occurring over a defined period, crucial for understanding disease risk, assessing causality, and evaluating the impact of preventive interventions. Epidemiological studies rely on both metrics to inform public health strategies, allocate resources effectively, and guide policy decisions aimed at disease control and prevention.
Calculation Methods for Prevalence
Prevalence is calculated by dividing the total number of existing cases of a disease or condition by the total population at a specific point in time, often expressed as a percentage or per 1,000 individuals. It differs from incidence, which measures new cases over a period, as prevalence captures both new and pre-existing cases, reflecting the overall disease burden. Accurate prevalence calculation requires comprehensive population data and consistent disease case definitions to ensure meaningful epidemiological analysis.
Calculation Methods for Incidence
Incidence quantifies new cases of a disease or condition occurring in a specified population during a defined time period, calculated by dividing the number of new cases by the total person-time at risk. Common methods include cumulative incidence, which uses the number of new cases divided by the population at risk at the beginning of the period, and incidence rate, which accounts for variable follow-up times by using person-years. Accurate calculation of incidence helps epidemiologists assess risk and disease dynamics more precisely than prevalence, which measures total existing cases regardless of onset timing.
Factors Influencing Prevalence and Incidence
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a specific time, influenced by factors such as disease duration, survival rates, and population demographics. Incidence refers to the number of new cases occurring within a defined period, affected primarily by exposure to risk factors, infection rates, and environmental changes. Understanding these distinctions helps in identifying disease dynamics and targeting public health interventions effectively.
Practical Applications in Public Health
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a specific time, providing insights into the burden and resource allocation for chronic conditions. Incidence tracks new cases over a defined period, essential for identifying emerging outbreaks, evaluating the effectiveness of interventions, and guiding preventive strategies. Public health programs utilize prevalence data to plan long-term healthcare services, while incidence data helps in monitoring disease trends and responding promptly to infectious disease threats.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a given time, while incidence refers to the number of new cases that develop over a specific period. A common misconception is that prevalence indicates the risk of developing a disease, but it actually reflects how widespread the disease is, influenced by both incidence and duration. Clarifications emphasize that incidence is more accurate for assessing disease risk and causation, whereas prevalence is useful for understanding the burden of chronic conditions.
Prevalence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com