Hypersomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime drowsiness or prolonged nighttime sleep that makes it difficult to stay awake and alert. It can stem from various causes, including sleep apnea, narcolepsy, or underlying medical conditions, impacting your daily functioning and overall health. Explore the rest of the article to understand symptoms, causes, and effective treatments for hypersomnia.
Table of Comparison
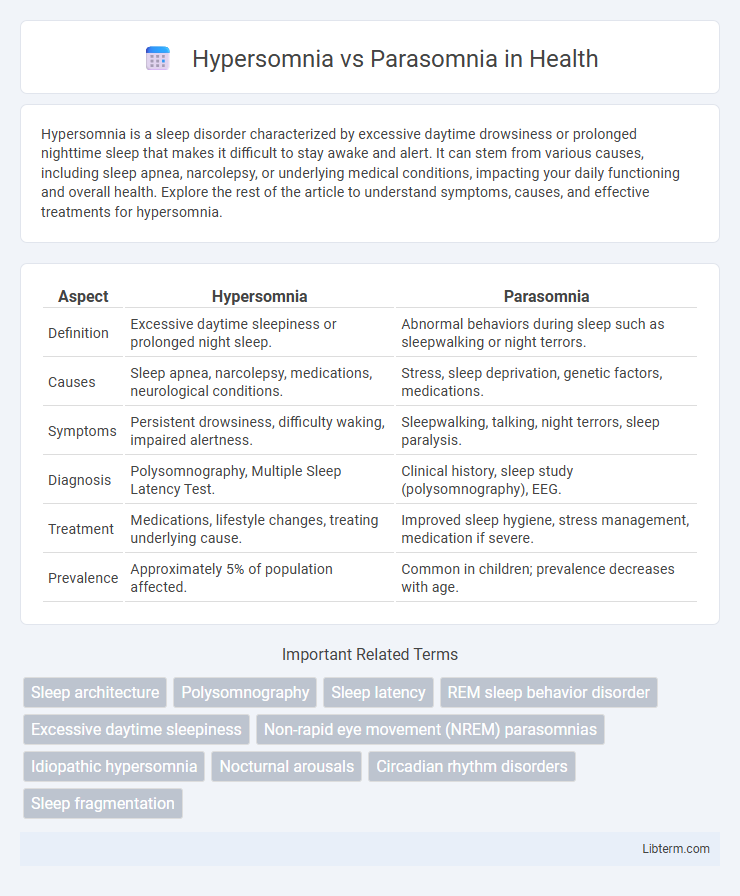
| Aspect | Hypersomnia | Parasomnia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive daytime sleepiness or prolonged night sleep. | Abnormal behaviors during sleep such as sleepwalking or night terrors. |
| Causes | Sleep apnea, narcolepsy, medications, neurological conditions. | Stress, sleep deprivation, genetic factors, medications. |
| Symptoms | Persistent drowsiness, difficulty waking, impaired alertness. | Sleepwalking, talking, night terrors, sleep paralysis. |
| Diagnosis | Polysomnography, Multiple Sleep Latency Test. | Clinical history, sleep study (polysomnography), EEG. |
| Treatment | Medications, lifestyle changes, treating underlying cause. | Improved sleep hygiene, stress management, medication if severe. |
| Prevalence | Approximately 5% of population affected. | Common in children; prevalence decreases with age. |
Understanding Hypersomnia: Definition and Causes
Hypersomnia is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness despite adequate or prolonged nighttime sleep, often linked to conditions such as narcolepsy, idiopathic hypersomnia, and sleep apnea. This disorder results from disruptions in the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, causing persistent fatigue and difficulty staying awake. Understanding the underlying causes, including neurological disorders, medication effects, and lifestyle factors, is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Parasomnia? Overview and Types
Parasomnia refers to a category of sleep disorders characterized by abnormal behaviors, movements, emotions, perceptions, or dreams occurring during sleep transitions. Common types of parasomnia include sleepwalking (somnambulism), night terrors, REM sleep behavior disorder, and sleep talking (somniloquy). These disorders disrupt the normal sleep cycle and can affect overall sleep quality and daytime functioning.
Key Differences Between Hypersomnia and Parasomnia
Hypersomnia primarily involves excessive daytime sleepiness and prolonged nighttime sleep, whereas parasomnia includes abnormal behaviors or experiences during sleep, such as sleepwalking or night terrors. Hypersomnia impairs daily functioning due to persistent sleepiness, while parasomnia disrupts sleep continuity through involuntary physical or vocal activities. Diagnosis of hypersomnia often relies on sleep studies measuring sleep latency, whereas parasomnia is identified through behavioral observations and polysomnographic recordings.
Common Symptoms of Hypersomnia
Hypersomnia is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, prolonged nighttime sleep, and difficulty waking up, while parasomnia involves abnormal behaviors during sleep such as sleepwalking, night terrors, or REM sleep behavior disorder. Common symptoms of hypersomnia include persistent fatigue despite adequate sleep, difficulty concentrating, and recurrent episodes of unintended sleep during the day. Understanding these distinguishing features is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders.
Typical Signs Associated with Parasomnia
Parasomnia is characterized by unusual behaviors during sleep, including sleepwalking, night terrors, and REM sleep behavior disorder, often causing physical movements, vocalizations, or confusion upon waking. These typical signs distinguish parasomnia from hypersomnia, where excessive daytime sleepiness and prolonged nighttime sleep dominate the clinical profile. Identifying parasomnia symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment to improve sleep quality and safety.
Diagnosis: How Hypersomnia and Parasomnia Are Identified
Hypersomnia diagnosis involves polysomnography and multiple sleep latency tests to measure excessive daytime sleepiness and sleep duration, while parasomnia is identified through clinical history, sleep studies, and video monitoring to observe abnormal behaviors during sleep stages. Sleep questionnaires, patient interviews, and actigraphy assist in differentiating symptoms and confirming the presence of conditions such as narcolepsy, sleepwalking, or REM sleep behavior disorder. Accurate diagnosis requires comprehensive evaluation by a sleep specialist to tailor appropriate treatment strategies.
Risk Factors Contributing to Hypersomnia and Parasomnia
Risk factors contributing to hypersomnia include chronic sleep deprivation, neurological disorders such as narcolepsy, and the use of sedative medications, which impair the body's ability to maintain normal wakefulness. Parasomnia risk factors involve irregular sleep schedules, stress, sleep apnea, and genetic predispositions that disrupt normal sleep architecture, leading to abnormal behaviors during sleep. Both conditions are often exacerbated by poor sleep hygiene and underlying psychiatric disorders like depression or anxiety.
Treatment Options for Hypersomnia
Treatment options for hypersomnia primarily include stimulants such as modafinil and amphetamines, which help improve wakefulness. Lifestyle modifications, including maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding alcohol or sedatives, support overall sleep health. In some cases, addressing underlying conditions like depression or sleep apnea with targeted therapies enhances the effectiveness of hypersomnia treatment.
Managing and Treating Parasomnia Disorders
Managing parasomnia disorders involves a comprehensive approach that includes improving sleep hygiene, creating a safe sleep environment, and addressing underlying medical or psychological conditions. Behavioral strategies like scheduled awakenings and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help reduce episodes of sleepwalking, night terrors, and REM sleep behavior disorder. In some cases, medications such as clonazepam or melatonin are prescribed to control parasomnia symptoms and improve sleep quality.
Living with Sleep Disorders: Tips for Better Sleep Health
Living with hypersomnia involves managing excessive daytime sleepiness by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful environment to improve sleep quality. Parasomnia, which includes abnormal behaviors during sleep such as sleepwalking or night terrors, requires safety measures and stress reduction techniques to minimize episodes. Both conditions benefit from regular medical consultation, cognitive behavioral therapy, and lifestyle adjustments that promote optimal sleep hygiene for better overall sleep health.
Hypersomnia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com