Intervention plays a crucial role in addressing challenges by providing timely support and structured strategies to promote positive outcomes. Effective intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into significant problems, enhancing both individual and community well-being. Discover how different types of interventions can transform situations by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
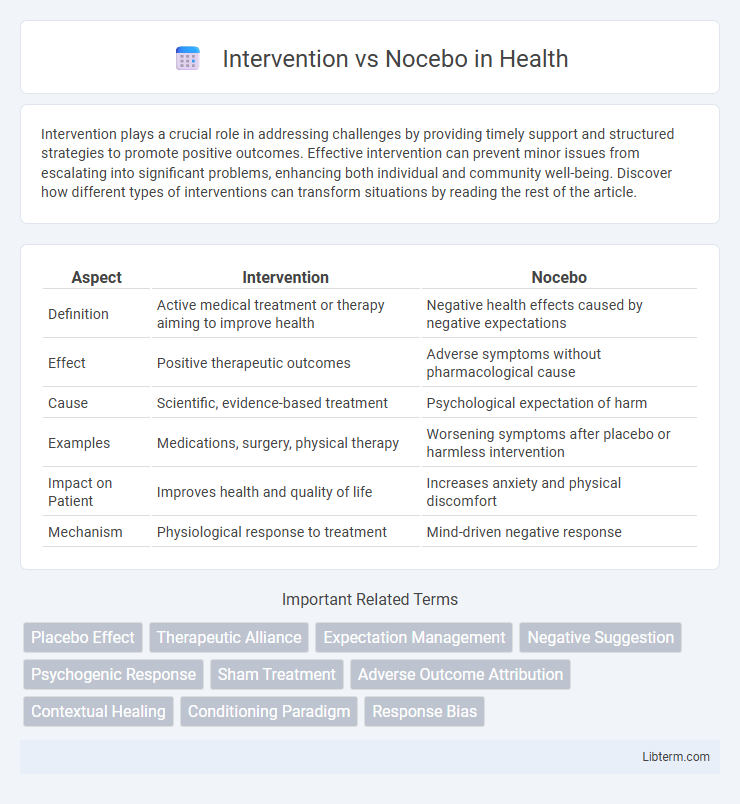
| Aspect | Intervention | Nocebo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active medical treatment or therapy aiming to improve health | Negative health effects caused by negative expectations |
| Effect | Positive therapeutic outcomes | Adverse symptoms without pharmacological cause |
| Cause | Scientific, evidence-based treatment | Psychological expectation of harm |
| Examples | Medications, surgery, physical therapy | Worsening symptoms after placebo or harmless intervention |
| Impact on Patient | Improves health and quality of life | Increases anxiety and physical discomfort |
| Mechanism | Physiological response to treatment | Mind-driven negative response |
Understanding Interventions: Definition and Purpose
Interventions refer to intentional actions or strategies implemented to produce a specific beneficial outcome, often in healthcare or psychological settings where the goal is to improve patient well-being. Unlike the nocebo effect, which involves negative outcomes caused by negative expectations or beliefs, interventions are designed based on evidence to promote positive changes. Understanding the definition and purpose of interventions is crucial for differentiating effective therapeutic strategies from unintended negative responses like the nocebo effect.
What is the Nocebo Effect?
The nocebo effect occurs when negative expectations or beliefs about a treatment cause harmful or adverse side effects, despite the treatment being inactive or harmless. This phenomenon contrasts with the intervention effect, where a genuine therapeutic action leads to beneficial outcomes. Understanding the nocebo effect is crucial in clinical settings to minimize patient harm caused by negative expectations during placebo-controlled trials or medical interventions.
Key Differences Between Intervention and Nocebo Responses
Intervention responses involve deliberate therapeutic actions designed to improve health outcomes, often producing measurable positive effects through physiological or psychological mechanisms. Nocebo responses arise from negative expectations or beliefs, leading to adverse effects without an active harmful agent, driven primarily by psychological factors such as anxiety or suggestion. Key differences lie in the origin--intervention is intentional and evidence-based, while nocebo is unintentional and expectation-induced--and in their impact, with interventions aiming to heal and nocebo potentially undermining treatment efficacy.
The Science Behind Medical Interventions
Medical interventions rely on evidence-based mechanisms to effect physiological changes, contrasting with the nocebo effect, which stems from negative expectations causing adverse symptoms without active treatment. Clinical studies reveal that the placebo effect can trigger real biochemical responses, whereas nocebo responses often result from anticipatory anxiety or negative conditioning. Understanding neurobiological pathways, such as endorphin release and brain activity patterns, is crucial for differentiating true therapeutic effects from nocebo-induced symptoms.
How Nocebo Effects Manifest in Patients
Nocebo effects manifest in patients through negative expectations and anxiety, leading to the worsening of symptoms or the appearance of new, adverse side effects despite receiving an inert substance or treatment. These effects often arise from verbal suggestions, prior experiences, or observational learning, influencing physiological and psychological responses such as increased pain perception, fatigue, or nausea. Understanding the neurobiological mechanisms underlying nocebo responses, including activation of the brain's pain and stress pathways, is crucial for minimizing harm during clinical interventions.
Factors Influencing Intervention Outcomes
Intervention outcomes are influenced by patient expectations, which can modulate perceived effectiveness through placebo or nocebo effects. Psychological factors such as anxiety and previous treatment experiences also play a critical role in shaping these outcomes. Biological mechanisms, including neurochemical responses and genetic predispositions, further affect the variability in intervention efficacy and adverse reactions.
The Psychological Impact of Nocebo in Clinical Settings
The psychological impact of nocebo in clinical settings can lead to increased patient anxiety, worsened symptoms, and reduced treatment efficacy, emphasizing the importance of minimizing negative expectations. Interventions that promote positive communication and patient education help counteract nocebo effects, improving overall outcomes and adherence to treatment plans. Research shows that the nocebo phenomenon can significantly influence patient perceptions and recovery, making it critical to address psychological factors in medical practice.
Strategies to Maximize Intervention Benefits
Strategies to maximize intervention benefits involve enhancing patient expectations and providing clear, positive communication to reduce nocebo effects that can undermine treatment outcomes. Personalized education about the therapeutic process and transparent discussion of potential side effects help to minimize anxiety and negative biases, thereby improving adherence and clinical efficacy. Incorporating psychological support and monitoring patient responses continuously ensures the intervention's positive impact outweighs any nocebo-induced adverse effects.
Minimizing Nocebo Effects in Healthcare
Minimizing nocebo effects in healthcare involves carefully crafting patient communication to avoid negative expectations that can trigger adverse symptoms. Healthcare providers enhance treatment outcomes by emphasizing the therapeutic benefits while transparently managing side effect information to reduce anxiety and stress-induced nocebo responses. Strategies such as patient education, empathetic dialogue, and positive framing are essential to distinguish intervention efficacy from nocebo influences.
Future Perspectives: Enhancing Interventions and Reducing Nocebo
Future perspectives in healthcare emphasize developing personalized interventions that leverage neurobiological insights to maximize therapeutic efficacy while minimizing nocebo responses. Advances in digital health technologies and artificial intelligence enable real-time monitoring and adaptive treatment adjustments, reducing negative expectations and side effects associated with nocebo phenomena. Integrating patient-centered communication strategies and predictive analytics holds promise for enhancing intervention outcomes and mitigating nocebo-related challenges in clinical practice.
Intervention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com